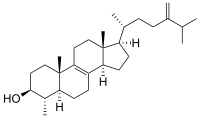
4α-methylfecosterol
4α-methylfecosterol is a metabolic intermediate of sterols made by certain fungis, can be converted to 24-Methylenelophenol by enzyme HYD1, or undergo 4-demethylation to fecosterol.[1][2]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C29H48O | |
| Molar mass | 412.702 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Kuchta, T; Bartková, K; Kubinec, R (30 November 1992). "Ergosterol depletion and 4-methyl sterols accumulation in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae treated with an antifungal, 6-amino-2-n-pentylthiobenzothiazole". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 189 (1): 85–91. doi:10.1016/0006-291x(92)91529-y. PMID 1449509.
- Kuchta, T; Léka, C; Farkas, P; Bujdáková, H; Belajová, E; Russell, NJ (July 1995). "Inhibition of sterol 4-demethylation in Candida albicans by 6-amino-2-n-pentylthiobenzothiazole, a novel mechanism of action for an antifungal agent". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 39 (7): 1538–41. doi:10.1128/aac.39.7.1538. PMC 162777. PMID 7492100.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.