Acetoacetyl-CoA
Acetoacetyl CoA is the precursor of HMG-CoA in the mevalonate pathway, which is essential for cholesterol biosynthesis. It also takes a similar role in the ketone bodies synthesis (ketogenesis) pathway of the liver. In the ketone bodies digestion pathway (in the tissue), it is no longer associated with having HMG-CoA as a product or as a reactant.
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.378 |
| MeSH | acetoacetyl+CoA |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
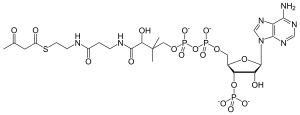
| C25H40N7O18P3S | |
| Molar mass | 851.609 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
It is created from acetyl-CoA, a thioester, which reacts with the enolate of a second molecule of acetyl-CoA in a Claisen condensation reaction,[1] and it is acted upon by HMG-CoA synthase to form HMG-CoA. During the metabolism of leucine, this last reaction is reversed.
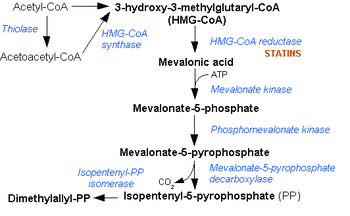
Mevalonate pathway
References
- Yurkanis, Bruice, Paula (2017). Organic chemistry. Pearson. ISBN 9780134042282. OCLC 974910578.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.