1966 United States Senate elections
The 1966 United States Senate elections were elections on November 8, 1966 for the United States Senate which occurred midway through the second (only full) term of President Lyndon B. Johnson. With divisions in the Democratic base over the Vietnam War, and with the traditional mid-term advantage of the party not holding the presidency, the Republicans took three Democratic seats. Despite Republican gains, the balance remained overwhelmingly in favor of the Democrats, who retained a 64–36 majority. These were also the first elections held after enactment of the Voting Rights Act of 1965.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
35 of the 100 seats in the United States Senate 51 seats needed for a majority | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
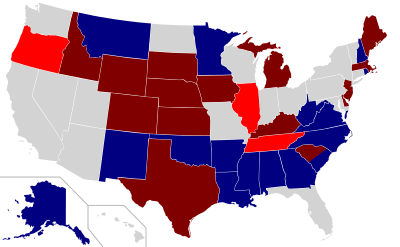 Results of the elections: Democratic gain Democratic hold Republican gain Republican hold No election | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Retirements
Republican holds
- Massachusetts: Leverett Saltonstall (R) was replaced by Edward Brooke (R)
- Wyoming: Milward L. Simpson (R) was replaced by Clifford Hansen (R)
Republican gain
- Oregon: Maurine Brown Neuberger (D) was replaced by Mark Hatfield (R)
Incumbents who lost their seats
Democratic holds
- South Carolina: Appointee Donald S. Russell (D) lost nomination to finish the term to Ernest Hollings (D), who went on to win the general election
- Virginia: Absalom Willis Robertson (D) lost renomination to William B. Spong Jr. (D), who went on to win the general election
Republican gains
- Illinois: Paul Douglas (D) lost to Charles H. Percy (R)
- Tennessee: Ross Bass (D) lost renomination to Frank G. Clement (D), who went on to lose the general election to Howard Baker (R)
Change in composition
Before the elections
| D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 | D6 | D7 | D8 | D9 | D10 |
| D20 | D19 | D18 | D17 | D16 | D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 |
| D21 | D22 | D23 | D24 | D25 | D26 | D27 | D28 | D29 | D30 |
| D40 | D39 | D38 | D37 | D36 | D35 | D34 | D33 | D32 | D31 |
| D41 | D42 | D43 | D44 | D45 | D46 | D47 | D48 Ala. Ran |
D49 Alaska Ran |
D50 Ark. Ran |
| Majority → | D51 Ga. Ran | ||||||||
| D60 Okla. Ran |
D59 N.C. Ran |
D58 N.M. Ran |
D57 N.H. Ran |
D56 Mont. Ran |
D55 Miss. Ran |
D54 Minn. Ran |
D53 La. Ran |
D52 Ill. Ran | |
| D61 Ore. Retired |
D62 R.I. Ran |
D63 S.C. (sp) Ran |
D64 Tenn. Ran |
D65 Va. (reg) Ran |
D66 Va. (sp) Ran |
D67 W.Va. Ran |
R33 Wyo. Retired |
R32 Texas Ran |
R31 S.D. Ran |
| R21 Idaho Ran |
R22 Iowa Ran |
R23 Kan. Ran |
R24 Ky. Ran |
R25 Me. Ran |
R26 Mass. Retired |
R27 Mich. Ran |
R28 Neb. Ran |
R29 N.J. Ran |
R30 S.C. Ran |
| R20 Del. Ran |
R19 Colo. Ran |
R18 | R17 | R16 | R15 | R14 | R13 | R12 | R11 |
| R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | R7 | R8 | R9 | R10 |
After the elections
| D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 | D6 | D7 | D8 | D9 | D10 |
| D20 | D19 | D18 | D17 | D16 | D15 | D14 | D13 | D12 | D11 |
| D21 | D22 | D23 | D24 | D25 | D26 | D27 | D28 | D29 | D30 |
| D40 | D39 | D38 | D37 | D36 | D35 | D34 | D33 | D32 | D31 |
| D41 | D42 | D43 | D44 | D45 | D46 | D47 | D48 Ala. Re-elected |
D49 Alaska Re-elected |
D50 Ark. Re-elected |
| Majority → | D51 Ga. Re-elected | ||||||||
| D60 R.I. Re-elected |
D59 Okla. Re-elected |
D58 N.C. Re-elected |
D57 N.M. Re-elected |
D56 N.H. Re-elected |
D55 Mont. Re-elected |
D54 Miss. Re-elected |
D53 Minn. Elected[lower-alpha 1] |
D52 La. Re-elected | |
| D61 S.C. (sp) Hold |
D62 Va. (reg) Hold |
D63 Va. (sp) Elected[lower-alpha 1] |
D64 W.Va. Re-elected |
R36 Wyo. Hold |
R35 Texas Re-elected |
R34 Tenn. Gain |
R33 S.D. Re-elected |
R32 S.C. (reg) Re-elected |
R31 Ore. Gain |
| R21 Idaho Re-elected |
R22 Ill. Gain |
R23 Iowa Re-elected |
R24 Kan. Re-elected |
R25 Ky. Re-elected |
R26 Me. Re-elected |
R27 Mass. Hold |
R28 Mich. Elected[lower-alpha 1] |
R29 Neb. Re-elected |
R30 N.J. Re-elected |
| R20 Del. Re-elected |
R19 Colo. Re-elected |
R18 | R17 | R16 | R15 | R14 | R13 | R12 | R11 |
| R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | R7 | R8 | R9 | R10 |
| Key: |
|
|---|
Race summaries
Special elections during the 89th Congress
In these special elections, the winner was seated during 1966 or before January 3, 1967; ordered by election date, then state.
| State | Incumbent | Results | Candidates | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Senator | Party | Electoral history | |||
| South Carolina (Class 3) |
Donald S. Russell | Democratic | 1965 (Appointed) | Incumbent lost nomination. New senator elected November 6, 1966. Democratic hold. |
|
| Virginia (Class 1) |
Harry F. Byrd Jr. | Democratic | 1965 (Appointed) | Interim appointee elected November 6, 1966. |
|
Elections leading to the next Congress
In these general elections, the winners were elected for the term beginning January 3, 1967; ordered by state.
All of the elections involved the Class 2 seats.
| State | Incumbent | Results | Candidates | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Senator | Party | Electoral history | |||
| Alabama | John Sparkman | Democratic | 1946 (Special) 1948 1954 1960 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Alaska | Bob Bartlett | Democratic | 1958 (New seat) 1960 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Arkansas | John L. McClellan | Democratic | 1942 1948 1954 1960 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Colorado | Gordon Allott | Republican | 1954 1960 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Delaware | J. Caleb Boggs | Republican | 1960 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Georgia | Richard Russell Jr. | Democratic | 1932 (Special) 1936 1942 1948 1954 1960 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Idaho | Leonard B. Jordan | Republican | 1962 (Appointed) 1962 (Special) |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Illinois | Paul Douglas | Democratic | 1948 1954 1960 |
Incumbent lost re-election. New senator elected. Republican gain. |
|
| Iowa | Jack Miller | Republican | 1960 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Kansas | James B. Pearson | Republican | 1962 (Appointed) 1962 (Special) |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Kentucky | John Sherman Cooper | Republican | 1946 (Special) 1948 (Lost) 1952 (Special) 1954 (Lost) 1956 (Special) 1960 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Louisiana | Allen J. Ellender | Democratic | 1936 1942 1948 1954 1960 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Maine | Margaret Chase Smith | Republican | 1948 1954 1960 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Massachusetts | Leverett Saltonstall | Republican | 1944 (Special) 1948 1954 1960 |
Incumbent retired. New senator re-elected. Republican hold. |
|
| Michigan | Robert P. Griffin | Republican | 1966 (Appointed) | Interim appointee elected. |
|
| Minnesota | Walter Mondale | Democratic | 1964 (Appointed) | Interim appointee elected. |
|
| Mississippi | James Eastland | Democratic | 1942 1948 1954 1960 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Montana | Lee Metcalf | Democratic | 1960 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Nebraska | Carl Curtis | Republican | 1954 1960 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| New Hampshire | Thomas J. McIntyre | Democratic | 1962 (Special) | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| New Jersey | Clifford P. Case | Republican | 1954 1960 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| New Mexico | Clinton P. Anderson | Democratic | 1948 1954 1960 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| North Carolina | B. Everett Jordan | Democratic | 1958 (Appointed) 1958 (Special) 1960 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Oklahoma | Fred R. Harris | Democratic | 1964 (Special) | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Oregon | Maurine Neuberger | Democratic | 1960 (Special) 1960 |
Incumbent retired. New senator re-elected. Republican gain. |
|
| Rhode Island | Claiborne Pell | Democratic | 1960 | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| South Carolina | Strom Thurmond | Republican | 1954 1954 (Appointed) 1956 (Resigned) 1956 (Special) 1960 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| South Dakota | Karl E. Mundt | Republican | 1948 1948 (Appointed) 1954 1960 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Tennessee | Ross Bass | Democratic | 1964 (Special) | Incumbent lost renomination. New senator elected. Republican gain. |
|
| Texas | John Tower | Republican | 1961 (Special) | Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Virginia | Absalom Willis Robertson | Democratic | 1946 (Appointed) 1948 1954 1960 |
Incumbent lost renomination. New senator elected. Democratic hold. |
|
| West Virginia | Jennings Randolph | Democratic | 1958 (Special) 1960 |
Incumbent re-elected. |
|
| Wyoming | Milward Simpson | Republican | 1962 (Special) | Incumbent retired. New senator re-elected. Republican hold. |
|
Alabama
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | John J. Sparkman (Incumbent) | 482,138 | 60.07% | ||
| Republican | John Grenier | 313,018 | 39.00% | ||
| Independent | Julian E. Elgin | 7,444 | 0.93% | ||
| None | Scattering | 8 | 0.00% | ||
| Majority | 169,120 | 21.07% | |||
| Turnout | 802,608 | ||||
| Democratic hold | |||||
Alaska
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Bob Bartlett (Incumbent) | 49,289 | 75.54% | ||
| Republican | Lee L. McKinley | 15,961 | 24.46% | ||
| Majority | 33,328 | 51.08% | |||
| Turnout | 65,250 | ||||
| Democratic hold | |||||
Arkansas
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | John Little McClellan (Incumbent) | Unopposed | -- | ||
| Democratic hold | |||||
Colorado
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Gordon L. Allott (Incumbent) | 368,307 | 58.02% | ||
| Democratic | Roy Romer | 266,198 | 41.93% | ||
| Write-In | Walter Cranson | 332 | 0.05% | ||
| Majority | 102,109 | 16.09% | |||
| Turnout | 634,837 | ||||
| Republican hold | |||||
Delaware
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | J. Caleb Boggs (Incumbent) | 97,268 | 59.12% | ||
| Democratic | James M. Tunnell Jr. | 67,263 | 40.88% | ||
| Majority | 30,005 | 18.24% | |||
| Turnout | 164,531 | ||||
| Republican hold | |||||
Georgia
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Richard B. Russell Jr. (Incumbent) | 631,002 | 99.95% | ||
| None | Scattering | 328 | 0.05% | ||
| Majority | 630,674 | 99.90% | |||
| Turnout | 631,330 | ||||
| Democratic hold | |||||
Idaho
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Leonard B. Jordan (Incumbent) | 139,819 | 55.38% | ||
| Democratic | Ralph R. Harding | 112,637 | 44.62% | ||
| Majority | 27,182 | 10.76% | |||
| Turnout | 252,456 | ||||
| Republican hold | |||||
Illinois
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Incumbent Democrat Paul Douglas, seeking a fourth term in the United States Senate, faced off against Republican Charles H. Percy, a businessman and the 1964 Republican nominee for Governor of Illinois. Also running was Robert Sabonjian (I), Mayor of Waukegan. A competitive election ensued, featuring campaign appearances by former Vice-President Richard M. Nixon on behalf of Percy.[2] Ultimately, Percy ended up defeating Senator Douglas by a fairly wide margin, allowing him to win what would be the first of three terms in the Senate.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ± | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Charles H. Percy | 2,100,449 | 54.95% | +9.75% | |
| Democratic | Paul H. Douglas (Incumbent) | 1,678,147 | 43.90% | -10.73% | |
| Independent | Robert Sabonjian | 41,965 | 1.10% | ||
| Write-ins | 2,163 | 0.05% | |||
| Majority | 422,302 | 11.05% | +1.61% | ||
| Turnout | 3,822,724 | ||||
| Republican gain from Democratic | Swing | ||||
Iowa
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Jack Miller (Incumbent) | 522,339 | 60.91% | ||
| Democratic | E. B. Smith | 324,114 | 37.80% | ||
| Constitution | Robert D. Dilley | 3,826 | 0.45% | ||
| Peace Independent | Charles H. Day | 3,050 | 0.36% | ||
| Iowa | Herbert F. Hoover | 2,085 | 0.24% | ||
| Prohibition | Verne Higens | 2,081 | 0.24% | ||
| None | Scattering | 1 | 0.00% | ||
| Majority | 198,225 | 23.11% | |||
| Turnout | 857,496 | ||||
| Republican hold | |||||
Kansas
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | James B. Pearson (Incumbent) | 350,077 | 52.15% | ||
| Democratic | James Floyd Breeding | 303,223 | 45.17% | ||
| Prohibition | Earl F. Dodge | 9,364 | 1.39% | ||
| Conservative | George W. Snell | 7,103 | 1.06% | ||
| None | Scattering | 1,528 | 0.24% | ||
| Majority | 46,854 | 6.98% | |||
| Turnout | 671,345 | ||||
| Republican hold | |||||
Kentucky
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | John Sherman Cooper (Incumbent) | 483,805 | 64.52% | ||
| Democratic | John Young Brown Sr. | 266,079 | 35.48% | ||
| Majority | 217,726 | 29.04% | |||
| Turnout | 749,884 | ||||
| Republican hold | |||||
Louisiana
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Allen J. Ellender (Incumbent) | 437,695 | 100.00% | ||
| Democratic hold | |||||
Maine
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Margaret Chase Smith (Incumbent) | 188,291 | 58.93% | ||
| Democratic | Elmer H. Violette | 131,136 | 41.04% | ||
| None | Scattering | 108 | 0.03% | ||
| Majority | 57,155 | 17.89% | |||
| Turnout | 319,535 | ||||
| Republican hold | |||||
Massachusetts
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Republican State Attorney General Edward Brooke defeated his challengers. Republican incumbent, Leverett Saltonstall, was retiring after serving for 22 years. Brooke was the first black U.S. senator elected since Reconstruction.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Endicott Peabody, Governor of Massachusetts from January 3, 1963 to January 7, 1965.[3] |
320,967 | 50.35% | |
| Democratic | John F. Collins, Mayor of Boston since 1960. |
265,016 | 41.85% | |
| Democratic | Thomas Boylston Adams, Academician and business executive of the Adams political family, running as an anti-war candidate. |
51,435 | 8.07% | |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ± | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Edward Brooke, Chairman of the Boston Finance Commission from 1961-1962 and Massachusetts Attorney General since 1962.[4] |
1,213,473 | 60.68% | +4.49% | |
| Democratic | Endicott Peabody | 774,761 | 38.74% | -4.72% | |
| Socialist Labor | Lawrence Gilfedder, Candidate for Lt. Governor in 1948. Ran for Governor in 1952 and 1954. Ran for Senate in 1958, 1960, 1962, 1964, 1966, and 1970.[5] |
6,790 | 0.34% | +0.10% | |
| Prohibition | Mark R. Shaw, Candidate for U.S. senator from Massachusetts in 1946, 1952, 1958, 1969, 1962, and 1970. He was also the party's candidate for governor of Massachusetts in 1948 and again in 1956. In 1964 he served as Prohibition Party candidate for vice-president of the United States. |
4,833 | 0.24% | +0.12% | |
| Majority | 438,712 | 21.94% | |||
| Turnout | 1,999,857 | ||||
| Republican hold | |||||
Michigan
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Robert P. Griffin (Incumbent) | 1,363,808 | 55.88% | ||
| Democratic | G. Mennen Williams | 1,070,484 | 43.86% | ||
| Socialist Labor | Ralph M. Muncy | 6,166 | 0.25% | ||
| None | Scattering | 185 | 0.01% | ||
| Majority | 293,324 | 12.02% | |||
| Turnout | 2,440,643 | ||||
| Republican hold | |||||
Minnesota
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Incumbent Democratic U.S. senator Walter Mondale, who had originally been appointed in 1964 to replace Hubert Humphrey after Humphrey was elected Vice President of the United States, defeated Republican challenger Robert A. Forsythe, to win a full term.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic (DFL) | Walter F. Mondale (Incumbent) | 410,841 | 90.97% | |
| Democratic (DFL) | Ralph E. Franklin | 40,785 | 9.03% | |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Robert A. Forsythe | 211,282 | 81.19% | |
| Republican | Henry A. Johnsen | 48,941 | 18.81% | |
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic (DFL) | Walter F. Mondale (Incumbent) | 685,840 | 53.94% | ||
| Republican | Robert A. Forsythe | 574,868 | 45.21% | ||
| Socialist Workers | Joseph Johnson | 5,487 | 0.43% | ||
| Industrial Government | William Braatz | 5,231 | 0.41% | ||
| Majority | 110,972 | 8.73% | |||
| Turnout | 1,271,426 | ||||
| Democratic (DFL) hold | |||||
Mississippi
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
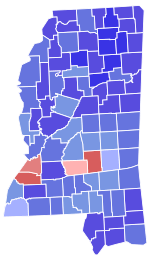 County Results: Eastland: 40-50% 50-60% 60-70% 70-80% 80-90% Walker: 40-50% 50-60% 60-70% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Incumbent James Eastland, who first entered the Senate in 1941, faced the opposition of Prentiss Walker, the first Republican representment since Reconstruction.[9][10]
Walker, who voted against the Civil Rights Act of 1964, ran on the right of Eastland and solely focused on the white vote, accusing him of not being hard enough in opposing integration and being friendly with President Johnson, accusations to which Eastland partisans opposed the fact Walker nominated a black constituent, Marvell Lang, to the Air Force Academy.[11][12][13] He proudly announced he went to a meeting of the Americans for the Preservation of the White Race, a Ku Klux Klan front, enabling Eastland to proudly announce he was opposed by both the Klan and the AFL-CIO.[13]
Eastland cast the civil rights movement with the tar of Communism and Black Power and raised the bloody shirt of Reconstruction against the candidacy of Walker.[12] He was supported by segregationists Tom Brady, George Wallace and Leander Perez.[13]
Most of the White voters stayed with Eastland, and Walker ironically won African-Americans in southwestern Mississippi who wanted to cast a protest vote against Eastland.[9]
Years later, Wirt Yerger, the chairman of the Mississippi Republican Party in the 1960s, said that Walker's decision to relinquish his House seat after one term for the vagaries of a Senate race against Eastland was "very devastating" to the growth of the GOP in Mississippi.[14]
Reverend Clifton Whitley also ran for the Mississippi Freedom Democratic Party.[12][15] A sore-loser law was invoked against Whitley, who ran in the Democratic primary, and he only won one week before the election, thereby preventing to enter any serious campaign or fundraising.[13]
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | James O. Eastland (Incumbent) | 258,248 | 65.56% | ||
| Republican | Prentiss Walker | 105,150 | 26.69% | ||
| Independent | Clifton R. Whitley | 30,502 | 7.74% | ||
| Majority | 153,098 | 38.87% | |||
| Turnout | 393,900 | ||||
| Democratic hold | |||||
Montana
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Incumbent United States senator Lee Metcalf, who was first elected to the Senate in 1960, ran for re-election. He won the Democratic primary uncontested, and moved on to the general election, where he was opposed by Tim Babcock, the Republican nominee and the Governor of Montana. Though the race remained close, Metcalf was able to expand on his 1960 margin of victory, and defeated Babcock to win a second term.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Lee Metcalf (Incumbent) | 73,975 | 100.00% | |
| Total votes | 73,975 | 100.00% | ||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Tim M. Babcock | 54,828 | 100.00% | |
| Total votes | 54,828 | 100.00% | ||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ± | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Lee Metcalf (Incumbent) | 138,166 | 53.17% | +2.44% | |
| Republican | Tim M. Babcock | 121,697 | 46.83% | -2.44% | |
| Majority | 16,469 | 6.34% | +4.87% | ||
| Turnout | 259,863 | ||||
| Democratic hold | Swing | ||||
Nebraska
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Carl T. Curtis (Incumbent) | 296,116 | 61.04% | ||
| Democratic | Frank B. Morrison | 187,950 | 38.74% | ||
| None | Scattering | 1,032 | 0.21% | ||
| Majority | 108,166 | 23.30% | |||
| Turnout | 485,098 | ||||
| Republican hold | |||||
New Hampshire
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Thomas J. McIntyre (Incumbent) | 123,888 | 54.04% | ||
| Republican | Harrison R. Thyng | 105,241 | 45.91% | ||
| None | Helen Bliss | 108 | 0.05% | ||
| Majority | 18,647 | 8.13% | |||
| Turnout | 229,237 | ||||
| Democratic hold | |||||
New Jersey
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Clifford P. Case (Incumbent) | 1,278,843 | 60.02% | ||
| Democratic | Warren W. Wilentz | 788,021 | 36.98% | ||
| Conservative | Robert Lee Schlachter | 53,606 | 2.52% | ||
| Socialist Labor | Julius Levin | 10,218 | 0.48% | ||
| Majority | 490,822 | 23.04% | |||
| Turnout | 2,130,688 | ||||
| Republican hold | |||||
New Mexico
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Clinton Presba Anderson (Incumbent) | 137,205 | 53.14% | ||
| Republican | Anderson Carter | 120,988 | 46.86% | ||
| Majority | 16,217 | 7.28% | |||
| Turnout | 258,193 | ||||
| Democratic hold | |||||
North Carolina
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | B. Everett Jordan (Incumbent) | 501,440 | 55.59% | ||
| Republican | John S. Shallcross | 400,502 | 44.40% | ||
| Write-In | Donald R. Badgley | 36 | 0.00% | ||
| Majority | 100,938 | 11.19% | |||
| Turnout | 901,978 | ||||
| Democratic hold | |||||
Oklahoma
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Fred R. Harris (Incumbent) | 343,157 | 53.72% | ||
| Republican | Pat H. Patterson | 295,585 | 46.28% | ||
| Majority | 47,572 | 7.44% | |||
| Turnout | 638,742 | ||||
| Democratic hold | |||||
Oregon
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Incumbent Senator Maurine Brown Neuberger did not seek re-election. Held during the escalation of United States involvement of the Vietnam War, the race was between Republican candidate and incumbent Governor of Oregon Mark Hatfield, who opposed the war, and Democratic congressman Robert B. Duncan, who supported the war. In an unusual move, Oregon's other Senator, Democrat Wayne Morse, who also opposed the war, crossed party lines to endorse Hatfield, who won in a close election, his first of five terms in the United States Senate.
In March 1960, first-term U.S. senator Richard L. Neuberger died in office. Despite calls to appoint his widow, Maurine Brown Neuberger, to the position, Governor Mark Hatfield instead appointed Oregon Supreme Court justice Hall S. Lusk to fill the position until a November special election. Hatfield stated that he intended to have appointed Neuberger, but that he wanted to appoint someone who would be focused on completing the remaining eight months of the term and not running in the regular-term Senate election as Neuberger had announced she would.[17] Some observers noted that Hatfield, a Republican, though required by state law to appoint someone of the same political party as the late Senator Neuberger, did not want to give the other party the political advantage of incumbency.[17][18]
Neuberger went on to win the special election over former Oregon governor Elmo Smith,[18] but despite the urging of Oregon congressman Robert B. Duncan,[19] she chose not to run for a second term in 1966, citing health issues, poor relations with Oregon's senior Senator Wayne Morse, and the burden of fundraising.[18] Duncan also urged fellow Oregon congressperson Edith Green to run for the post, but Green also declined.[19]
On the seventh anniversary of his inauguration as Oregon's 29th governor, Hatfield announced his candidacy for the Republican nomination.[20] In his announcement, Hatfield focused on the economic achievements in the state since his election, citing record-high employment and the creation of 138,000 jobs.[21] Hatfield was considered vulnerable on the subject of the Vietnam War, which he opposed, in contrast with 75% of Oregonians, who favored the war.[22] Hatfield's views on the war had been strongly affected by his own experiences: as a U.S. Navy ensign in World War II, he had been among the first to walk through the devastation caused by the atomic bombing of Hiroshima; in a later assignment in Vietnam, he saw first-hand how imperialism led to incredible disparity, with countless Vietnamese living in poverty next to opulent French mansions.[22] The war issue gave Hatfield competition from several minor candidates on the right, but Hatfield nonetheless won by a wide margin, besting his nearest competitor, conservative evangelist Walter Huss, by a nearly 6–1 margin.[23]
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Mark Hatfield | 174,280 | 75.18% | |
| Republican | Walter Huss | 31,368 | 13.53% | |
| Republican | Jim Bacaloff | 19,547 | 8.43% | |
| Republican | George Altvater | 6,637 | 2.86% | |
| Total votes | 231,832 | 100.00% | ||
In March 1966, Duncan announced his candidacy for the Democratic nomination, which was quickly endorsed by Neuberger.[25] In his speech announcing his candidacy, Duncan reiterated his strong support for President Lyndon B. Johnson's escalation of the Vietnam War with its goal of stopping Communist expansion in Asia.[25] Duncan's strong announcement exposed a rift among Oregon Democrats, including Oregon's senior Senator Wayne Morse, a leading anti-war voice,[25] and Duncan's House colleague, Edith Green. Green had urged Duncan to run, but Duncan's hawkish statement troubled her.[26] Soon after Duncan announced his candidacy, Howard Morgan, a former member of the Federal Power Commission, announced he was running as an anti-war option to Duncan. Morgan had the support of Morse and Green (though Green's endorsement did not come until the final week of the campaign),[26][27][28] and Duncan had the endorsement of most of the party organization and the major newspapers in the state. When the results were announced, Duncan won by a nearly 2-1 margin in one of the first elections in which the Vietnam War was a central issue.[29]
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Robert B. Duncan | 161,189 | 62.20% | |
| Democratic | Howard Morgan | 89,174 | 34.41% | |
| Democratic | Gilbert L. Meyer | 8,788 | 3.39% | |
| Total votes | 259,151 | 100.00% | ||
The general election was now set up between two participants whose views on the Vietnam War were in direct opposition to many in their party: Duncan, a pro-war Democrat and Hatfield, an anti-war Republican.[19][31] With more than three-quarters of Oregonians sharing his view on the war, Duncan used the issue to attack Hatfield, stating that the outcome of the war would determine "whether Americans will die in the buffalo grass of Vietnam or the rye grass of Oregon."[22][32] Duncan also stressed that his election was necessary to provide a pro-Government voice for Oregon to counteract the anti-war views of Senator Morse.[32] Morse, who had strongly supported Duncan's rival in the primary, now went across party lines and threw his support to Hatfield, though he did not campaign for him.[19][32]
Hatfield, whose popularity as Governor had made him the favorite in the race, soon found his campaign in trouble. Morse's support backfired among many Republicans; Morse had left their party in 1952 to join the Democrats a few years later, and many worried that Hatfield would follow the same path.[33][34] At a June conference of governors of all 50 states, Hatfield was the lone dissenter on a resolution expressing support for the war, calling the resolution a "blank check" for President Johnson's conduct of the war.[32][35] By the middle of the summer, fueled by the departure of Republican hawks (such as former Oregon State Treasurer and 1962 Senate candidate Sig Unander who wholeheartedly endorsed Duncan), and with a strong majority of voters in the state already registered as Democrats, Duncan surged to a lead in most polls.[33]
While Hatfield did not back away from his war stance, he sought to focus his campaign on other issues, chiefly focusing on the Johnson administration's economic policies that, in Hatfield's view, had created a recession that was creating unemployment in Oregon's timber industry.[19][33] As the election neared in early fall, Hatfield had pulled even with Duncan with momentum on his side.[33] Hatfield won in 27 of Oregon's 36 counties en route to a solid but narrow 52%-48% victory.[36][37] In his victory speech, Hatfield maintained that the vote was not a referendum on the war and that "neither Hanoi nor Washington should misread the results."[36]
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Mark Hatfield | 354,391 | 51.75% | |||
| Democratic | Robert B. Duncan | 330,374 | 48.25% | |||
| Total votes | 684,765 | 100.00% | ||||
| Republican gain from Democratic | ||||||
Hatfield would be re-elected to five more terms, most comfortably, before retiring from the Senate in 1996. Duncan sought revenge against Morse in the Democratic primary of the 1968 Senate election, but came in second in a close three-way primary that he might have won had not a third candidate drawn off some anti-Morse votes.[19] After Morse's loss to Bob Packwood in the 1968 general election, Duncan and Morse again squared off for the Democratic nomination in the 1972 Senate election to face Hatfield. Morse won again, and lost to Hatfield in the general election.[19] In 1974, Duncan was re-elected to the House of Representatives. He served three terms before being defeated in the Democratic primary by Ron Wyden in 1980.[19][39]
Rhode Island
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Claiborne Pell (Incumbent) | 219,331 | 67.66% | ||
| Republican | Ruth M. Briggs | 104,838 | 32.34% | ||
| Majority | 114,493 | 35.32% | |||
| Turnout | 324,169 | ||||
| Democratic hold | |||||
South Carolina
There were two elections, due to the death of Olin D. Johnston in 1965.
South Carolina (Regular)
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Incumbent Strom Thurmond, who had switched parties from Democratic to Republican in 1964, easily defeated state senator Bradley Morrah in the general election.
The two Democrats who could have defeated Thurmond competed against each other in the special election to serve the remaining two years of Olin D. Johnston's six-year term. As a result, little known state senator Bradley Morrah of Greenville won the South Carolina Democratic Party primary election on June 14 against John Bolt Culbertson to become the nominee in the general election.
| Democratic Primary | ||
|---|---|---|
| Candidate | Votes | % |
| Bradley Morrah | 167,401 | 55.9% |
| John Bolt Culbertson | 131,870 | 44.1% |
Senator Strom Thurmond faced no opposition from South Carolina Republicans and avoided a primary election.
Morrah faced an uphill struggle against Senator Thurmond because the Democratic resources were primarily poured into the special election to help Fritz Hollings and in the gubernatorial contest for Robert Evander McNair. Furthermore, Thurmond refused to debate Morrah and Thurmond boasted of the endorsements he received from Southern Democratic senators Richard Russell Jr., John C. Stennis, and Herman Talmadge. Morrah was easily dispatched by Thurmond in the general election and he also lost re-election to his state senate seat. He would never again hold public office, which was a routine occurrence for Thurmond's opponents.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ± | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Strom Thurmond | 271,297 | 62.2% | +62.2% | |
| Democratic | Bradley Morrah | 164,955 | 37.8% | -62.2% | |
| Majority | 106,342 | 24.4% | -75.6% | ||
| Turnout | 436,252 | 49.1% | -6.3% | ||
| Republican hold | |||||
South Carolina (Special)

The election resulted from the death of Senator Olin D. Johnston in 1965. Then-Governor Donald S. Russell entered in a prearranged agreement with Lieutenant Governor Robert Evander McNair in which Russell would resign his post so that he could be appointed Senator. However, former Governor Fritz Hollings won the Democratic primary election and went on to beat Republican state senator Marshall Parker in the general election to fill the remaining two years of the unexpired term.
In the 1962 gubernatorial election, Donald S. Russell had stated that he would he serve out a full term and not seek a higher office. However, midway through his term he resigned from the governorship so that he could be appointed to the United States Senate. Russell faced a challenge in the Democratic primary from former Governor Fritz Hollings, who had lost to Olin D. Johnston in the 1962 primary for the same Senate seat. On June 14, the South Carolina Democratic Party held their primary election and Hollings scored a comfortable victory over Russell to become the Democratic nominee.
| Democratic Primary | ||
|---|---|---|
| Candidate | Votes | % |
| Fritz Hollings | 196,405 | 60.8% |
| Donald S. Russell | 126,595 | 39.2% |
The South Carolina Republican Party was in the beginning stages of becoming a major political party in South Carolina politics. It had few elected officials in the state and when state senator Marshall Parker from Oconee County sought the Republican nomination, he did not face any opposition.
Parker faced an uphill battle in winning the Senate seat. First, the state was dominated by the Democratic Party and any Republican politician faced a tough time seeking election. Although there was hope for Republicans because Barry Goldwater had won the state in the 1964 presidential election. Secondly, most of the resources of the Republican party were allocated for Strom Thurmond's re-election campaign and Joseph O. Rogers Jr. gubernatorial election. Nevertheless, Parker was able to kept the race close and almost unseated Hollings in the general election.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ± | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Fritz Hollings | 223,790 | 51.3% | -5.9% | |
| Republican | Marshall Parker | 212,032 | 48.7% | +5.9% | |
| Majority | 11,758 | 2.6% | -11.8% | ||
| Turnout | 435,822 | 49.1% | +2.2% | ||
| Democratic hold | |||||
Hollings's first Senate victory was also his closest and he was easily re-elected in 1968 (full term), 1974, 1980, and 1986, with somewhat tougher races in 1992 and 1998, although neither with a margin as narrow as that of his initial election. He eventually became seventh longest-serving senator in history (just behind Robert Byrd, Thurmond, Ted Kennedy, Daniel Inouye, Carl Hayden and John C. Stennis). He and Thurmond were also the longest-serving Senate duo. Because of this, despite his length of service, Hollings spent 36 years as the junior Senator, even though - with his penultimate term - he had gained seniority of all but four of his colleagues - Byrd, Thurmond, Inouye and Kennedy. Hollings went on to become a nationally important political figure, e.g., serving as Chairman of the Budget committee.
South Dakota
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Karl Mundt (Incumbent) | 150,517 | 66.28% | ||
| Democratic | Donn H. Wright | 76,563 | 33.72% | ||
| Majority | 73,954 | 32.56% | |||
| Turnout | 227,080 | ||||
| Republican hold | |||||
Tennessee
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
Republican Howard Baker won the U.S. Senate election in Tennessee, he defeated the Democratic nominee, Frank G. Clement.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Howard Baker | 483,063 | 55.72% | |
| Democratic | Frank G. Clement | 383,843 | 44.27% | |
| None | Write-Ins | 55 | 0.01% | |
| Majority | 99,220 | 10.45% | ||
| Turnout | 866,961 | |||
| Republican gain from Democratic | ||||
Texas
| |||||||||||||||||
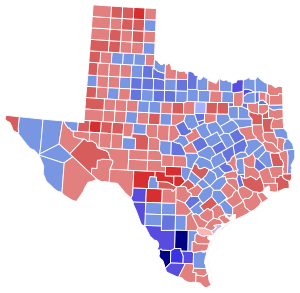 County results Tower: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% Carr: 50–60% 60–70% 70–80% 80–90% 90–100% | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | John Tower (Incumbent) | 841,501 | 56.39% | ||
| Democratic | Waggoner Carr | 643,855 | 43.15% | ||
| Constitution | James Baker Holland | 6,778 | 0.45% | ||
| None | Scattering | 45 | 0.00% | ||
| Majority | 197,646 | 13.24% | |||
| Turnout | 1,492,179 | ||||
| Republican hold | |||||
Virginia
There were two elections, due to the resignation of Harry F. Byrd Sr. in 1965.
Virginia (Regular)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Democratic State Senator William B. Spong Jr. defeated Republican James P. Ould Jr. and Independent F. Lee Hawthorne.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ± | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | William B. Spong Jr. | 429,855 | 58.57% | -22.70% | |
| Republican | James P. Ould Jr. | 245,681 | 33.48% | +33.48% | |
| Independent | F. Lee Hawthorne | 58,251 | 7.94% | ||
| Write-ins | 92 | 0.01% | -0.17% | ||
| Majority | 184,174 | 25.10% | -41.93% | ||
| Turnout | 733,879 | ||||
| Democratic hold | |||||
Virginia (Special)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Incumbent Senator Harry F. Byrd Sr. had resigned the previous year due to health reasons, and his son Harry F. Byrd Jr. had been appointed to replace him. Byrd defeated Republican Lawrence M. Traylor and independent candidate John W. Carter, and was able to finish the rest of his father's term.
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ± | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Harry F. Byrd Jr. (Incumbent) | 389,028 | 53.30% | -10.50% | |
| Republican | Lawrence M. Traylor | 272,804 | 37.38% | +18.35% | |
| Independent | John W. Carter | 57,692 | 7.90% | ||
| Independent | J.B. Brayman | 10,180 | 1.39% | -1.91% | |
| Write-ins | 135 | 0.02% | +0.01% | ||
| Majority | 116,224 | 15.92% | -28.85% | ||
| Turnout | 729,839 | ||||
| Democratic hold | |||||
West Virginia
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Jennings Randolph (Incumbent) | 292,325 | 59.51% | ||
| Republican | Francis J. Love | 198,891 | 40.49% | ||
| Majority | 93,434 | 19.02% | |||
| Turnout | 491,216 | ||||
| Democratic hold | |||||
Wyoming
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Republican | Clifford P. Hansen | 63,548 | 51.80% | ||
| Democratic | Teno Roncalio | 59,141 | 48.20% | ||
| Majority | 4,407 | 3.60% | |||
| Turnout | 122,689 | ||||
| Republican hold | |||||
See also
Notes
- Appointee elected
References
- "Statistics of the Congressional Election of November 8, 1966" (PDF). Clerk.house.gov. Retrieved April 5, 2015.
- Perlstein, Rick. Nixonland: The Rise of a President and the Fracturing of America. New York: Scribner, 2008. Print.
- Endicott Peabody at ourcampaigns.com
- Edward Brooke at ourcampaigns.com
- Lawrence Gilfedder at ourcampaigns.com
- "MN US Senate - DFL Primary Race - Sep 13, 1966". Our Campaigns. Retrieved December 19, 2017.
- "MN US Senate - R Primary Race - Sep 13, 1966". Our Campaigns. Retrieved December 19, 2017.
- "MN US Senate Race - Nov 08, 1966". Our Campaigns. Retrieved December 19, 2017.
- "Nation: Choosing Up". Time. June 17, 1966. ISSN 0040-781X. Retrieved January 6, 2018.
- "Our Campaigns - MS US Senate Race - Nov 08, 1966". www.ourcampaigns.com. Retrieved January 6, 2018.
- Danielson, Chris. "Right Turn? The Republican Party and African-American Politics in Post-1965 Mississippi". Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Asch, Chris Myers (February 1, 2011). The Senator and the Sharecropper: The Freedom Struggles of James O. Eastland and Fannie Lou Hamer. Univ of North Carolina Press. pp. 238–242. ISBN 9780807878057.
- Annis, J. Lee (July 21, 2016). Big Jim Eastland: The Godfather of Mississippi. Univ. Press of Mississippi. ISBN 9781496806154.
- The Journal of Mississippi History. Mississippi Department of Archives and History. 1985. p. 256.
- "Whitley, Clifton". crdl.usg.edu. Retrieved January 6, 2018.
- "Report of the Official Canvass of the Vote Cast at the Primary Election Held in the State of Montana, August 16, 1966". Montana Secretary of State. Retrieved July 2, 2014.
- "Oregon Justice, Democrat, gets Neuberger's seat in U. S. Senate" (PDF). The New York Times. March 16, 1960. Retrieved June 17, 2011.
- "Women in Congress: Maurine B. Neuberger, Senator from Oregon". United States Congress. Archived from the original on July 23, 2011. Retrieved June 17, 2011.
- Mapes, Jeff (April 30, 2011). "Bob Duncan and his three losing—but history-making—U.S. Senate races". The Oregonian. Retrieved June 17, 2011.
- "Hatfield seeks seat in Senate". The Register-Guard. January 12, 1966. Retrieved June 17, 2011.
- "Hatfield announces his candidacy for the Senate" (PDF). The New York Times. January 13, 1966. Retrieved June 17, 2011.
- Walth, Brent (December 29, 1996). "Mark of distinction". The Oregonian.
- "Oregon: one war foe loses, another wins". The Miami News. May 25, 1966. Retrieved June 17, 2011.
- "Unofficial Totals of Primary Election". The Register-Guard. May 26, 1966. Retrieved June 17, 2011.
- Abell, Ron (March 2, 1966). "Duncan joins Senate race". The Register-Guard. Retrieved June 17, 2011.
- Duscha, Julius (May 24, 1966). "Oregon anti-war candidate gains Rep. Green's support". The Spokesman-Review. Retrieved June 17, 2011.
- Abell, Ron (March 11, 1966). "Morgan joins Senate race". The Register-Guard. Retrieved June 17, 2011.
- "Supporter of Viet war wins Oregon primary". The Rochester Sentinel. May 25, 1966. Retrieved June 17, 2011.
- Davies, Lawrence E (May 25, 1966). "Vietnam critic defeated" (PDF). The New York Times. Retrieved June 17, 2011.
- "Oregon US Senate Democratic Primary Race, May 24, 1966". ourcampaigns.com. Retrieved June 17, 2011.
- Balmer, Donald G. (June 1967). "The 1966 Election in Oregon". The Western Political Quarterly. 20 (2): 593–601. doi:10.2307/446088. JSTOR 446088.
- Johnson, Robert David (2006). Congress and the Cold War. New York: Cambridge University Press. p. 134. ISBN 978-0-521-82133-9.
- Turner, Wallace (November 6, 1966). "Hatfield stages Oregon recovery" (PDF). The New York Times. Retrieved June 17, 2011.
- Evans, Rowland; Robert Novak (October 5, 1966). "Oregon vote won't be Viet Nam referendum". The Free Lance Star. Retrieved June 17, 2011.
- "Governors back Viet action". The Register-Guard. July 8, 1966. Retrieved June 17, 2011.
- "Hatfield, McCall win". The Register-Guard. November 9, 1966. Retrieved June 17, 2011.
- "Hatfield defeats Duncan in Oregon" (PDF). The New York Times. November 9, 1966. Retrieved June 17, 2011.
- "Oregon US Senate Race, Nov 8, 1966". ourcampaigns.com. Retrieved June 17, 2011.
- "Five-Term Congressman is Defeated in Oregon". The New York Times. May 21, 1980. Retrieved June 17, 2011.
- Cook, Rhodes (October 26, 2017). America Votes 32: 2015-2016, Election Returns by State. ISBN 9781506368993.
Sources
- Massachusetts Race details at ourcampaigns.com
- "Supplemental Report of the Secretary of State to the General Assembly of South Carolina." Reports and Resolutions of South Carolina to the General Assembly of the State of South Carolina. Volume II. Columbia, SC: 1967, pp. 16, 41.
- Bass, Jack; Marilyn W. Thompson (1998). Ol' Strom: An Unauthorized Biography of Strom Thurmond. Longstreet. pp. 222–223.
- "Supplemental Report of the Secretary of State to the General Assembly of South Carolina." Reports and Resolutions of South Carolina to the General Assembly of the State of South Carolina. Volume II. Columbia, SC: 1967, pp. 16, 41.
- "South Carolina's New Senator". Time. April 30, 1965. Retrieved February 2, 2008.



















