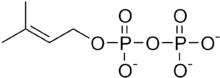
Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate
Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP; or alternatively, dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMADP); also isoprenyl pyrophosphate) is an isoprenoid precursor. It is a product of both the mevalonate pathway and the MEP pathway of isoprenoid precursor biosynthesis. It is an isomer of isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and exists in virtually all life forms. The enzyme isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase catalyzes isomerization between DMAPP and IPP.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl diphosphate | |
| Other names
Dimethylallyl diphosphate; isoprenyl pyrophosphate; isoprenyl diphosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | 3,3-dimethylallyl+pyrophosphate |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H12O7P2 | |
| Molar mass | 246.092 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
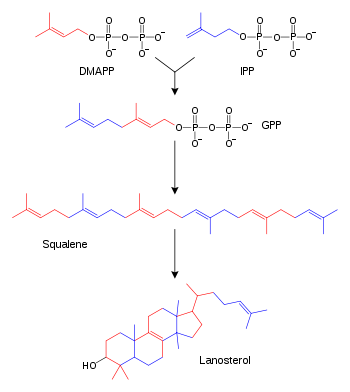
In the mevalonate pathway DMAPP is synthesised from mevalonic acid. In contrast, DMAPP is synthesised from HMBPP in the MEP pathway.
At present, it is believed that there is crossover between the two pathways in organisms that use both pathways to create terpenes and terpenoids, such as in plants, and that DMAPP is the crossover product.
References
- Wang, W.; Oldfield, E. (2014). "Bioorganometallic Chemistry with Ispg and Isph: Structure, Function, and Inhibition of the [Fe4s4] Proteins Involved in Isoprenoid Biosynthesis". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53: 4294–4310. doi:10.1002/anie.201306712. PMC 3997630. PMID 24481599.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
External links
