Parliament of the Czech Republic
The Parliament of the Czech Republic (Czech: Parlament České republiky) or just Parliament (Czech: Parlament) is the legislative body of the Czech Republic, seated in Malá Strana, Prague.
Parliament of the Czech Republic Parlament České republiky | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Houses | Senate Chamber of Deputies |
| History | |
| Founded | 1 January 1993 |
| Preceded by | Federal Assembly |
| Leadership | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 281 81 Senators 200 Deputies |
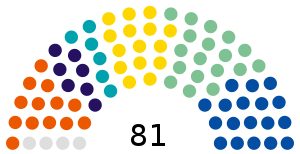 | |
Senate political groups | Government (20)
Opposition (61)
|
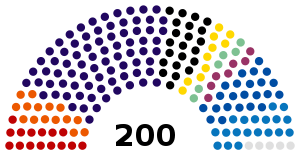 | |
Chamber of Deputies political groups | Government (92)
Supported by (15)
Opposition (93) |
| Elections | |
| Two-round system | |
| Proportional representation | |
Senate last election | 5–6 October 2018 12–13 October 2018 |
Chamber of Deputies last election | 20–21 October 2017 |
| Meeting place | |
| Palaces in Malá Strana, Prague | |
| Website | |
| Senate Chamber of Deputies | |
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of the Czech Republic |
|
|
|
|
Executive |
|
It consists of two chambers, both elected in direct elections:
- the Lower House: Chamber of Deputies
- the Upper House: Senate
Art. 15 of the Constitution stipulates its name as the "Parliament".[1] The Parliament exercises competences usual in parliamentary systems: it holds and passes bills, has the right to modify the Constitution, ratifies international agreements; if necessary, it declares war, approves presence of foreign military forces in the Czech Republic or a dispatch of Czech military forces abroad.
History

The tradition of modern parliamentarianism in the Bohemian lands dates back to times of the Austrian Empire (and then Cisleithanian part of Austria-Hungary), where the Imperial Council (Reichsrat, Říšská rada) was created in 1861.
After proclamation of Czechoslovakia in 1918 its National Assembly (Národní shromáždění) undertook legislative duties both of the Imperial Council and State Diets (Bohemian, Moravian, Silesian).[2] In 1938–39 and between 1948–89 there existed a parliament within non-democratic regimes (semi-authoritarian or Communist regime, respectively). As a consequence of federalization of Czechoslovakia (1968), national councils of Czech and Slovak parts of the country were created.
The Chamber of Deputies keeps continuity with the Czech National Council (Česká národní rada), while the Senate was established in 1996 (with reference to the First Czechoslovak Republic one).
References
- 2015, FG Forrest, a.s., www.fg.cz. "The Constitution of the Czech Republic - Prague Castle". Prague Castle. Retrieved 2017-05-25.CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)
- Balík, S.-Hloušek, V.-Holzer, J.-Šedo, J.: Politický systém českých zemí 1848-1989. Brno 2006, p. 81.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Parliament of the Czech Republic. |
