National Assembly of Belarus
The National Assembly of the Republic of Belarus (Belarusian: Нацыянальны сход Рэспублікі Беларусь, Nacyjanalny schod Respubliki Biełaruś; Russian: Национальное собрание Республики Беларусь, Natsionalnoye sobran'ye Respubliki Belarus) is the bicameral parliament of Belarus. The two chambers of the National Assembly are:
- Council of the Republic - The upper house
- House of Representatives - The lower house
National Assembly of Belarus Нацыянальны сход Рэспублікі Беларусь Национальное собрание Республики Беларусь | |
|---|---|
| National Assembly of the Republic of Belarus | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Houses | Council of the Republic House of Representatives |
| History | |
| Founded | 11 November 1996 |
| Preceded by | Supreme Soviet of Belarus |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 174 members 110 representatives 64 councilors |
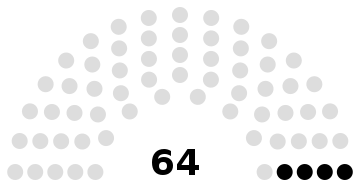 | |
Council of the Republic political groups | Government (64)
Independents (46)
Liberal Democratic Party (1)
|
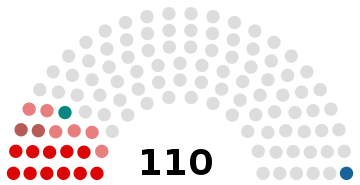 | |
House of Representatives political groups | Government (110)
Independents (89)
(Belaya Rus, 68 MPs) Liberal Democratic Party (1)
|
| Elections | |
Council of the Republic voting system | Indirect election by regional assemblies, Appointment by the President of the Republic |
House of Representatives voting system | First-past-the-post |
House of Representatives last election | 17 November 2019 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Website | |
| www www | |
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Belarus |
|
|
|
Judiciary |
|
Administrative divisions |
|
|
|
While each chamber has specific duties, both chambers have the ability to veto the decrees of local administrations that deviate from the Constitution of Belarus.
The chambers of the National Assembly are convened to two regular sessions every year: the first session opens 2 October and its duration cannot be more than 80 days; the second session opens 2 April and does not last more than 90 days.
The House of Representatives and the Council of the Republic may be convened to an extraordinary session. Extraordinary sessions are convened under a particular agenda upon an initiative of the President or upon a request of at least two-thirds majority of the full membership of each of the chambers.[1]
Any bill must be initially considered in the House of Representatives and then in the Council of the Republic.
In practice, the National Assembly has little real power. The Belarusian political system concentrates nearly all governing power in the hands of President Alexander Lukashenko. Notably, the National Assembly has little control over government spending; according to the Constitution, any bill that impacts the state budget must be approved by the president or the government before being considered. Presidential decrees have greater weight than ordinary legislation. However, since it took its current form in 1996, the National Assembly has been dominated by Lukashenko's supporters in any event, and there is no substantive opposition to presidential decisions.[2]
Its predecessor was the Supreme Council of Belarus (until 1996).
Sources
- "Парламент – Национальное собрание Республики Беларусь". www.pravo.by. Retrieved 2020-05-27.
- "Why Does Europe Engage With Belarus's Rubber Stamp Parliament?". Archived from the original on 2017-07-26. Retrieved 2016-08-25.
.svg.png)