Frankenfield Glacier
Frankenfield Glacier (71°52′S 98°13′W) is a small glacier in the northeast part of Noville Peninsula, Thurston Island, in Antarctica. It flows east-northeast to the Bellingshausen Sea between Mount Feury and Mulroy Island. The glacier was first roughly delineated from air photos taken by U.S. Navy Operation Highjump in December 1946, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Lieutenant Chester Frankenfield, a meteorologist on the U.S. Navy Bellingshausen Sea Expedition, who established an automated weather station on Thurston Island in February 1960.[1]
| Frankenfield Glacier | |
|---|---|
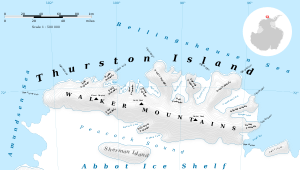 Map of Thurston Island | |
 Location of Frankenfield Glacier in Antarctica | |
| Location | Ellsworth Land |
| Coordinates | 71°52′00″S 98°13′00″W |
| Thickness | unknown |
| Terminus | Bellingshausen Sea |
| Status | unknown |

Satellite image of Thurston Island.
Maps
- Thurston Island – Jones Mountains. 1:500000 Antarctica Sketch Map. US Geological Survey, 1967.
- Antarctic Digital Database (ADD). Scale 1:250000 topographic map of Antarctica. Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR). Since 1993, regularly upgraded and updated.
References
- "Frankenfield Glacier". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 2012-04-06.

| Types |
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anatomy |
| ||||||
| Processes | |||||||
| Measurements | |||||||
| Volcanic relations | |||||||
| Landforms |
| ||||||
| |||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.