Acetyl-CoA hydrolase
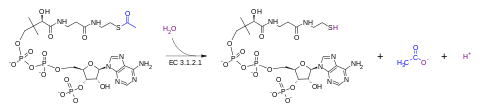
In enzymology, an acetyl-CoA hydrolase (EC 3.1.2.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
| acetyl-CoA hydrolase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 3.1.2.1 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 9027-54-7 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are acetyl-CoA and H2O, whereas its two products are CoA and acetate. It is present in many species including animals (see reference below).
This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolases, specifically those acting on thioester bonds. The systematic name of this enzyme class is acetyl-CoA hydrolase. Other names in common use include acetyl-CoA deacylase, acetyl-CoA acylase, acetyl coenzyme A hydrolase, acetyl coenzyme A deacylase, acetyl coenzyme A acylase, and acetyl-CoA thiol esterase. This enzyme participates in pyruvate metabolism.
Structural studies
As of late 2007, only one structure has been solved for this class of enzymes, with the PDB accession code 2H4U.
See also
- Acetyl-CoA synthetase and ACSS2, enzymes that perform the reverse reaction using ATP
References
- Gergely J, Hele P, Ramakrishnan CV (1952). "Succinyl and acetyl coenzyme A deacylases". J. Biol. Chem. 198 (1): 323–334. PMID 12999747.