Erdut Agreement
The Erdut Agreement (Serbo-Croatian: Erdutski sporazum / Ердутски споразум, French: Accord d'Erdut, Russian: Эрдутское соглашение, Spanish: Acuerdo de Erdut, Chinese: 伊尔杜协议, Arabic: اتفاقية أردوت), officially the Basic Agreement on the Region of Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Sirmium, was an agreement reached on 12 November 1995 between the authorities of the Republic of Croatia and the local Serb authorities of the Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Syrmia region on the peaceful resolution to the Croatian War of Independence in eastern Croatia. It initiated process of peaceful reintegration of the region to the central government control (implemented by the United Nations) and provided set of guarantees on minority rights and refugee return. It was named after Erdut, the village in which it was signed.
Long name:
| |
|---|---|
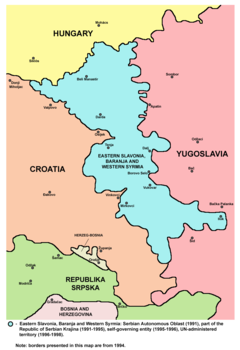 Map of Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Syrmia | |
| Type | Peace agreement |
| Signed | 12 November 1995[1] |
| Location | Erdut, Croatia |
| Signatories | Hrvoje Šarinić Milan Milanović |
| Parties |
(local administration in Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Syrmia) Witnessed by: |
The signers were Hrvoje Šarinić, the former prime minister of Croatia, and Milan Milanović, a local Serb politician representing the self-proclaimed Republic of Serbian Krajina (RSK) under instructions from the authorities of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. The witnesses were Peter Galbraith, the ambassador of the United States to Croatia at the time, and Thorvald Stoltenberg, the United Nations intermediary.[2]
The territory of Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Sirmium had previously been controlled by the RSK, and before that by the SAO Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Syrmia. The agreement was acknowledged by the United Nations Security Council Resolution 1023, and it paved the way to the establishment of the United Nations Transitional Authority for Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Sirmium. UNTAES was not designed as an ordinary UN mission but rather as an transitional administration, partially modeled on the United Nations Transitional Authority in Cambodia, therefore providing the UNTAES with direct and supreme governing mandate over the region which was an effective United Nations protectorate.
Background
In 1995 mini Contact Group of foreign ambassadors in Zagreb drafted a comprehensive proposal to Croatian President Franjo Tuđman and the leaders of the Republic of Serbian Krajina in Knin aimed at peaceful resolution of the Croatian War of Independence. The proposal was known as the Z-4 Plan and it proposed reintegration of Krajina to Croatian constitutional framework on the basis of a new Constitutional Agreement which defined Krajina as an autonomous region of Croatia. The plan did not envisage special autonomy for Eastern Slavonia but rather two years long transitional period. Krajina leaders in Knin refused to receive the draft proposal which subsequently led to Operation Flash and Operation Storm and complete military defeat of Krajina resulting in over 200,000 Croatian Serb refugees who left their homes.
Rump and geographically separated territory of Eastern Slavonia, Baranja and Western Syrmia (commonly known as Eastern Slavonia) remained the only part of Croatia under Serb control. Contrary to Krajina, Eastern Slavonia shared a long border with the Republic of Serbia. It was also economically and socially dependent and politically much more closely aligned with authorities in Belgrade and Novi Sad than Krajina.[3] This led international community to belief that Croatian intervention in Eastern Slavonia will trigger Yugoslav military reaction and will lead to the larger escalation of hostilities.[4] At the same time military defeat of Krajina and signing of the Washington Agreement opened the space to resolve the armed conflict in Bosnia which US Administration wanted to use before the 1996 United States presidential election.[5] Croatia conditioned its participation at the Dayton Peace Conference on the resolution of conflict in Eastern Slavonia, while international community insisted on avoidance of any new major escalation of Yugoslav crisis. This created conditions in which peaceful resolution was preferred or acceptable to all parties concerned.
Agreement history
As a part of his Bosnia peace efforts United States President Bill Clinton also stated:
There must be a long-term plan for resolving the situation in Eastern Slavonia ... based on Croatian sovereignty and the principles of the Z-4 Plan (e.g. Serb home rule, the right of refugees to return, and the other guarantees for Serbs who live there).[1]
Despite territorial autonomy's prominent place in President Clinton's plans and effort by the US ambassador Peter Galbraith to model this autonomy proposal on recently suspended precedent of the Autonomous District of Glina and Knin from the Constitutional Act on National and Ethnic Communities or Minorities, this proposal was rejected by Croatian Government which preferred military solution over territorial autonomy.[1] This convinced international community to focus on the models of non-territorial national personal autonomy, minority rights and inter-municipal cooperation.
Provisions
Return of refugees
United Nations Transitional Administration was requested to ensure the possibility for the return of refugees and displaced persons to their homes of origin. The same rights were to be enjoyed both to those who have left the region or those who have come to the region from other parts of Croatia.
Inter-communal power sharing
Joint Implementation Committees formed both by local Croat and Serb communities assisted the UNTAES in governing the region. Local police forces were organized to have equal number of ethnic Croats and Ethnic Serbs plus additional smaller number from all the other communities in the region.
Minority rights provisions
The agreement itself and subsequent developments and commitments during the UNTAES mandate represent the basis on which numerous minority institutions operate today. Establishment of the Joint Council of Municipalities, with a Serbian majority population was one of explicit rights granted to the Serb community. Other institutions such as Serb National Council and weekly magazine Novosti were established at the same time, while some, such as Radio Borovo, were registered in accordance with Croatian laws. Agreement requires respect of the highest levels of internationally recognized human rights and fundamental freedoms.
International impact
Erdut Agreement was quoted as an precedent and comparable case by the Ukrainian diplomats for implementation of Minsk II package of measures agreed within the framework of Minsk Protocol aimed at halting the War in Donbass.[6]
See also
- Josip Reihl-Kir (25 July 1955 – 1 July 1991; assassinated police chief from Osijek during SFR Yugoslavia known for his peacemaking initiatives)
- Dayton Agreement (Erdut Agreement was major precondition for the 1995 conference)
- Croatia–Serbia border dispute
- Croatia–Serbia genocide case
References
- Galbraith, Peter. "Negotiating Peace in Croatia: a personal account of the road to Erdut". In Blitz, Brad K. (ed.). War and Change in the Balkans. Cambridge University Press. p. 124-131. ISBN 0-521-86042-3.
- Lukic, Renéo (2006). La politique étrangère de la Croatie, de son indépendance à nos jours, 1991-2006. Les Presses de l'Université Laval. p. 193. ISBN 2763780199.
- Hayball, Harry Jack (April 2015). Serbia and the Serbian Rebellion in Croatia (1990-1991) (PDF) (Doctor of Philosophy). Goldsmiths College. Retrieved 4 July 2020.
- Ramsbotham, Oliver; Woodhouse, Tom (1999). Encyclopedia of International Peacekeeping Operations. Santa Barbara, California: ABC-CLIO. ISBN 0874368928.
- Dover, Edwin D. The Presidential Election of 1996: Clinton's Incumbency and Television. Westport, Connecticut & London: Praeger Publishers. ISBN 0-275-96259-8.
- Тимошенко, Денис (19 February 2020). "Эрдутское соглашение в Хорватии во многом напоминает Минск-2 – Левченко о совместном патрулировании на Донбассе". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. Retrieved 4 July 2020.
Sources
- Albert Bing (October 2008). "Sjedinjene Američke Države i reintegracija hrvatskog Podunavlja" [The United States of America and the reintegration of the Croatian Danube Region]. Scrinia Slavonica (in Croatian). Slavonski Brod: Croatian Institute of History. 8 (1). Retrieved 2013-02-21.
External links
| Croatian Wikisource has original text related to this article: |
| Serbian Wikisource has original text related to this article: |
- Full text of Erdut Agreement, UN Peacemaker (in English, French, Chinese, Arabic, Russian and Spanish)



