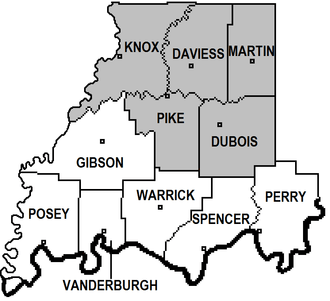
Martin County, Indiana
Martin County is a county in the U.S. state of Indiana. As of the 2010 United States Census, the population was 10,334.[1] The county seat is Shoals at the center of the county,[2] and the county's only incorporated city is Loogootee, on the county's western border.[3]
Martin County | |
|---|---|
 Martin County Courthouse | |
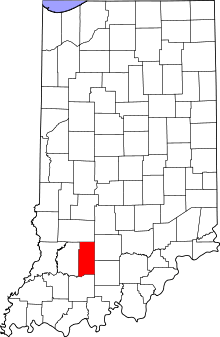 Location within the U.S. state of Indiana | |
 Indiana's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 38°43′N 86°48′W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | 20 January 1820 |
| Named for | Major John T. Martin |
| Seat | Shoals |
| Largest city | Loogootee |
| Area | |
| • Total | 340.41 sq mi (881.7 km2) |
| • Land | 335.74 sq mi (869.6 km2) |
| • Water | 4.67 sq mi (12.1 km2) 1.37% |
| Population | |
| • Estimate (2018) | 10,217 |
| • Density | 31/sq mi (12/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Congressional district | 8th |
| Website | www |
| Indiana county number 51 | |
History
The Indiana Territory achieved statehood near the end of 1816. Shortly thereafter, the new State legislature created Dubois (December 1817) and Daviess (February 1818) counties. Due to the inflow of settlers into southwest Indiana, and the difficulty of accessing the county seats of those counties, Martin County was partitioned off from parts of those counties, being authorized on 20 January 1820. It was named for Maj. John T. Martin of Newport, Kentucky.[4][5]
Geography
The hills of Martin County are largely wooded and cut with drainages;[3] the available area is devoted to agriculture, development, or is under control of the US Government - about a third of the county belongs to the Naval Surface Warfare Center Crane Division, and about a quarter of the county belongs to Hoosier National Forest. The highest point (870 feet/265 meters ASL) is in Mitcheltree Township, within NSWC Crane.[6]
The East Fork of the White River flows southwestward through the lower part of the county. The central part of the county is drained by Indian Creek, which discharges into White River near the center of the county. The upper part of the county is drained by Boggs Creek, which discharges into White River near the county's western edge.[3]
According to the 2010 census, the county has a total area of 340.41 square miles (881.7 km2), of which 335.74 square miles (869.6 km2) (or 98.63%) is land and 4.67 square miles (12.1 km2) (or 1.37%) is water.[7]
Adjacent counties
- Greene County - north
- Lawrence County - east
- Orange County - southeast
- Dubois County - south
- Daviess County - west
Protected areas
- Hoosier National Forest (part)[8] in northeast and southeast parts of Martin County. Administered by US Forest Service
- Martin State Forest - in eastern part of Martin County. Administered by Indiana Department of Natural Resources
Lakes
- Greenwood Lake
- Seed Tick Lake
- West Boggs Lake (part)[3]
Highways






Unincorporated communities
- Bramble
- Burns City (census-designated place)
- Cale
- Dover Hill (census-designated place)
- Hindostan Falls
- Indian Springs
- Ironton
- Lacy
- Mount Olive
- Mount Pleasant
- Natchez
- Padanaram
- Pleasant Valley
- Rusk
- Scenic Hill
- Shoals Overlook
- South Martin
- Trinity Springs
- Whitfield
- Willow Valley
- Windom
- Yenne
Townships
Climate and weather
| Shoals, Indiana | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In recent years, average temperatures in Shoals have ranged from a low of 19 °F (−7 °C) in January to a high of 86 °F (30 °C) in July, although a record low of −23 °F (−31 °C) was recorded in January 1994 and a record high of 104 °F (40 °C) was recorded in July 1954. Average monthly precipitation ranged from 2.92 inches (74 mm) in February to 5.60 inches (142 mm) in May.[9]
Government
The county government is a constitutional body, and is granted specific powers by the Constitution of Indiana, and by the Indiana Code.
County Council: The legislative branch of the county government; controls spending and revenue collection in the county. Representatives are elected to four-year terms from county districts. They are responsible for setting salaries, the annual budget, and special spending. The council has limited authority to impose local taxes, in the form of an income and property tax that is subject to state level approval, excise taxes, and service taxes.[10][11]
Board of Commissioners: The executive body of the county; commissioners are elected county-wide to staggered four-year terms. One commissioner serves as president. The commissioners execute the acts legislated by the council, collect revenue, and manage the county government.[10][11]
Court: The county maintains a small claims court that handles civil cases. The judge on the court is elected to a term of four years and must be a member of the Indiana Bar Association. The judge is assisted by a constable who is also elected to a four-year term. In some cases, court decisions can be appealed to the state level circuit court.[11]
County Officials: The county has other elected offices, including sheriff, coroner, auditor, treasurer, recorder, surveyor, and circuit court clerk. Officers are elected to four-year terms. Members elected to county government positions are required to declare party affiliations and to be residents of the county.[11]
Martin County is part of Indiana's 8th congressional district; Indiana Senate district 39;[12] and Indiana House of Representatives districts 62 and 63.[13]
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third parties |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 76.9% 3,697 | 18.3% 881 | 4.8% 231 |
| 2012 | 68.8% 3,262 | 28.5% 1,351 | 2.7% 130 |
| 2008 | 63.7% 3,122 | 34.8% 1,706 | 1.5% 75 |
| 2004 | 68.3% 3,414 | 30.5% 1,522 | 1.2% 60 |
| 2000 | 65.3% 3,008 | 32.9% 1,518 | 1.8% 83 |
| 1996 | 48.3% 2,281 | 39.2% 1,848 | 12.5% 591 |
| 1992 | 46.4% 2,523 | 37.1% 2,018 | 16.5% 897 |
| 1988 | 58.8% 3,066 | 40.9% 2,132 | 0.4% 21 |
| 1984 | 63.1% 3,363 | 36.3% 1,937 | 0.6% 32 |
| 1980 | 53.3% 3,082 | 42.9% 2,479 | 3.8% 218 |
| 1976 | 48.6% 2,702 | 50.8% 2,827 | 0.7% 36 |
| 1972 | 63.0% 3,470 | 36.7% 2,021 | 0.3% 18 |
| 1968 | 46.2% 2,512 | 42.6% 2,315 | 11.2% 608 |
| 1964 | 38.9% 2,000 | 61.0% 3,137 | 0.2% 9 |
| 1960 | 51.6% 2,756 | 48.4% 2,585 | 0.1% 5 |
| 1956 | 55.6% 2,946 | 44.2% 2,343 | 0.1% 7 |
| 1952 | 51.7% 2,757 | 47.8% 2,546 | 0.5% 29 |
| 1948 | 44.0% 2,230 | 55.0% 2,788 | 1.1% 55 |
| 1944 | 49.4% 2,467 | 50.3% 2,515 | 0.3% 15 |
| 1940 | 52.3% 2,902 | 47.5% 2,638 | 0.2% 11 |
| 1936 | 46.6% 2,583 | 52.7% 2,923 | 0.7% 40 |
| 1932 | 40.3% 2,106 | 58.8% 3,072 | 0.9% 47 |
| 1928 | 51.9% 2,450 | 47.5% 2,245 | 0.6% 27 |
| 1924 | 46.8% 2,470 | 50.5% 2,669 | 2.7% 142 |
| 1920 | 52.3% 2,747 | 46.5% 2,443 | 1.2% 65 |
| 1916 | 48.9% 1,534 | 49.4% 1,549 | 1.7% 52 |
| 1912 | 32.3% 975 | 47.7% 1,440 | 20.0% 605 |
| 1908 | 48.4% 1,667 | 50.3% 1,733 | 1.4% 48 |
| 1904 | 52.2% 1,809 | 45.4% 1,574 | 2.4% 82 |
| 1900 | 49.9% 1,712 | 48.4% 1,660 | 1.7% 59 |
| 1896 | 44.4% 1,384 | 55.1% 1,719 | 0.5% 16 |
| 1892 | 44.0% 1,283 | 47.8% 1,391 | 8.2% 239 |
| 1888 | 47.0% 1,391 | 52.6% 1,558 | 0.4% 11 |
Education
| School | Type | Enrollment | Mascot | Colors | IHSAA Class | Athletic Conference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loogootee High School | Public | 325 | Lions | A | Blue Chip Conference | |
| Shoals High School | Public | 223 | JugRox | A | Blue Chip Conference | |
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1820 | 1,032 | — | |
| 1830 | 2,010 | 94.8% | |
| 1840 | 3,875 | 92.8% | |
| 1850 | 5,941 | 53.3% | |
| 1860 | 8,975 | 51.1% | |
| 1870 | 11,103 | 23.7% | |
| 1880 | 13,475 | 21.4% | |
| 1890 | 13,973 | 3.7% | |
| 1900 | 14,711 | 5.3% | |
| 1910 | 12,950 | −12.0% | |
| 1920 | 11,865 | −8.4% | |
| 1930 | 10,103 | −14.9% | |
| 1940 | 10,300 | 1.9% | |
| 1950 | 10,678 | 3.7% | |
| 1960 | 10,608 | −0.7% | |
| 1970 | 10,969 | 3.4% | |
| 1980 | 11,001 | 0.3% | |
| 1990 | 10,369 | −5.7% | |
| 2000 | 10,369 | 0.0% | |
| 2010 | 10,334 | −0.3% | |
| Est. 2018 | 10,217 | [15] | −1.1% |
| US Decennial Census[16] 1790-1960[17] 1900-1990[18] 1990-2000[19] 2010-2013[1] | |||
2010 Census
As of the 2010 United States Census, there were 10,334 people, 4,216 households, and 2,832 families in the county.[20] The population density was 30.8 inhabitants per square mile (11.9/km2). There were 4,786 housing units at an average density of 14.3 per square mile (5.5/km2).[7] The racial makeup of the county was 98.4% white, 0.3% Asian, 0.3% American Indian, 0.1% black or African American, 0.2% from other races, and 0.7% from two or more races. Those of Hispanic or Latino origin made up 0.7% of the population.[20] In terms of ancestry, 27.8% were German, 19.2% were Irish, 14.9% were English, and 12.7% were American.[21]
Of the 4,216 households, 30.5% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 52.8% were married couples living together, 9.2% had a female householder with no husband present, 32.8% were non-families, and 28.7% of all households were made up of individuals. The average household size was 2.43 and the average family size was 2.98. The median age was 41.8 years.[20]
The median income for a household in the county was $47,697 and the median income for a family was $55,017. Males had a median income of $41,411 versus $30,503 for females. The per capita income for the county was $21,750. About 8.6% of families and 13.0% of the population were below the poverty line, including 21.2% of those under age 18 and 9.1% of those age 65 or over.[22]
References
- "Martin County QuickFacts". US Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 7 June 2011. Retrieved 25 September 2011.
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Retrieved 7 June 2011.
- Martin County IN (Google Maps, accessed 2 August 2020)
- De Witt Clinton Goodrich & Charles Richard Tuttle (1875). An Illustrated History of the State of Indiana. Indiana: R. S. Peale & Co. p. 567.
- Gannett, Henry (1905). The Origin of Certain Place Names in the United States. Government Printing Office. p. 201.
- Martin County High Point, Indiana (PeakBagger.com, accessed 2 August 2020)
- "Population, Housing Units, Area, and Density: 2010 - County". US Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 12 February 2020. Retrieved 10 July 2015.
- Map of Hoosier National Forest, showing its NW portion extending into the northeast and southeast parts of Martin County (US Forest Service, accessed 2 August 2020)
- "Monthly Averages for Shoals IN". The Weather Channel. Retrieved 27 January 2011.
- Indiana Code. "Title 36, Article 2, Section 3". IN.gov. Retrieved 16 September 2008.
- Indiana Code. "Title 2, Article 10, Section 2" (PDF). IN.gov. Retrieved 16 September 2008.
- Indiana Senate Districts (accessed 2 August 2020)
- Indiana House Districts (accessed 2 August 2020)
- Leip, David. "Atlas of US Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved 18 May 2018.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved July 26, 2019.
- "US Decennial Census". US Census Bureau. Retrieved July 10, 2014.
- "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved July 10, 2014.
- "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". US Census Bureau. Retrieved July 10, 2014.
- "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). US Census Bureau. Retrieved July 10, 2014.
- "Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 Demographic Profile Data". US Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 13 February 2020. Retrieved 10 July 2015.
- "Selected Social Characteristics in the US – 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". US Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 14 February 2020. Retrieved 10 July 2015.
- "Selected Economic Characteristics – 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". US Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 14 February 2020. Retrieved 10 July 2015.