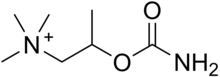
Bethanechol
Bethanechol is a parasympathomimetic choline carbamate that selectively stimulates muscarinic receptors without any effect on nicotinic receptors. Unlike acetylcholine, bethanechol is not hydrolyzed by cholinesterase and will therefore have a long duration of action. Bethanechol is sold under the brand names Duvoid (Roberts), Myotonachol (Glenwood), Urecholine (Merck Frosst) and Urocarb (Hamilton). The name bethanechol refers to its structure as the urethane of beta-methylcholine.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Urecholine |
| Other names | 2-[(aminocarbonyl)oxy]- N,N,N-trimethyl- 1-propanaminium Carbamyl-β-methylcholine |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682849 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral, subcutaneous |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C7H17N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 161.225 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Uses
Bethanechol alleviates dry mouth[1] and is sometimes given orally or subcutaneously to treat urinary retention resulting from general anesthetic, diabetic neuropathy of the bladder, or a side effect of antidepressants; or to treat gastrointestinal lack of muscular tone. The muscarinic receptors in the bladder and gastrointestinal tract stimulate contraction of the bladder and expulsion of urine, and increased gastrointestinal motility, respectively. Bethanechol should be used to treat these disorders only after mechanical obstruction is ruled out as a possible cause.
Its potential benefit in the treatment of cerebral palsy has been investigated.[2] Bethanechol is a powerful cholinergic agent which does not cross the blood - brain barrier and may have powerful nootropic properties in enhancement of neural signaling and processing speed as well.
Atropine is given preoperatively to prevent voiding of the bowel/bladder during surgery, Bethanechol is then given postoperatively to revert this action.[3]
Contraindications
Use of bethanechol, as well as all other muscarinic receptor agonists, is contraindicated in patients with asthma, coronary insufficiency, peptic ulcers, intestinal obstruction and hyperthyroidism. The parasympathomimetic action of this drug will exacerbate the symptoms of these disorders.
See also
- Pilocarpine and Cevimeline, similar parasympathomimetic medicines for dry mouth (xerostomia).
References
- Gorsky M, Epstein JB, Parry J, Epstein MS, Le ND, Silverman S (February 2004). "The efficacy of pilocarpine and bethanechol upon saliva production in cancer patients with hyposalivation following radiation therapy". Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology, and Endodontics. 97 (2): 190–5. doi:10.1016/j.tripleo.2003.08.031. PMID 14970777.
- Carter WJ (September 2008). "Unexpected benefits of bethanechol in adults with cerebral palsy". The Medical Journal of Australia. 189 (5): 293. PMID 18759732.
- Obied H (2011). Cholinergic Pharmacology. CSU.