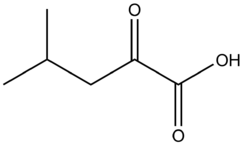
alpha-Ketoisocaproic acid
α-Ketoisocaproic acid (α-KIC) and its conjugate base, α-ketoisocaproate, are metabolic intermediates in the metabolic pathway for L-leucine.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
4-Methyl-2-oxopentanoic acid | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
4-Methyl-2-oxopentanoic acid[1] | |
| Other names
4-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 3DMet | |
| 1701823 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.304 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Alpha-ketoisocaproic+acid |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3265 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H10O3 | |
| Molar mass | 130.143 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.055 g cm−3 (at 20 °C) |
| Melting point | 8 to 10 °C (46 to 50 °F; 281 to 283 K) |
| Boiling point | 85 °C (185 °F; 358 K) at 13 mmHg |
| log P | 0.133 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.651 |
| Basicity (pKb) | 11.346 |
| Hazards | |
EU classification (DSD) (outdated) |
|
| R-phrases (outdated) | R34 |
| S-phrases (outdated) | S26, S36/37/39, S45 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Leucine metabolism
gollark: Oh, this is really cool, Random PSIDeas has a thing which allows me to move my camera position.
gollark: ... right, the dirt, silly me.
gollark: It would also expose the stone brick roof to the surface.
gollark: <@280423421555507203> I would but there's a farm which would need moving.
gollark: Going to need to move it down a block.
References
- CID 70 from PubChem
- Wilson JM, Fitschen PJ, Campbell B, Wilson GJ, Zanchi N, Taylor L, Wilborn C, Kalman DS, Stout JR, Hoffman JR, Ziegenfuss TN, Lopez HL, Kreider RB, Smith-Ryan AE, Antonio J (February 2013). "International Society of Sports Nutrition Position Stand: beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate (HMB)". Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. 10 (1): 6. doi:10.1186/1550-2783-10-6. PMC 3568064. PMID 23374455.
- Kohlmeier M (May 2015). "Leucine". Nutrient Metabolism: Structures, Functions, and Genes (2nd ed.). Academic Press. pp. 385–388. ISBN 978-0-12-387784-0. Retrieved 6 June 2016.
Energy fuel: Eventually, most Leu is broken down, providing about 6.0kcal/g. About 60% of ingested Leu is oxidized within a few hours ... Ketogenesis: A significant proportion (40% of an ingested dose) is converted into acetyl-CoA and thereby contributes to the synthesis of ketones, steroids, fatty acids, and other compounds
Figure 8.57: Metabolism of L-leucine
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.