Cumbie Glacier
Cumbie Glacier (77°13′S 154°12′W) is a short, steep glacier just east of the Scott Nunataks, flowing north into the Swinburne Ice Shelf along the southwest side of Sulzberger Bay. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and from U.S. Navy air photos, 1959–66, and named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for William A. Cumbie, Jr., U.S. Navy. An aviation electronics technician, Cumbie was a radioman on the ski-equipped R4D aircraft carrying Rear Admiral George Dufek that was the first to land at the geographic South Pole, October 31, 1956.
| Cumbie Glacier | |
|---|---|
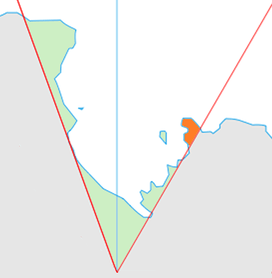 Location of King Edward VII Land (marked in orange) within the Ross Dependency | |
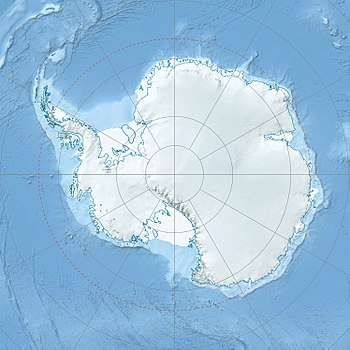 Location of Cumbie Glacier in Antarctica | |
| Type | steep |
| Location | King Edward VII Land |
| Coordinates | 77°13′S 154°12′W |
| Thickness | unknown |
| Terminus | Sulzberger Bay |
| Status | unknown |
References

| Types |
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anatomy |
| ||||||
| Processes | |||||||
| Measurements | |||||||
| Volcanic relations | |||||||
| Landforms |
| ||||||
| |||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.