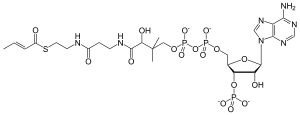
Crotonyl-CoA
Crotonyl-coenzyme A is an intermediate in the fermentation of butyric acid, and in the metabolism of lysine and tryptophan.[1] It is important in the metabolism of fatty acids and amino acids.[2]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.360 |
| MeSH | Crotonyl-coenzyme+A |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C25H40N7O17P3S | |
| Molar mass | 835.609 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Ray, Lauren; Valentic, Timothy R; Miyazawa, Takeshi; Withall, David M; Song, Lijiang; Milligan, Jacob C; Osada, Hiroyuki; Takahashi, Shunji; Tsai, Shiou-Chuan; Challis, Gregory L (2016). "A crotonyl-CoA reductase-carboxylase independent pathway for assembly of unusual alkylmalonyl-CoA polyketide synthase extender units". Nature Communications. 7: 13609. doi:10.1038/ncomms13609. PMC 5187497. PMID 28000660.
- "Crotonyl-CoA".
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.