Kitakyushu
Kitakyushu (Japanese: 北九州市, Hepburn: Kitakyūshū-shi) is a city located in Fukuoka Prefecture, Japan.
Kitakyushu 北九州市 | |
|---|---|
| City of Kitakyushu[1] | |
 Clockwise from top: the Riverwalk shopping center; Kokura Castle; Mojiko Station; the former Higashida blast furnace; a night view of Kokura from Mount Adachi; the Tanga Market in Kokura | |
 Flag  Emblem | |
Location of Kitakyushu in Fukuoka Prefecture | |
 | |
 Kitakyushu Location in Japan | |
| Coordinates: 33°53′N 130°53′E | |
| Country | Japan |
| Region | Kyushu |
| Prefecture | Fukuoka Prefecture |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Kenji Kitahashi |
| Area | |
| • Total | 491.95 km2 (189.94 sq mi) |
| Population (June 1, 2019) | |
| • Total | 940,978 |
| • Density | 1,900/km2 (5,000/sq mi) |
| Symbols | |
| • Tree | Ichiigashi (Japanese beech) |
| • Flower | Tsutsuji (Azalea) Himawari (Sunflower) |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (JST) |
| City hall address | 1-1 Jōnai, Kokura Kita-ku, Kitakyushu-shi, Fukuoka-ken 803-8501 |
| Website | www |
As of June 1, 2019, Kitakyushu has an estimated population of 940,978, making it the second-largest city in both Fukuoka Prefecture and the island of Kyushu after the city of Fukuoka. It is one of Japan's 20 designated cities, one of three on Kyushu, and is divided into 7 wards.
Kitakyushu was formed in 1963 from a merger of municipalities centered on the historic city of Kokura, and its name literally means "North Kyushu City" in Japanese. It is located at the northernmost point of Kyushu on the Kanmon Straits, separating the island from Honshu, across from the city of Shimonoseki. Kitakyushu and Shimonoseki are connected by numerous transport links including the Kanmon Bridge and the Kanmon Tunnel. Kitakyushu's Urban Employment Area forms part of the Fukuoka-Kitakyushu Greater Metropolitan Region, which, with a population of 5,738,977 (2005-2006), is the largest metropolitan area in Japan west of the Keihanshin region.
History
Kokura Prefecture
Kokura Prefecture was founded separately from Fukuoka Prefecture in 1871 when the clan system was abolished. The old wooden-built Kokura Prefectural Office is still standing and is being restored. It is opposite Riverwalk Kitakyūshū. In 1876, Kokura Prefecture was absorbed by Fukuoka Prefecture. The city of Kokura was founded in 1900.
World War II
Yahata in Kitakyushu was the target for the beginning of the US bombing raids on the home islands on June 16, 1944, when 75 Boeing B-29 Superfortresses flew out from mainland China.[2]
Kokura was the primary target of the nuclear weapon "Fat Man" on August 9, 1945. Major Charles Sweeney had orders to drop the bomb visually. All three attempts failed due to clouds and smoke from Yahata, which is only 7 km west of Kokura and had air raids on the previous day, preventing him from identifying the target clearly. Additionally, a smoke screen was created by industrial workers burning barrels of coal tar and/or electric plant workers releasing steam.[3][4] The bomb was ultimately dropped on the city of Nagasaki, the secondary target, at 11:02 JST.
City
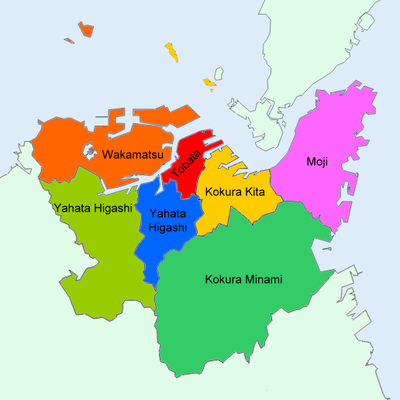
The city of Kitakyushu was founded on February 10, 1963 and was designated on April 1, 1963 by government ordinance. The city was born from the merger of five municipalities (Moji, Kokura, Tobata, Yahata and Wakamatsu) centered around the ancient feudal city of Kokura. The city's symbol mark is a flower with the character "north" (北, kita) in the middle and five petals representing the towns that merged.
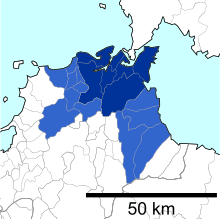
Wards
Kitakyushu has seven wards (ku):
| Wards of Kitakyushu | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Place Name | Map of Kitakyushu | ||||
| Rōmaji | Kanji | Color | Land area in km2 | ||
| 1 | Kokurakita-ku (administrative center) |
小倉北区 | 39.27 |
| |
| 2 | Kokuraminami-ku | 小倉南区 | 170.25 | ||
| 3 | Moji-ku | 門司区 | 73.37 | ||
| 4 | Tobata-ku | 戸畑区 | 16.66 | ||
| 5 | Yahatahigashi-ku | 八幡東区 | 36.36 | ||
| 6 | Yahatanishi-ku | 八幡西区 | 83.04 | ||
| 7 | Wakamatsu-ku | 若松区 | 67.86 | ||
The city of Nakama, Fukuoka was to become the eighth ward of Kitakyushu in 2005 (to be called Nakama-ku). However, the merger was rejected on December 24, 2004 by Nakama's city council, despite having been initiated by Nakama City.
Demographics
As of 1 October 2018, the city had an estimated population of 945,595 and a total area of 491.95 km2 (189.94 sq mi).[5] The average population density is 1,922 persons /km2 (4,980/sq mi). It is now the country's 15th most populated city.[5] It has a much larger total area than that of Fukuoka which is only 343.39 km2 (132.58 sq mi).[5]
Culture
The 1986 family movie Koneko Monogatari was filmed here. The English version of the film, which is the story of the friendship of a kitten and a pug dog, was released in America in 1989 as The Adventures of Milo and Otis.
The 1958 comedy Rickshaw Man is based on a local folk hero of Kokura called Muhomatsu or "Wild Pine" and has been called the Japanese "Desperado." He is celebrated in the Kokura Gion Yamagasa festival. Toshiro Mifune plays the taiko drum in this movie.
Kitakyushu is featured in the late 2012 Call of Duty: Black Ops II game developed by Treyarch and published by Activision as a DLC map called Magma. In the map the city has been abandoned due to a volcanic eruption, and parts of the city are completely covered in lava.
Festivals
There are festivals (matsuri) held in the summer in the city, including the Tobata Gion Yamagasa festival in Tobata-ku, Kitakyūshū.
- Kurosaki Gion (July)
It has been designated as an intangible cultural asset of Fukuoka Prefecture. People spin highly decorated “battle floats” as they pull them through the streets.[6]
- Tobata Gion (July)
People carry yamagasa (tiered floats decorated with flags by day and lanterns by night) on their shoulders.
- Kokura Gion (July)
People pull yamagasa parade floats along the street.
All the Gion festivals date back about 400 years. They were instituted to celebrate surviving an epidemic.[7]
- Moji Minato Festival (May)
This port-city festival involves colorfully costumed people pulling floats through the streets.[8]
- Wakamatsu Minato Festival (July)
This port-city festival celebrates fire, drums, and kappa (mythical amphibious creatures who love cucumbers).[9]
- Wasshoi Hyakuman Festival (August)
The Wasshoi Hyakuman Natsumatsuri brings all the festivals together for a grand parade and finale near City Hall in Kokura Kita ward. Kitakyushu was formed by the merging of Kokura, Yahata, Wakamatsu, Moji, and Tobata. As a result, the city began, on its tenth anniversary, to combine these local festivals into one. On the 25th anniversary, it was renamed Wasshoi Hyakuman because the city population had reached one million.
- Green Park Flea Market (monthly, except August and December)
There are over 200 shops.[10]
Center for Contemporary Art (CCA) Kitakyushu.
The Center for Contemporary Art opened in May 1997 by a former Japan Foundation chief curator Nobuo Nakamura and Akiko Miyake. The centre has shown works of internationally renowned artists such as Maurizio Cattelan and Anri Sala, and runs an internationally acclaimed studio programme for emerging artists.
Notable places


Kokura Castle (小倉城, Kokura-jō) was built by Hosokawa Tadaoki in 1602. It was the property of the Ogasawara clan (from Harima) between 1632 and 1860. The castle was burnt down in 1865 in the war between the Kokura and Choshu clans.
Hiraodai (平尾台, lit. Flat Tail Plateau) karst plateau and Mount Adachi (足立山, Adachi-san) in Kokura Minami ward and Mount Sarakura (皿倉山, Sarakura-san) and Kawachi Dam (河内貯水池, Kawachi-chosuichi) in Yahata Higashi ward are noted walking areas with fine scenery. The limestone outcroppings on Hiraodai are said to resemble grazing sheep, so the plateau, the highest in Kyushu at 400–600 meters, is also known as the Yogun Plain. Some of the limestone caverns are open to the public.[11] The area contains the Sugao and Nanae Waterfalls. Sugao is about 20 meters. Nanae means "seven stages."
Economy
Nippon Steel Corporation is a major employer, but the Yahata and Tobata plants are much reduced from their heyday of the 1960s. The Zenrin company known for its mapping and navigation software is based here[12] and so is Toto Ltd.[13] and Yaskawa Electric Corporation.[14] StarFlyer, an airline, is headquartered on the grounds of Kitakyushu Airport in Kokuraminami-ku, Kitakyūshū.[15] Previously the airline's headquarters were in the Shin Kokura Building (新小倉ビル, Shin-Kokura Biru) in Kokurakita-ku, Kitakyūshū.[16][17]

A smaller scale shopping center known as Cha Cha Town, next to the Sunatsu bus depot in Kokura Kita ward, was created by the Nishi-Nippon Railroad and bus company.

In 2009 Bridgestone Corporation opened a plant in Kitakyushu to produce large and ultralarge off-the-road radial tires for construction and mining vehicles.
The GDP in Greater Kitakyushu, Kitakyushu Metropolitan Employment Area was US$55.7 billion in 2010.[18][19]
Transportation
Located at a strategic position on the south side of the Kanmon Straits, Kitakyushu is an important transport hub for traffic between Honshu and Kyushu and has a large port.
Rail
Kokura Station, the city's central train station, is the penultimate stop on the JR West Sanyō Shinkansen before the Fukuoka terminus and all Shinkansen services stop here. It is served by local and express trains on JR Kyushu's Kagoshima and Nippō Main Lines. In the city, transport is provided the Kitakyushu Monorail and buses.
Mojikō Station in Moji-ku is the northern terminus of the Kagoshima Main Line, the most important line in the JR Kyushu network.
A tram network operated by the Nishi-Nippon Railroad known as the Kitakyushu Line once operated in the city; after dwindling passenger numbers in the 1970s the line was shut down in stages between 1980 and 2000. A railway using tram cars, the Chikuhō Electric Railroad, runs between Kurosaki-Ekimae and Chikuhō-Nōgata stations, serving Yahatanishi-ku and the neighboring city of Nōgata.
Air
The Kitakyushu Airport opened on March 16, 2006. It is larger than the previous Kokura Airport and supports 24-hour operations thanks to its location on an artificial island in the Seto Inland Sea. It will eventually be connected with Kokura Station by a new fast rail link. A new airline based in the city called StarFlyer began operations when the airport opened.
Sea

Kitakyushu is the largest ferry port in Kyushu, Chūgoku, and Shikoku. Ferry services operate between Kitakyushu and Shimonoseki, Matsuyama, Tokushima, Kōbe, Ōsaka, Tokyo, Ulsan (Korea), Busan (Korea) and isolated islands in the city limits. The main ferry port is at Shin-Moji, and there are ferries at Moji and near Kokura Station.
In the Kanmon-Kitakyushu area, there are three commuter lines: the Wakato Ferry, the Kanmon Straits Ferry, and the Kanmon Straits Liner.
Roads
Expressways
The metropolitan area of Kitakyushu is covered by the Kitakyushu Expressway, which has five routes serving the city, totaling 53 kilometers of four-lane expressways. Some of these expressways are elevated, especially around the city center. Route 1 serves the city center, while route 2 serves the port area. Route 3 is a short connector between routes 1 and 2, and route 4 is the longest of the Kitakyushu Expressway network, serving most of the city from north to south. Route 5 is a short link serving the inner port area.
In addition, Kitakyushu is bypassed by the Kyushu Expressway, the main north-south route on the island of Kyushu. The new Higashikyushu Expressway begins in Kitakyushu and runs along the eastern coast of Kyushu. North of Kitakyushu, the Kyushu Expressway crosses the six-lane Kanmonkyo Bridge and turns into the Chūgoku Expressway, the second longest in Japan, serving western Honshu.
Bridges
There are several bridges in Kitakyushu and between the city and other places. The largest ones are the Kanmonkyo Bridge linking Kitakyushu and Shimonoseki (on Kyushu and Honshū respectively) via the Kanmon Straits and the Wakato Bridge linking the wards of Tobata and Wakamatsu. There are smaller bridges over the Onga River on the western border of the city.
On September 30, 2005, ownership of the Wakato Bridge was transferred from Japan Highway Public Corporation to Kitakyushu; on April 1, 2006 the bridge was transferred to the control of the Kitakyushu City Road Public Corporation.
Notable figures

Samurai
- Miyamoto Musashi, samurai swordsman, author of The Book of Five Rings and founder of the Hyoho Niten Ichi-ryū, famous for its use of two swords, lived in the Kokura castle under the patronage of the Ogasawara and Hosokawa clans from 1633 until his death.
Writers
- The novelist Mori Ōgai lived in Kokura for years and his house is open to the public in Kokura Kita ward. He wrote Kokura Nikki (Kokura diary) here. It is a ten-minute walk from Kokura Station.
- The writer Seichō Matsumoto was born in Kokura. Matsumoto Seicho Memorial Museum dedicated to his work is located in the city center near Kokura Castle.
- The writer Ashihei Hino was born in Wakamatsu ward and his birthplace can be visited.
Scientists
- Professor Ted Fujita, popularly known as "Mr. Tornado" in America, was born in Kikugaoka in what is now Kokura Minami ward.
Film Directors
- Yamazaki Tokujirō - Director of Call of the Foghorn and the Jiken Kisha series
- Aoyama Shinji - Director of Eureka and Sad Vacation
- Oda Motoyoshi - Director of Godzilla Raids Again
- Hirayama Hideyuki - Director of Forget me Not
Education
Universities and colleges
National universities
Public universities
Private universities
- Kyushu International University
- Kyushu Kyoritsu University
- Kyushu Nutrition Welfare University
- Kyushu Polytechnic College
- Kyushu Women's University
- Nishinippon Institute of Technology
- Seinan Women's University
- University of Occupational and Environmental Health
Junior colleges
- Higashi Chikushi Junior College
- Kyushu Women's Junior College
- Orio Aishin Junior College
- Seinan Jo Gakuin University Junior College
Technology colleges
- Kitakyushu National College of Technology
Vocational colleges
- Kyushu Medical Sports School
Research Institutes and graduate Schools
- Kitakyushu Science and Research Park
- Graduate School of International Environmental Engineering, The University of Kitakyushu
- Fukuoka University Institute for Recycling and Environmental Control Systems
- Graduate School of Life Science and Systems Engineering, Kyushu Institute of Technology
- Graduate School of Information, Production and Systems/Information, Production and Systems Research Center, Waseda University
Sports
Professional teams
- Giravanz Kitakyushu - Soccer, J3
Sporting venues
- Anō Dome
- Mikuni World Stadium Kitakyushu - Home stadium for Giravanz Kitakyushu
- Honjō Athletic Stadium
- Kitakyushu Media Dome - Indoor Keirin stadium
- Kitakyushu Municipal Baseball Stadium
- Kitakyushu Municipal Gymnasium
- JRA Kokura Racecourse
- Sayagatani Stadium
- Wakamatsu Kyōteijō - Wakamatsu Boat Races
Sister cities
Kitakyushu is twinned with the following cities outside Japan.[22]






One city in Japan is twinned with Kitakyushu city.
References
- Kitakyushu's official English name Archived 2012-05-11 at WebCite
- Shigeru Mizuki, A History of Japan Vol 3 Showa 1944-1953, p.152
- "Steel mill worker reveals blocking view of U.S. aircraft on day of Nagasaki atomic bombing". Mainichi. Mainichi Japan. 26 July 2014. Retrieved 29 July 2014.
- "Nagasaki: The Last Bomb". The New Yorker. The New Yorker. 7 August 2015. Retrieved 8 August 2015.
- "Population News of Major Cities". City of Yokohama. Oct 1, 2018. Archived from the original on January 13, 2016. Retrieved 2018-11-17.
- "Kurosaki Gion Yamakasa (Float) Festival". Crossroad Fukuoka. Fukuoka Prefecture Tourist Association. Retrieved 2013-12-09.
- "Kokura Gion". Fukuoka Internet TV. Retrieved 2013-12-09.
- 北九州ぐるりん観光ナビ【門司みなと祭】. Kitakyushu-area.jp. Retrieved on 2013-12-09.
- Festivals. Kqkicks.antazi.com. Retrieved on 2013-12-09.
- フリーマーケット出店者の皆様へお知らせ - グリーンパーク【響灘緑地】 Archived 2013-06-13 at the Wayback Machine. Kpfmmf.jp. Retrieved on 2013-12-09.
- Kyushu Tourism Promotion Organization (2010). Kyushu's Must-See Tourist Spots.
- "Corporate Info." Zenrin. Retrieved on March 6, 2019.
- "Corporate Data." TOTO. Retrieved on April 9, 2014.
- "Corporate Data". Yaskawa Electric Corporation. Archived from the original on 2014-12-11. Retrieved April 9, 2014.
- "会社概要." StarFlyer. Retrieved on December 20, 2010. "本社 〒800-0306 福岡県北九州市小倉南区空港北町6番 北九州空港スターフライヤー本社ビル"
- "Company Profile." StarFlyer. Retrieved on May 26, 2009. Location Shin-Kokura Bldg., 2-2-1 Komemachi Kokurakita-ku, Kitakyusyu-shi Fukuoka 802-0003 JPN
- "会社概要." StarFlyer. March 24, 2008. Retrieved on December 20, 2010. "本社 〒802-0003 福岡県北九州市小倉北区米町二丁目2番1号 新小倉ビル JR小倉駅より徒歩10分."
- Yoshitsugu Kanemoto. "Metropolitan Employment Area (MEA) Data". Center for Spatial Information Science, The University of Tokyo.
- Conversion rates - Exchange rates - OECD Data
- 175R – Free listening, concerts, stats, & pictures at. Last.fm. Retrieved on 2013-12-09.
- "1000 Travels of Jawaharlal". Last.fm.
- 姉妹・友好都市の紹介 [Introduction of sisters · friendship cities]. City of Kitakyushu (in Japanese). Retrieved 25 January 2015.
- 姉妹都市・交流都市 [Sister city, exchange city]. Minamikyushu city (in Japanese). Retrieved 23 February 2015.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Kitakyushu. |