Gila County, Arizona
Gila County is located in the central part of the U.S. state of Arizona. As of the 2010 census its population was 53,597.[1] The county seat is Globe.[2]
Gila County | |
|---|---|
 Gila County Courthouse in Globe | |
 Seal | |
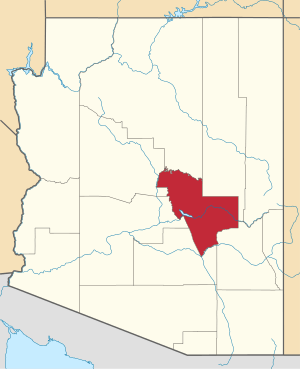 Location within the U.S. state of Arizona | |
 Arizona's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 33°47′28″N 110°50′11″W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | February 8, 1881 |
| Seat | Globe |
| Largest town | Payson |
| Area | |
| • Total | 4,795 sq mi (12,420 km2) |
| • Land | 4,758 sq mi (12,320 km2) |
| • Water | 38 sq mi (100 km2) 0.8%% |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 53,597 |
| • Estimate (2019) | 54,018 |
| • Density | 11/sq mi (4.3/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−7 (Mountain) |
| Congressional districts | 1st, 4th |
| Website | www |
Gila County comprises the Payson, Arizona Micropolitan Statistical Area.
Gila County contains parts of Fort Apache Indian Reservation and San Carlos Indian Reservation.
History
The county was formed from parts of Maricopa County and Pinal County on February 8, 1881.[3] The boundary was then extended eastward to the San Carlos River by public petition in 1889. The original county seat was in the mining community of Globe City, now Globe, Arizona.
Popular theory says that the word Gila was derived from a Spanish contraction of Hah-quah-sa-eel, a Yuma word meaning "running water which is salty".[4]
In the 1880s, a long range war broke out in Gila County that became the most costly feud in American history, resulting in an almost complete annihilation of the families involved. The Pleasant Valley War (also sometimes called the Tonto Basin Feud or Tonto Basin War) matched the cattle-herding Grahams against the sheep-herding Tewksburys. Once partisan feelings became tense and hostilities began, Frederick Russell Burnham, who later became a celebrated scout and the inspiration for the boy scouts, was drawn into the conflict on the losing side.[5][6] Burnham shot many men in the feud, and was himself nearly killed by a bounty hunter.[7] Tom Horn, a famous assassin, was also known to have taken part as a killer for hire, but it is unknown as to which side employed him, and both sides suffered several murders to which no suspect was ever identified. In the 1960s, it was home of Gerald Gault, who was the subject of the 1967 U.S. Supreme Court ruling, in re Gault, that stated juveniles have the same rights as adults when arrested to be notified of the charges against them, the rights to attorneys, for family members to be notified of their arrests and to confront their accusers and to not be punished harsher than adults who are convicted of the same crime, especially if an adult's penalty for the crime would be less than a juvenile convict's.
Geography


According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 4,795 square miles (12,420 km2), of which 4,758 square miles (12,320 km2) is land and 38 square miles (98 km2) (0.8%) is water.[8]
Adjacent counties
- Yavapai County - northwest
- Maricopa County - west
- Pinal County - south
- Graham County - southeast
- Navajo County - east, northeast
- Coconino County - north
National protected areas
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1890 | 2,021 | — | |
| 1900 | 4,973 | 146.1% | |
| 1910 | 16,348 | 228.7% | |
| 1920 | 25,678 | 57.1% | |
| 1930 | 31,016 | 20.8% | |
| 1940 | 23,867 | −23.0% | |
| 1950 | 24,158 | 1.2% | |
| 1960 | 25,745 | 6.6% | |
| 1970 | 29,255 | 13.6% | |
| 1980 | 37,080 | 26.7% | |
| 1990 | 40,216 | 8.5% | |
| 2000 | 51,335 | 27.6% | |
| 2010 | 53,597 | 4.4% | |
| Est. 2019 | 54,018 | [9] | 0.8% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[10] 1790–1960[11] 1900–1990[12] 1990–2000[13] 2010–2018[1] | |||
2000 census
As of the census[14] of 2000, there were 51,335 people, 20,140 households, and 14,098 families living in the county. The population density was 11 people per square mile (4/km²). There were 28,189 housing units at an average density of 6 per square mile (2/km²). The racial makeup of the county was 77.82% White, 0.38% Black or African American, 12.92% Native American, 0.43% Asian, 0.05% Pacific Islander, 6.59% from other races, and 1.80% from two or more races. 16.65% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race. 9.84% reported speaking Spanish at home, while 6.29% speak Western Apache.[15]
There were 20,140 households out of which 26.30% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 55.10% were married couples living together, 10.80% had a female householder with no husband present, and 30.00% were non-families. 25.80% of all households were made up of individuals and 12.30% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.50 and the average family size was 2.99.
In the county, the population was spread out with 25.10% under the age of 18, 6.40% from 18 to 24, 22.30% from 25 to 44, 26.40% from 45 to 64, and 19.80% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 42 years. For every 100 females there were 96.80 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 94.20 males.
The median income for a household in the county was $30,917, and the median income for a family was $36,593. Males had a median income of $31,579 versus $22,315 for females. The per capita income for the county was $16,315. About 12.60% of families and 17.40% of the population were below the poverty line, including 25.90% of those under age 18 and 7.90% of those age 65 or over.
2010 census
As of the 2010 census, there were 53,597 people, 22,000 households, and 14,294 families living in the county.[16] The population density was 11.3 inhabitants per square mile (4.4/km2). There were 32,698 housing units at an average density of 6.9 per square mile (2.7/km2).[17] The racial makeup of the county was 76.8% white, 14.8% American Indian, 0.5% Asian, 0.4% black or African American, 0.1% Pacific islander, 5.3% from other races, and 2.0% from two or more races. Those of Hispanic or Latino origin made up 17.9% of the population.[16] In terms of ancestry, 17.4% were German, 13.3% were English, 11.4% were Irish, and 3.4% were American.[18]
Of the 22,000 households, 25.3% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 48.6% were married couples living together, 11.1% had a female householder with no husband present, 35.0% were non-families, and 29.3% of all households were made up of individuals. The average household size was 2.39 and the average family size was 2.94. The median age was 47.9 years.[16]
The median income for a household in the county was $37,580 and the median income for a family was $46,292. Males had a median income of $41,698 versus $30,023 for females. The per capita income for the county was $19,600. About 11.6% of families and 18.9% of the population were below the poverty line, including 27.4% of those under age 18 and 10.0% of those age 65 or over.[19]
Politics
Historically Gila County has been a Democratic-leaning county in largely Republican Arizona – for instance it voted for Adlai Stevenson II in 1952, Hubert Humphrey in 1968 and (very narrowly in a three-way contest) for John W. Davis in 1924. In much of the “dealignment” period from 1960 to 1980, when Arizona was the only state never carried by a Democrat, Gila was the second most-Democratic county in Arizona behind massively unionized Greenlee. Only during very large Presidential landslides was Gila County carried by Republicans before 2000: indeed, apart from Ronald Reagan and Richard Nixon in 1972 no Republican before 2000 ever carried the county by more than seven percentage points.
Since 2000, however, like Greenlee County, Gila County has trended heavily towards the Republican Party, and Hillary Clinton’s 2016 performance was the worst ever by a Democratic presidential nominee.
| Year | Republican | Democratic | Others |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | 63.0% 14,182 | 31.1% 7,003 | 5.9% 1,330 |
| 2012 | 62.3% 13,455 | 35.6% 7,697 | 2.1% 443 |
| 2008 | 62.9% 14,095 | 35.2% 7,884 | 2.0% 438 |
| 2004 | 59.1% 12,343 | 39.8% 8,314 | 1.1% 220 |
| 2000 | 51.6% 9,158 | 43.4% 7,700 | 5.0% 878 |
| 1996 | 36.8% 6,407 | 49.3% 8,577 | 13.9% 2,427 |
| 1992 | 31.3% 5,781 | 41.0% 7,571 | 27.7% 5,126 |
| 1988 | 51.4% 7,861 | 46.7% 7,147 | 1.9% 291 |
| 1984 | 56.0% 8,543 | 42.7% 6,509 | 1.3% 197 |
| 1980 | 55.3% 7,405 | 37.8% 5,068 | 6.9% 926 |
| 1976 | 42.9% 5,136 | 53.8% 6,440 | 3.2% 386 |
| 1972 | 54.7% 5,673 | 41.4% 4,295 | 3.9% 404 |
| 1968 | 37.2% 3,610 | 49.8% 4,831 | 13.0% 1,265 |
| 1964 | 35.2% 3,713 | 64.7% 6,821 | 0.0% 3 |
| 1960 | 42.0% 3,806 | 57.9% 5,251 | 0.1% 8 |
| 1956 | 51.3% 4,234 | 48.7% 4,026 | |
| 1952 | 43.3% 3,770 | 56.7% 4,928 | |
| 1948 | 32.1% 2,329 | 65.8% 4,780 | 2.2% 156 |
| 1944 | 31.8% 2,260 | 67.8% 4,818 | 0.4% 29 |
| 1940 | 31.2% 2,624 | 68.4% 5,752 | 0.4% 31 |
| 1936 | 23.2% 1,526 | 74.0% 4,859 | 2.8% 183 |
| 1932 | 27.8% 1,865 | 68.8% 4,625 | 3.4% 228 |
| 1928 | 50.6% 3,436 | 49.2% 3,341 | 0.2% 13 |
| 1924 | 34.6% 2,193 | 34.9% 2,218 | 30.5% 1,937 |
| 1920 | 53.4% 3,311 | 46.6% 2,894 | |
| 1916 | 26.1% 1,495 | 64.3% 3,686 | 9.6% 552 |
| 1912 | 10.3% 210 | 38.1% 779 | 51.6% 1,056[lower-alpha 1] |
Transportation
Major highways






Airports
The following public-use airports are located in the county:
Communities

City
- Globe (county seat)
Towns
- Hayden (partly in Pinal County)
- Miami
- Payson
- Star Valley
- Winkelman (partly in Pinal County)
Ghost towns
Census-designated places
- Bear Flat
- Beaver Valley
- Canyon Day
- Carrizo
- Cedar Creek
- Central Heights-Midland City
- Christopher Creek
- Claypool
- Copper Hill
- Cutter
- Deer Creek
- Dripping Springs
- East Globe
- East Verde Estates
- El Capitan
- Flowing Springs
- Freedom Acres
- Geronimo Estates
- Gisela
- Haigler Creek
- Hunter Creek
- Icehouse Canyon
- Jakes Corner
- Kohls Ranch
- Mead Ranch
- Mesa del Caballo
- Oxbow Estates
- Peridot
- Pinal
- Pine
- Rock House
- Roosevelt
- Round Valley
- Rye
- San Carlos
- Six Shooter Canyon
- Strawberry
- Tonto Basin
- Tonto Village
- Top-of-the-World
- Washington Park
- Wheatfields
- Whispering Pines
- Young
Other communities
Indian communities
County population ranking
The population ranking of the following table is based on the 2010 census of Gila County.[22][23]
† county seat
| Rank | City/Town/etc. | Population (2010 Census) | Municipal type | Incorporated |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Payson | 15,301 | Town | |
| 2 | † Globe | 7,532 | City | 1875 (founded) |
| 3 | San Carlos | 4,038 | CDP | |
| 4 | Central Heights-Midland City | 2,534 | CDP | |
| 5 | Star Valley | 2,310 | Town | 2005 |
| 6 | Pine | 1,963 | CDP | |
| 7 | Miami | 1,837 | Town | |
| 8 | Claypool | 1,538 | CDP | |
| 9 | Tonto Basin | 1,424 | CDP | |
| 10 | Peridot | 1,350 | CDP | |
| 11 | Canyon Day | 1,209 | CDP | |
| 12 | Six Shooter Canyon | 1,019 | CDP | |
| 13 | Strawberry | 961 | CDP | |
| 14 | Wheatfields | 785 | CDP | |
| 15 | Mesa del Caballo | 765 | CDP | |
| 16 | Icehouse Canyon | 677 | CDP | |
| 17 | Young | 666 | CDP | |
| 18 | Hayden (partially in Pinal County) | 662 | Town | |
| 19 | Gisela | 570 | CDP | |
| 20 | Round Valley | 487 | CDP | |
| 21 | Pinal | 439 | CDP | |
| 22 | Winkelman (partially in Pinal County) | 353 | Town | |
| 23 | Cedar Creek | 318 | CDP | |
| 24 | Tonto Village | 256 | CDP | |
| 25 | Dripping Springs | 235 | CDP | |
| t-26 | Beaver Valley | 231 | CDP | |
| t-26 | Top-of-the-World | 231 | CDP | |
| 27 | East Globe | 226 | CDP | |
| 28 | Oxbow Estates | 217 | CDP | |
| 29 | Deer Creek | 216 | CDP | |
| 30 | East Verde Estates | 170 | CDP | |
| 31 | Christopher Creek | 156 | CDP | |
| 32 | Whispering Pines | 148 | CDP | |
| 33 | Carrizo | 127 | CDP | |
| 34 | Copper Hill | 108 | CDP | |
| 35 | Freedom Acres | 84 | CDP | |
| 36 | Rye | 77 | CDP | |
| 37 | Jakes Corner | 76 | CDP | |
| 38 | Cutter | 74 | CDP | |
| 39 | Washington Park | 70 | CDP | |
| 40 | Geronimo Estates | 60 | CDP | |
| 41 | Rock House | 50 | CDP | |
| 42 | Hunter Creek | 48 | CDP | |
| 43 | Kohls Ranch | 46 | CDP | |
| 44 | Flowing Springs | 42 | CDP | |
| 45 | Mead Ranch | 38 | CDP | |
| 46 | El Capitan | 37 | CDP | |
| 47 | Roosevelt | 28 | CDP | |
| 48 | Haigler Creek | 19 | CDP | |
| 49 | Bear Flat | 18 | CDP |
Notable people
- David Gowan
See also
Notes
- This comprises 542 votes (26.5%) for Progressive Theodore Roosevelt, 501 votes (25.1%) for Socialist Eugene V. Debs, and 13 votes (0.6%) for Prohibition Party candidate Eugene W. Chafin.
References
- "State & County QuickFacts". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on June 7, 2011. Retrieved May 18, 2014.
- "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on May 31, 2011. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2012-10-12. Retrieved 2013-07-14.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Gila National Forest (archived)". United States Forest Service. 2003-12-04. Archived from the original on January 11, 2006. Retrieved 2007-10-16.
- Forrest, Earle R. (1936). Arizona's Dark and Bloody Ground; an authentic account of the sanguinary Pleasant Valley vendetta that swept through Arizona's cattleland in the latter eighteen eighties--the Graham-Tewksbury feud. Caldwell, Idaho: Caxton Printers, Ltd. pp. 15, 292. OCLC 1825248.
- Burnham, Frederick Russell (1926). Scouting on Two Continents. Doubleday, Page & company. pp. 2, Chapters 3 & 4. OCLC 407686.
- Lott, Jack (1981). "Chapter 8. The Making of a Hero: Burnham in the Tonto Basin". In Boddington, Craig (ed.). America -- The Men and Their Guns That Made Her Great. Petersen Publishing Co. p. 90. ISBN 0-8227-3022-7.
- "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. August 23, 2012. Retrieved August 23, 2015.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". Retrieved May 10, 2019.
- "U.S. Decennial Census". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved May 18, 2014.
- "Historical Census Browser". University of Virginia Library. Retrieved May 18, 2014.
- "Population of Counties by Decennial Census: 1900 to 1990". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved May 18, 2014.
- "Census 2000 PHC-T-4. Ranking Tables for Counties: 1990 and 2000" (PDF). United States Census Bureau. Retrieved May 18, 2014.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved May 14, 2011.
- "Language Map Data Center". apps.mla.org.
- "DP-1 Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 Demographic Profile Data". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 2020-02-13. Retrieved 2016-01-20.
- "Population, Housing Units, Area, and Density: 2010 - County". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 2020-02-13. Retrieved 2016-01-20.
- "DP02 SELECTED SOCIAL CHARACTERISTICS IN THE UNITED STATES – 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 2020-02-13. Retrieved 2016-01-20.
- "DP03 SELECTED ECONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS – 2006-2010 American Community Survey 5-Year Estimates". United States Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 2020-02-13. Retrieved 2016-01-20.
- Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org.
- Scammon, Richard M. (compiler); America at the Polls: A Handbook of Presidential Election Statistics 1920-1964; pp. 42-44 ISBN 0405077114
- "2010 U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2013-02-10.
- Geography, US Census Bureau. "2010 Census Block Maps". www.census.gov. Retrieved 23 March 2018.
External links
- County website
