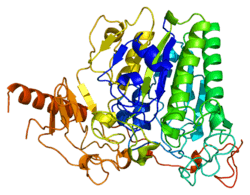
Arylsulfatase A
Arylsulfatase A (or cerebroside-sulfatase) is an enzyme that breaks down sulfatides, namely cerebroside 3-sulfate into cerebroside and sulfate. In humans, arylsulfatase A is encoded by the ARSA gene.[5][6]
Pathology
A deficiency is associated with metachromatic leukodystrophy, an autosomal recessive disease.[7]
Biochemistry
Enzyme regulation
Arylsulfatase A is inhibited by phosphate, which forms a covalent bond with the active site 3-oxoalanine.[8]
gollark: I have some books on that.
gollark: Of course. It's trivial.
gollark: https://github.com/janet-lang/pkgs/blob/master/pkgs.janet you.
gollark: I'm sure you'd like to think so.
gollark: I wrote lyricly's and 7.
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000100299 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000022620 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Stein C, Gieselmann V, Kreysing J, Schmidt B, Pohlmann R, Waheed A, Meyer HE, O'Brien JS, von Figura K (January 1989). "Cloning and expression of human arylsulfatase A". J. Biol. Chem. 264 (2): 1252–9. PMID 2562955.
- Matzner U, Herbst E, Hedayati KK, Lüllmann-Rauch R, Wessig C, Schröder S, Eistrup C, Möller C, Fogh J, Gieselmann V (May 2005). "Enzyme replacement improves nervous system pathology and function in a mouse model for metachromatic leukodystrophy". Hum. Mol. Genet. 14 (9): 1139–52. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddi126. PMID 15772092.
- Sevin C, Aubourg P, Cartier N (April 2007). "Enzyme, cell and gene-based therapies for metachromatic leukodystrophy". J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 30 (2): 175–83. doi:10.1007/s10545-007-0540-z. PMID 17347913.
- "Arylsulfatase A / ARSA". Sino Biological. Retrieved 12 September 2014.
Further reading
- Narahara K, Takahashi Y, Murakami M, et al. (1992). "Terminal 22q deletion associated with a partial deficiency of arylsulphatase A". J. Med. Genet. 29 (6): 432–3. doi:10.1136/jmg.29.6.432. PMC 1016000. PMID 1352356.
- Gieselmann V, Zlotogora J, Harris A, et al. (1995). "Molecular genetics of metachromatic leukodystrophy". Hum. Mutat. 4 (4): 233–42. doi:10.1002/humu.1380040402. PMID 7866401.
- DeLuca C, Brown JA, Shows TB (1979). "Lysosomal arylsulfatase deficiencies in humans: Chromosome assignments for arylsulfatase A and B". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 76 (4): 1957–61. doi:10.1073/pnas.76.4.1957. PMC 383512. PMID 36611.
- Fujii T, Kobayashi T, Honke K, et al. (1992). "Proteolytic processing of human lysosomal arylsulfatase A". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1122 (1): 93–8. doi:10.1016/0167-4838(92)90132-W. PMID 1352993.
- Kappler J, von Figura K, Gieselmann V (1992). "Late-onset metachromatic leukodystrophy: molecular pathology in two siblings". Ann. Neurol. 31 (3): 256–61. doi:10.1002/ana.410310305. PMID 1353340.
- Li ZG, Waye JS, Chang PL (1992). "Diagnosis of arylsulfatase A deficiency". Am. J. Med. Genet. 43 (6): 976–82. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320430614. PMID 1357970.
- Polten A, Fluharty AL, Fluharty CB, et al. (1991). "Molecular basis of different forms of metachromatic leukodystrophy". N. Engl. J. Med. 324 (1): 18–22. doi:10.1056/NEJM199101033240104. PMID 1670590.
- Kondo R, Wakamatsu N, Yoshino H, et al. (1991). "Identification of a mutation in the arylsulfatase A gene of a patient with adult-type metachromatic leukodystrophy". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 48 (5): 971–8. PMC 1683039. PMID 1673291.
- Nelson PV, Carey WF, Morris CP (1991). "Population frequency of the arylsulphatase A pseudo-deficiency allele". Hum. Genet. 87 (1): 87–8. doi:10.1007/BF01213099. PMID 1674719.
- Bohne W, von Figura K, Gieselmann V (1991). "An 11-bp deletion in the arylsulfatase A gene of a patient with late infantile metachromatic leukodystrophy". Hum. Genet. 87 (2): 155–8. doi:10.1007/BF00204172. PMID 1676699.
- Gieselmann V, Fluharty AL, Tønnesen T, Von Figura K (1991). "Mutations in the arylsulfatase A pseudodeficiency allele causing metachromatic leukodystrophy". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 49 (2): 407–13. PMC 1683316. PMID 1678251.
- Fluharty AL, Fluharty CB, Bohne W, et al. (1992). "Two new arylsulfatase A (ARSA) mutations in a juvenile metachromatic leukodystrophy (MLD) patient". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 49 (6): 1340–50. PMC 1686463. PMID 1684088.
- Kreysing J, von Figura K, Gieselmann V (1990). "Structure of the arylsulfatase A gene". Eur. J. Biochem. 191 (3): 627–31. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19167.x. PMID 1975241.
- Gieselmann V, Polten A, Kreysing J, von Figura K (1990). "Arylsulfatase A pseudodeficiency: loss of a polyadenylylation signal and N-glycosylation site". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86 (23): 9436–40. doi:10.1073/pnas.86.23.9436. PMC 298511. PMID 2574462.
- Geurts van Kessel AH (1981). "Regional localization of the genes coding for human ACO2, ARSA, and NAGA on chromosome 22". Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 28 (3): 169–72. doi:10.1159/000131527. PMID 7192199.
- Barth ML, Fensom A, Harris A (1995). "Identification of seven novel mutations associated with metachromatic leukodystrophy". Hum. Mutat. 6 (2): 170–6. doi:10.1002/humu.1380060210. PMID 7581401.
- Schmidt B, Selmer T, Ingendoh A, von Figura K (1995). "A novel amino acid modification in sulfatases that is defective in multiple sulfatase deficiency". Cell. 82 (2): 271–8. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(95)90314-3. PMID 7628016.
- Barth ML, Ward C, Harris A, et al. (1995). "Frequency of arylsulphatase A pseudodeficiency associated mutations in a healthy population". J. Med. Genet. 31 (9): 667–71. doi:10.1136/jmg.31.9.667. PMC 1050073. PMID 7815433.
External links
- GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Arylsulfatase A Deficiency - Metachromatic Leukodystrophy
- OMIM entries on ARSA Deficiency
- Arylsulfatase+A at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Human ARSA genome location and ARSA gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.
- Overview of all the structural information available in the PDB for UniProt: P15289 (Human Arylsulfatase A) at the PDBe-KB.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.