Toyota, Aichi
Toyota (豊田市, Toyota-shi) is a city in Aichi Prefecture, Japan. As of 1 October 2019, the city had an estimated population of 426,162 and a population density of 464 persons per km². The total area was 918.32 square kilometres (354.57 sq mi). It is located about 35 minutes from Nagoya by way of the Meitetsu Toyota Line.
Toyota 豊田市 | |
|---|---|
   From upper left: Toyota Stadium, Toyota Motor Corporation, Asuke Town, Toyota City Skyline, Kōrankei | |
 Flag  Seal | |
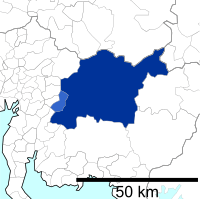
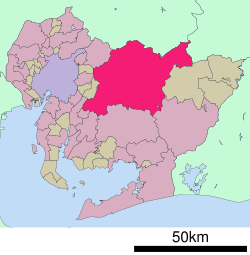 Location of Toyota in Aichi Prefecture | |
 Toyota  Toyota Toyota (Asia) | |
| Coordinates: 35°4′56.8″N 137°9′22.8″E | |
| Country | |
| Region | Chūbu (Tōkai) |
| Prefecture | Aichi |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Toshihiko Ota |
| Area | |
| • Total | 918.32 km2 (354.57 sq mi) |
| Population (October 1, 2019) | |
| • Total | 426,162 |
| • Density | 460/km2 (1,200/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Japan Standard Time) |
| – Tree | Zelkova serrata |
| – Flower | Sunflower |
| Phone number | 0565-31-1212 |
| Address | 3–60 Nishimachi, Toyota-shi, Aichi-ken 471-8501 |
| Website | Official website |


Several of Toyota Motor Corporation's manufacturing plants, including the Tsutsumi plant, are located here. The longstanding ties between the Toyota Motor Corporation and the town of Toyota-shi, formerly known as Koromo (挙母市, Koromo-shi), gave the town its current name.
Geography
Toyota is located in north-central Aichi Prefecture, and is the largest city in the prefecture in terms of area. The city area is mountainous to the north, with peaks averaging around 1000 meters in height along its northern border with Nagano and Gifu Prefectures. Much of the mountainous northern portion of the city is within the Aichi Kōgen Quasi-National Park. The central and southern portions of the city have rolling hills and agricultural flatlands.
Toyota is within a two-hour drive of Nagoya.[1]
 Downtown
Downtown Iyama
Iyama.jpg) Kuroda Lake
Kuroda Lake- Mikawa Lake
- Okuyahagi Lake
Demographics
Per Japanese census data,[2] the population of Toyota has been increasing steadily over the past 50 years.
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1960 | 151,632 | — |
| 1970 | 234,078 | +54.4% |
| 1980 | 315,871 | +34.9% |
| 1990 | 370,858 | +17.4% |
| 2000 | 395,224 | +6.6% |
| 2010 | 421,552 | +6.7% |
Climate
The city has a climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and relatively mild winters (Köppen climate classification Cfa). The average annual temperature in Toyota is 15.1 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1812 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 27.38 °C, and lowest in January, at around 3.6 °C.[3]
| Climate data for Toyota (1981-2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 17.8 (64.0) |
22.2 (72.0) |
24.6 (76.3) |
30.5 (86.9) |
34.4 (93.9) |
36.2 (97.2) |
38.6 (101.5) |
39.1 (102.4) |
38.1 (100.6) |
32.2 (90.0) |
25.6 (78.1) |
22.6 (72.7) |
39.1 (102.4) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 8.9 (48.0) |
9.9 (49.8) |
13.7 (56.7) |
19.8 (67.6) |
24.1 (75.4) |
27.2 (81.0) |
30.9 (87.6) |
32.7 (90.9) |
28.8 (83.8) |
22.9 (73.2) |
17.1 (62.8) |
11.6 (52.9) |
20.6 (69.1) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 3.3 (37.9) |
4.1 (39.4) |
7.8 (46.0) |
13.4 (56.1) |
17.9 (64.2) |
21.9 (71.4) |
25.6 (78.1) |
26.8 (80.2) |
23.2 (73.8) |
16.9 (62.4) |
11.0 (51.8) |
5.7 (42.3) |
14.8 (58.6) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −1.7 (28.9) |
−1.3 (29.7) |
1.9 (35.4) |
7.2 (45.0) |
12.2 (54.0) |
17.3 (63.1) |
21.5 (70.7) |
22.4 (72.3) |
19.0 (66.2) |
12.1 (53.8) |
5.9 (42.6) |
0.6 (33.1) |
9.8 (49.6) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −8.6 (16.5) |
−8.8 (16.2) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
−2.6 (27.3) |
0.8 (33.4) |
8.2 (46.8) |
14.7 (58.5) |
14.1 (57.4) |
6.5 (43.7) |
1.1 (34.0) |
−2.5 (27.5) |
−7.6 (18.3) |
−8.8 (16.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 44.0 (1.73) |
59.2 (2.33) |
112.1 (4.41) |
116.8 (4.60) |
149.1 (5.87) |
202.9 (7.99) |
187.1 (7.37) |
115.7 (4.56) |
212.0 (8.35) |
120.3 (4.74) |
71.9 (2.83) |
43.2 (1.70) |
1,451.4 (57.14) |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 159.4 | 167.4 | 188.8 | 197.5 | 184.9 | 142.8 | 159.8 | 202.3 | 154.5 | 164.6 | 163.0 | 167.8 | 2,056.2 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency[4] | |||||||||||||
History
The area of present-day Toyota City has been inhabited since prehistoric times, and archaeologists have found a continuous record of artifacts from the Japanese paleolithic period onwards. In early proto-historic times, the area was under the control of the Mononobe clan, who built numerous kofun burial mounds. The local place name “Koromo” is mentioned in the Kojiki and other early Japanese documents.
During the Edo period, parts of the area of the current city were under the control of Koromo Domain, a feudal han under the Tokugawa shogunate; however, most of the area of the current city was tenryō territory controlled directly by the government in Edo and administered through hatamoto class appointed administrators. The village of “Tokugawa”, from which Tokugawa Ieyasu took his clan name, was located within what is now the city of Toyota.
After the Meiji restoration, the area was organized into the towns of Asuke and Koromo and numerous villages under Higashikamo District and Nishikamo District with the establishment of the modern municipalities system.
The area was a major producer of silk and prospered from the Meiji period through the Taishō periods. As the demand for raw silk declined in Japan and abroad, Koromo entered a period of gradual decline after 1930.[5] The decline encouraged Kiichiro Toyoda, cousin of Eiji Toyoda, to look for alternatives to the family's automatic loom manufacturing business. The search led to the founding of what became the Toyota Motor Corporation. Toyota built the first manufacturing facility, known as Toyota Honsha plant in November 1938, breaking ground in December 1935.[6]
On March 1, 1951, Koromo gained city status, and absorbed the village of Takahashi from Nishikamo District on September 30, 1956. Due to the fame and economic importance of its major employer, the city of Koromo (挙母市) changed its name to Toyota on January 1, 1959.
Toyota became a sister city with Detroit, Michigan, United States in 1960. It continued to expand by annexing the towns of Kamigo (Hekikai District) on March 1, 1964, and Takaoka (Hekikai District) on September 1, 1965, and Sanage (Nishikamo District) on April 1, 1967, as well as the village of Matsudaira (Higashikamo District) on April 1, 1970.
In 1979 the Nagoya Railroad (Meitetsu) opened the Toyota New Line (now Toyota Line), and in 1988: The Aichi Loop Line was opened, thus considerably improving access to the city via rail transport.
Toyota became a Core City in 1998, with increased local autonomy.
On March 25, 2005, Expo 2005 opened with its main site in Nagakute and additional activity in Seto and Toyota. The Expo continued until September 25, 2005.
On April 1, 2005, Toyota absorbed the town of Fujioka, and the village of Obara (both from Nishikamo District), the towns of Asuke, Asahi and Inabu, and the village of Shimoyama (all from Higashikamo District) to create the new and expanded city of Toyota.
Mitsuru Obe and Eric Pfanner of The Wall Street Journal stated that by 2015 Toyota was recovering from an economic depression "so deep that some were comparing it to Detroit."[7]
 Sanage shinto shrine
Sanage shinto shrine Asuke area (Groups of Traditional Buildings)
Asuke area (Groups of Traditional Buildings)- Koromo Castle
.jpg) City center of Toyota
City center of Toyota
Government
Toyota has a mayor-council form of government with a directly elected mayor and a unicameral city legislature of 45 members. The city contributes five members to the Aichi Prefectural Assembly. In terms of national politics, the city is divided between Aichi District 11 and Aichi District 14 of the lower house of the Diet of Japan.
Transportation
Toyota, as the home city of Toyota Motors is well-served by expressways and national highways. However, it was the largest city in Japan which was not served by the Japanese National Railways (JNR) during its existence. The closest Shinkansen station is Mikawa-Anjō Station in the city of Anjō, although the limited-stop Nozomi and Hikari services do not stop there.
Railway
- Sanage – Hiratobashi – Koshido – Umetsubo – Toyotashi – Uwagoromo – Tsuchihashi – Takemura – Wakabayashi – Mikawa Yatsuhashi
![]()
- Mikawa-Kamigō – Ekaku – Suenohara – Mikawa-Toyota – Shin-Uwagoromo – Shin-Toyota – Aikan-Umetsubo – Shigō – Kaizu –Homi – Sasabara – Yakusa
Japan National Route








 Toyotashi Station
Toyotashi Station Shin-Toyota Station
Shin-Toyota Station Toyota JCT
Toyota JCT Toyota-Higashi JCT
Toyota-Higashi JCT Toyota big bridge
Toyota big bridge Toyota Arrows Bridge
Toyota Arrows Bridge
Economy

The main headquarters of Toyota is located in a 14-story building in Toyota. As of 2006 the head office has the "Toyopet" Toyota logo and the words "Toyota Motor". The Toyota Technical Center, a 14-story building, and the original Honsha plant, Toyota's first plant engaging in mass production and formerly named the Koromo plant, are adjacent to one another in a location near the headquarters. Vinod Jacob from The Hindu described the main headquarters building as "modest".[1] In 2013 company head Akio Toyoda reported that it had difficulties retaining foreign employees at the headquarters due to the lack of amenities in Toyota.[8]
Education
Colleges and universities
Primary and secondary education
Toyota has 78 public elementary schools and 27 public middle schools operated by the city government and 12 public high schools operated by the Aichi Prefectural Board of Education. There are also two private middle schools and eight private high schools. The prefecture also operates two special education schools for the handicapped.
International schools
- Escola Alegria de Saber – Brazilian school[9]
- Escola NECTAR – Brazilian primary school[9]
- Escola Pintando o Sete – Brazilian primary school[9]
Sister city relations
Local attractions
- Asuke area (Groups of Traditional Buildings)
- Toyota Municipal Museum of Art
- Toyota Automobile Museum
- Kōrankei Gorge
- Obara shikizakura
- The ruins of Matsudaira
- Asuke Castle
 Kōrankei Gorge
Kōrankei Gorge Sanshu Asuke Yashiki
Sanshu Asuke Yashiki Kōjaku-ji
Kōjaku-ji Obara shikizakura
Obara shikizakura The ruins of Matsudaira
The ruins of Matsudaira
Sports facilities
Notable people from Toyota
- Suzuki Shōsan, Edo period Zen prelate
- Yoshio Markino, artist, author
- Miliyah Kato, singer
- Masami Mitsuoka, singer
- Etsuko Nishio, singer, actress
- Katsuaki Watanabe, former president of Toyota Motors
- Tadashi Sugiura, professional baseball player
- Masato Naito, Olympic hurdler
References
- Jacob, Vinod. "In Toyota land Archived 2010-07-21 at the Wayback Machine." The Hindu Business Line. August 18, 2006. Retrieved on May 9, 2013.
- Toyota population statistics
- Toyota climate data
- "豊田 1981-2010年". JMA. Retrieved 2016-07-12.
- "Municipalities of Aichi (Japan)". Archived from the original on 21 October 2012. Retrieved 22 May 2011.
- "Toyota Honsha Plant history". Archived from the original on 2015-03-06. Retrieved 2015-06-27.
- Obe, Mitsuru and Eric Pfanner. "Abe’s Backing Is Lukewarm, Even in Toyota’s Town Archived 2016-03-05 at the Wayback Machine" (Archive Archived 2019-02-06 at the Wayback Machine). The Wall Street Journal. December 11, 2014. Retrieved on August 12, 2015.
- Greimel, Hans. "Dreary HQ city is a handicap in global glitz plan." (Archive) Automotive News. May 6, 2013. Retrieved on May 9, 2013.
- "Escolas Brasileiras Homologadas no Japão" (Archive). Embassy of Brazil in Tokyo. Retrieved on October 13, 2015.
- "International Exchange". List of Affiliation Partners within Prefectures. Council of Local Authorities for International Relations (CLAIR). Archived from the original on 24 December 2015. Retrieved 21 November 2015.
.jpg)