September 1962
| << | September 1962 | >> | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Su | Mo | Tu | We | Th | Fr | Sa |
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 | ||||||

September 30, 1962: James Meredith escorted to the all-white University of Mississippi

September 12, 1962: U.S. President Kennedy speaks at Houston, pledges to land a man on the Moon by end of decade

September 17, 1962: The next group of American astronauts introduced
The following events occurred in September 1962:
September 1, 1962 (Saturday)
- A 7.1 magnitude earthquake in northwest Iran destroyed 91 villages and killed 12,225 people. The epicenter was near Buin Zahra in the Qazvin Province.[1][2]
- In a referendum in Singapore, voters overwhelmingly supported a proposition to merge with the Malayan Federation to become part of Malaysia, with limited autonomy. Out of 561,559 ballots cast, there were 397,626 in favor of making all Singapore residents Malaysian citizens, while allowing independence in matters of labor and education. Another 144,077 ballots were left blank as a protest.[3]
- Typhoon Wanda struck Hong Kong, killing 134 people and injuring more than 200.[4]
- Died: Hans-Jürgen von Arnim, 73, former German military leader
September 2, 1962 (Sunday)
- All non-military air travel in the United States and Canada was halted for five hours as part of "Exercise Sky Shield III".[5]
- The Soviet Union announced that it has signed an agreement on military and industrial assistance with Cuba, following an August meeting in Yalta between Soviet premier Nikita Khrushchev and Cuban Economics Minister Che Guevara.[6]
- The Malta Independence Act was approved by the United Kingdom, providing that the British colony would become its own nation on September 21, 1964.[7]
- The 1962 UCI Road World Championships took place in Salò, Italy.
- Nerskogen Chapel in Rennebu, Norway, was consecrated by Bishop Tord Godal.
- The fourth Taça Brasil football competition began in Brazil.
- Born: Prachya Pinkaew, Thai film director, producer and screenwriter, in Nakhon Ratchasima Province
- Died: William R. Blair, Irish-born American physicist and inventor, most famous for the 1937 creation of the "Object Locating System" better known as radar. He was not allowed to apply for a patent until after World War II, and was granted U.S. Patent No. 2,803,819 five years before his death.[8]
September 3, 1962 (Monday)
- Jens Otto Krag succeeded the ailing Viggo Kampmann as Prime Minister of Denmark.[9]
- Round 1 of the 1962–63 Football League Cup began in England.
- Died:
- E. E. Cummings, 67, American poet and author, following a cerebral hemorrhage the night before.[10] Edward Elstin Cummings had written his last words the afternoon before, about delphinium flowers, chopped some wood, sharpened the axe, then collapsed in his home.[11]
- Franz Schrönghamer-Heimdal, 81, German Catholic, Nazi, and anti-Semitic author
September 4, 1962 (Tuesday)
- The Beatles made their first recording of a song that would become a hit single, "Love Me Do". It would become their fourth #1 song in the United States, in 1964.[12]
- The closing ceremony of the 1962 Asian Games was held in Jakarta, Indonesia, following an attack on India's embassy by 1,000 rioters. Earlier, Asian Games Federation Vice-President G. D. Sondhi had announced that he was seeking to have the executive council declare that the competition was not part of the name "Asian Games", because AGF members Israel and Nationalist China (Taiwan) had had their teams excluded.[13]
- Born:
- Patrice Lagisquet, French rugby player for the France national rugby union team, and assistant coach, in Arcachon
- Ulla Tørnæs, Danish politician and former Minister for Science, Technology, Information and Higher Education
September 5, 1962 (Wednesday)
- Sputnik 4, a Soviet mockup of a manned spaceship, fell out of orbit after 843 days, having been launched on May 15, 1960.[14] What was believed to be a 20-pound fragment landed at the intersection of North 8th Street and Park Street in Manitowoc, Wisconsin, which was along the path where the craft disintegration took place.[15]
- "Cedar Hill", the home of Frederick Douglass, located at 1411 W Street S.E. in Washington, D.C., was acquired by the U.S. National Park Service and became "the first black national historic site".[16] On the same date, Park Service acquired "Glenmont", the home (and laboratory) or Thomas Edison in West Orange, New Jersey.[17]
- The composition of the American penny was changed to 95% copper and 5% zinc, which remained until 1982, when pennies became 97.5% zinc and 2.5% copper.[18]
- Gilbert Chandler became leader of the Victorian Legislative Council in Australia.
- Died: Sekarmadji Maridjan Kartosuwirjo, 57, Indonesian Islamic mystic and leader of the Darul Islam rebellion against the Sukarno regime, was executed by a firing squad
September 6, 1962 (Thursday)
- The first of the "Blackfriars Ships" was discovered by archaeologist Peter Marsden in London, buried in the mud of the Thames River and literally "under the shadow of Blackfriars Bridge". With a cofferdam to hold back the waters during low tide, and assistance from the London Fire Brigade, the oak craft was excavated. From pottery shards in the wreckage, Marsden estimated that the ship sank during the 2nd century AD, when Britain was ruled by the Roman Empire.[19]
September 7, 1962 (Friday)
- Robert Sténuit of Belgium was brought back from the bottom of the Mediterranean Sea, where he had become the first person to spend 24 hours on the ocean floor. Sténuit, who was lowered off the coast of France near Cap Ferrat, stayed inside a pressurized airtight cylinder designed by Edwin Link. Scheduled to remain below for two days in a 3.5 meter long cylinder, Sténuit was brought up early, after one day instead, but became the first living person to stay at least 24 hours in an underwater habitat on the ocean floor.[20]
- Former French Prime Minister Georges Bidault, who had fled from France to Italy after being indicted for anti-government activities, was taken into custody at Rome and ordered to leave Italy, with transportation "to the frontier of his choice".[21]
- The Buckfastleigh, Totnes and South Devon Railway, in England, was closed by the Western Region of British Railways.
- Filming of Sergei Bondarchuk's War and Peace began, and would continue for another six years.
- Died:
- Karen Blixen, 77, Danish author known by her pen name of Isak Dinesen. As Dinesen, she wrote the memoir Out of Africa in 1937, which would become the basis for the 1985 film of the same name.
- Morris Louis, 49, American painter
September 8, 1962 (Saturday)
- The Cuban Missile Crisis began as the first consignment of Soviet R-12 (called SS-4 by NATO) offensive missiles arrived in Cuba, on board the freighter Omsk.[22] The medium range ballistic missiles, which could be fitted with nuclear warheads and could strike targets in the U.S. within 2,000 km or 1,300 miles of Cuba.[23]
- In the Sino-Indian War, two companies of Communist Chinese troops crossed the McMahon Line that had marked the border between India and China, to confront soldiers at the recently established Indian Army border post at Dhola.[24]
September 9, 1962 (Sunday)
- While India's Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru was out of the country for the Commonwealth Prime Ministers' Conference in London, Defence Minister V. K. Krishna Menon gave the order for the Indian Army to "evict" Chinese troops from south of the McMahon Line, even though there were Indian troops north of the line in China. The decision proved to be a disaster.[25][26]
- For the first time since Taiwan began U-2 overflights over Mainland China in January, one of the pilots of the Black Cat Squadron, the 35th Reconnaissance Squadron of the Republic of China Air Force, was shot down. Colonel Chen Huai-seng's U-2 plane was struck by an SA-2 Guideline missile near Nanchang, and Colonel Chen did not survive the crash. Another of the Black Cats, Major Wang Cheng-wen, was killed on the same day in an unrelated accidental crash of his U-2 plane.[27]
- Pravda, the Soviet Communist Party newspaper, published the article "Plans, Profits, and Bonuses", by economics professor Evsei Liberman of the Kharkiv National University of Economics, as the Communist Party introduced discussion of new policies that would become a reality in the 1965 Soviet economic reform. Liberman's proposal was to depart from the Communist system, of measuring factory efficiency by whether a pre-set production quota had been met, and judging performance instead by the amount of the factories' profit, with the goal of increasing the quality and quantity of products.[28]
- Jack Nicklaus won the first "World Series of Golf", a made-for-television exhibition organized by the NBC television network as a competition between the champions of the four major professional golf tournaments [29]. With a 138 on 36 holes, Nicklaus (winner of the U.S. Open) won the $50,000 first prize by finishing four strokes ahead of ahead of Masters and British Open champion Arnold Palmer and PGA Championship winner Gary Player, who tied at 139.
- Born:
- Liza Marklund, Swedish journalist and crime writer, in Pålmark
- Jack Trudeau, American football player and radio presenter, in Forest Lake, Minnesota
- Died: Paavo Aaltonen, 42, Finnish gymnast and a three-time Olympic champion
September 10, 1962 (Monday)

Rod Laver
- Rod Laver of Australia became only the second person in history to win the "Grand Slam" of tennis, after taking the men's singles title in the U.S. Open, by defeating fellow Queenslander Roy Emerson, 6-2, 6-4, 5-7 and 6-4. Earlier in 1962, he won the Australian Open (January), the French Open (June) and Wimbledon (July).[30]
- The railroad line between Taunton and Chard Junction, within Somerset, became the first casualty of the "Beeching cuts" after the Chairman of British Railways, Richard Beeching, began shutting down unprofitable railroad lines. For the next 13 years, passenger service would be halted permanently at 29 separate rail routes, a process accelerated after the publishing of the "Beeching Report" on March 27, 1963. An author would note later that 4,500 miles of routes, 2,500 stations, and 67,700 jobs would be ended the closures.[31]
- Speaking for the U.S. Supreme Court, Justice Hugo Black halted further stays against enforcement of a lower court decision, and ordered the immediate admission of James Meredith as the first African-American student at the then-segregated University of Mississippi. Black wrote that the enrollment of Meredith as a student "can do no appreciable harm to the university".[32][33]
- Born: Co Stompé, Dutch darts player and 2010 World Cup of Darts champion; in Amsterdam
September 11, 1962 (Tuesday)
- Weeks before the discovery of nuclear missiles that would lead to the Cuban Missile Crisis, the Soviet Union publicly warned that a U.S. attack on Cuba, or on Soviet ships carrying supplies to the island, would mean war.[34] In a statement read at the Foreign Office in Moscow, the government declared "One cannot now attack Cuba and expect that the aggressor will be free from punishment for this attack. If such an attack is made, this will be the beginning of unleashing war... which might plunge the world into the disaster of a universal world war with the use of thermonuclear weapons."[35]
- Thurgood Marshall was confirmed by the U.S. Senate as a judge on the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit, 353 days after he had been nominated, by a vote of 56-14.[36] Marshall, an African-American who had argued the landmark case of Brown v. Board of Education, and who would later be elevated to the U.S. Supreme Court, had been serving for eleven months after President Kennedy had made an appointment, subject to Senate approval, while Congress was not in session.[37]
- Big Sur, by Jack Kerouac, was first published. Paul Maher, Jr., Kerouac: His Life and Work (Taylor Trade Publications, 2007) p428
- Died: Robert Soblen, 61, an American spy who had been awaiting extradition to the United States to begin a life sentence in prison on conviction of espionage for the Soviet Union, died five days after he lapsed into a coma from a barbiturate overdose. Minutes before he was to board Pan Am Flight 101 from London to New York, Soblen collapsed at the London Airport (now called Heathrow).[38][39] Although suicide was an obvious motive, investigators speculated that Soblen may have been poisoned by the Soviet KGB in order to prevent him from revealing the identities of other spies.[40]
September 12, 1962 (Wednesday)
- President John F. Kennedy, in a speech at the football stadium of Rice University in Houston, reaffirmed that the U.S. would put a man on the Moon by the end of the decade.[41] On hand were 40,000 people, mostly students.[42] Kennedy had declared, on May 25, 1961, his belief that the nation should commit to a manned moon landing, which would be achieved on July 20, 1969.[43]
- The 1962 European Athletics Championships opened at the Partizan Stadium in Belgrade.
September 13, 1962 (Thursday)
- Governor of Mississippi Ross Barnett delivered a 20-minute address on statewide television and radio to urge state officials not to obey the federal court order to integrate the University of Mississippi, signing a legal document to implement the legal doctrine of interposition, whereby state law superseded a contrary federal government action. The Governor declared, "We will not drink from the cup of genocide. There is no case in history where the Caucasian race has survived integration." Barnett then made a proclamation, saying "I hereby direct each official to uphold and enforce the laws duly and legally enacted by the legislature of the State of Mississippi, regardless of this unwarranted, illegal and arbitrary usurpation of power," and added, "There is no cause which is more moral and just than the protection of the integrity of our races."[44]
- In elections in Grenada for the 15-member Legislative Council of the British Crown Colony, Chief Minister Herbert Blaize's Grenada National Party won six of the ten elected seats.[45]
September 14, 1962 (Friday)
- Teledu Cymru (now Wales West and North Television) began broadcasting to the North and West Wales region of Britain, extending the ITV Network to the whole of the United Kingdom.[46] Transmitters were located at Pembroke, Caernarvon and Flint.[47]
- Frederick S. Modise, a minister of South Africa's Zion Christian Church, was inspired to form a separate Christian denomination while in the Coronation Hospital in Johannesburg for what was diagnosed as an incurable illness. Modise, who would found the International Pentecost Holiness Church of South Africa, would say later that a voice had told him that he would be healed and would be able to return home on October 3. For the remainder of his life, Reverend Modise would minister to other ill patients.[48]
- Died: William Lindsay Gresham, 53, American novelist and non-fiction author, took an overdose of sleeping pills after having been diagnosed with incurable cancer.
September 15, 1962 (Saturday)
- The first Soviet medium-range missiles were deployed in Cuba, a week after their arrival.[23] On the same day, American electronic intelligence detected that Soviet high-altitude surface-to-air missiles had become operational. An SA-2 (or S-75) Dvina missile had downed the U-2 spy plane flown by Francis Gary Powers in 1960, and the weapons, located near the port of Mariel, were capable of stopping further American attempts to verify a missile buildup.[49]
- Iran's foreign minister Abbas Aram, and Soviet Union Ambassador Nikolai Pegov, signed an agreement providing that Iran would not allow any foreign nation to set up rocket bases on its soil.[50]
- Died: William Coblentz, 88, American physicist
September 16, 1962 (Sunday)
- The first semiconductor laser began operation, using a gallium arsenide compound. The initial test was done by Gunter Fenner at the General Electric Research Laboratory in Schenectady, New York.[51]
- The Italian Grand Prix was held at Monza and won by Graham Hill.
- Born: Josephus Thimister, Belgian designer, in Maastricht
September 17, 1962 (Monday)
- Nine new American astronauts, officially members of NASA Astronaut Group 2, were introduced at a press conference in Houston.[52] The "New Nine" were Neil Armstrong, Frank Borman, Pete Conrad, Jim Lovell, James McDivitt, Elliot See, Thomas P. Stafford, Ed White and John Young. Armstrong would become the first man to walk on the Moon (Conrad would be third and Young ninth). Borman and Lovell would orbit the Moon; White would be the first American to "walk in space", but would die in the fire of Apollo 1; Young would command the space shuttle's first launched mission, and See would die in a plane crash before he could be launched into space.[53]

A Mil Mi-8
- The final prototype of the Mil Mi-8 helicopter, with 1,500 shaft horsepower engines, was given its initial test flight. The Soviet, and later Russian-built machine would sell more units than any other helicopter in history.[54]
- Khalid al-Azm became Prime Minister of Syria for the sixth (and last) time, succeeding Bashir al-Azma. The Ba'ath Party would overthrow the Syrian government on March 8, 1963, and al-Azm would be arrested.[55]
- BBC Wales Today was broadcast for the first time. As of September 17, 2012, it will have been on the air for fifty years as one of the world's longest-running daily television news programmes.
- Born:
- BeBe Winans, American gospel singer, in Detroit
- Paul Feig, American TV director and actor, in Royal Oak, Michigan
September 18, 1962 (Tuesday)
- U.S. Marine Corps helicopters flew a combat mission from Da Nang, South Vietnam, for the first time, airlifting South Vietnamese troops into the hills south of Da Nang.[56]
- Died: Therese Neumann, 64, German Catholic mystic and stigmatic. Her followers said that she had inedia, the ability to survive without food, and that she had stopped eating in 1926.[57]
September 19, 1962 (Wednesday)

The last Imam of Yemen
- Prince Saif Al-Islam Muhammad al-Badr became the new Imam of Yemen, following the death of his 71-year-old father, the 71-year-old Imam Ahmad bin Yahya, who was described at his death as "despotic", "the perennial target of assassins", and a man "said to have died from natural causes hastened by old wounds. The following day, al-Badr was proclaimed at the Imam Al-Mansoor Billah.[58] His reign would last for a week before he was overthrown.[59]

"Vicious ugliness'- the Dyna-Soar
- A full-scale mockup of the Boeing X-20 Dyna-Soar spaceplane was unveiled for reporters in Las Vegas, where the Air Force Association was holding its annual convention, and the six pilots who would be the first to fly the X-20 were introduced. "Technical men familiar with sketches and photographs of the X-20 were startled by the vicious ugliness" of the plane, the Associated Press reported, noting that "With its uptruned wingtips and long snout, the X-20 looks like its designer had somehow managed to cross a manta ray with a shark." "Our Black Dyna-Soar Shows Its Ugly Snout"[60] The Dyna-Soar project, scheduled for a 1965 launch, would be cancelled after cost overruns, and none were ever built.
- The United States Intelligence Board reviewed all available data on arms shipments to Cuba, and reported to President Kennedy (erroneously) that there was no basis for speculation that nuclear missiles would be placed on the Caribbean island.[61]
- The first episode of The Virginian, starring James Drury in the title role (the character's real name was never revealed), was shown on NBC as the first 90-minute weekly TV series. It would run nine seasons, ending in 1971.[62]
- Died: Nikolai Pogodin, 61, Soviet playwright
September 20, 1962 (Thursday)
- Escorted by federal marshals James Meredith arrived at Oxford, Mississippi, in order to become the first African-American to enroll at the University of Mississippi. Governor Ross Barnett personally blocked Meredith's entrance into the admissions building.[63]
- Voting was conducted for Algeria's first Constituent Assembly since the nation's independence, with voters being given a choice of "yes" or "no" for the 196 candidates from the National Liberation Front, led by Ahmed Ben Bella.[64]
The MGB
- The MGB sports car was introduced by MG Cars. Over the next 18 years, 500,000 MGBs would be sold, making it the best selling sports car in history.[65]
- Died:
- Robert Colquhoun, 47, Scottish painter, printmaker and theatre set designer
- Conrad Emil Lambert Helfrich, 75, Dutch naval commander of World War II
September 21, 1962 (Friday)
- Composer Igor Stravinsky returned to Russia after an absence of 48 years, as a guest of the Soviet Union.[66]
- The UN General Assembly approved a ceasefire agreement between Indonesia and the Netherlands, with UN military observers from six nations monitoring the agreement. A larger UN Security Force would arrive at West Irian on October 3.[67]
- The British music magazine New Musical Express published a story about two 13-year-old schoolgirls, "Sue" and "Mary", releasing a disc on Decca, and added that "A Liverpool group, The Beatles, have recorded 'Love Me Do' for Parlophone Records, set for October 5 release."
- Born: Rob Morrow, American actor, in New Rochelle, New York
- Died: Marie Bonaparte, 80, French author and psychoanalyst
September 22, 1962 (Saturday)
- Autostrada 1, a 125-mile long superhighway between Rome and Naples, was opened to traffic. Travel time between the two Italian cities was cut almost in half, from 3 1/2 hours to two hours.[68]
- India's Defence Ministry officials met to discuss plans to drive out Chinese troops from the disputed border area at Thang La ridge. Despite the argument by General P.N. Thaper, the Chief of the Army Staff of Indian Army, that Chinese troops at the border outnumbered those from India, General Thaper was given a written order to "prepare and throw out the Chinese as soon as possible".[26]
- Born: Sirous Ghayeghran, Iranian footballer, in Bandar Anzali (died 1998)
September 23, 1962 (Sunday)

The new Philharmonic Hall
- The Jetsons - George, Jane, Judy and Elroy - were introduced in a primetime cartoon of the same name at 7:30 pm Eastern time on the ABC television network. Despite having only 24 episodes, the science fiction show, about a family living about 100 years in the future, would be rerun for 23 years until new episodes were commissioned for a syndicated revival in 1985.[69]
- The Lincoln Center for the Performing Arts, including its modern Philharmonic Hall, later Avery Fisher Hall, opened in New York City. The inaugural concert, which was televised live on CBS, featured Leonard Bernstein, the New York Philharmonic Orchestra, and a host of operatic stars such as Eileen Farrell and Robert Merrill.[70]
- Unbeknownst to the world, Pope John XXIII was diagnosed with terminal stomach cancer. He would pass away on June 3, 1963.[71]
- The Soviet Union Council of Ministers approved the development of the Global Rocket 1 (GR-1) missile, with the goal of a weapon with a range of 20,000 km or 12,500 miles, capable of hitting a target anywhere on Earth. The project was cancelled in 1964 in favor of the R-36 orbiting missile, designated as the SS-18 by NATO.[72]
- Flying Tiger Line Flight 923 crashed into the Atlantic Ocean after three of its four engines failed. The L-1049H Super Constellation was on its way from the United States to West Germany when it ditched at sea with 76 people on board, of whom 28 died. The other 48 were rescued by the Swiss ship Celerina.[73] The crash investigation determined that the accident was caused by the failure of engine No. 3, the accidental closing of a shutoff valve on engine No. 1 by the flight engineer, and the failure of engine No. 2 as the plane was proceeding to the nearest available airport.[74]
- Born: Robert Molle, Canadian athlete who won a silver Olympic medal in wrestling in 1984, and later captained the Winnipeg Blue Bombers of the Canadian Football League; in Saskatoon
September 24, 1962 (Monday)
- Samuel Barber's Piano Concerto, performed by John Browning, premiered at the Philharmonic Hall.[75]
- Born:
- Ally McCoist, Scottish footballer, manager and television personality, in Bellshill
- Sergey Schepkin, Russian pianist, in St. Petersburg
September 25, 1962 (Tuesday)
- Sonny Liston and Floyd Patterson fought for the world heavyweight boxing title in Chicago. Liston made history by being the first man ever to knock out a reigning heavyweight champion in the first round, downing the titleholder in 2 minutes and 6 seconds.[76]
- In Yemen, Abdullah as-Sallal launched a coup d'état aimed at the overthrow of the new Imam, Muhammad al-Badr. Sallal's troops shelled the royal palace, thought they had buried the Imam in the rubble, and proclaimed his death on Aden radio. But al-Badr had escaped and would attempt a rebellion against the newly proclaimed[77]
- Ferhat Abbas was elected the President of Algeria by the new Constitutional Assembly, which formally proclaimed the foundation of the Democratic and Popular Republic of Algeria during their opening session.[78]
September 26, 1962 (Wednesday)

Irene Ryan and Buddy Ebsen
- The Beverly Hillbillies, a television situation comedy about a poor Ozark Mountains family who became multi-millionaires after oil was found on their land, began a nine-year run on the CBS network, with the first episode premiering at 9:00 pm Eastern time. UPI television critic Rick Du Brow wrote the next day that the series "is going to be a smash hit" in that it was similar in premise to TV program The Real McCoys, but added that "The nicest thing I can say... is that it is really not like 'The Real McCoys'... The McCoys are a civilized rural clan; these new hillbillies make L'il Abner and his mob look like a bunch of sophisticates [79] Within three weeks, it was the most-watched series on American television, and stayed at #1 in its first two seasons. The show had 274 episodes, with the final one broadcast on March 23, 1971.[80]
- A flash flood in the Catalan region of Spain killed 445 people, in Barcelona and in the nearby villages of Sabadell and Terrassa.[81]
- As the North Yemen Civil War progressed, all areas of the Yemeni city of San'a were in the hands of the new Yemen government, led by Abdullah as-Sallal, and he proclaimed the Yemen Arab Republic.[82]
- Born:
- Chunky Pandey, Indian actor
- Dragan Mance, Serbian footballer, in Belgrade (died 1985)
- Mark Haddon, English author of children's books, in Northampton
September 27, 1962 (Thursday)
- Rachel Carson's book Silent Spring was released, giving rise to the modern environmentalist movement.[83]
- The 25th Canadian Parliament opened its first and only session, adjourning on February 6, 1963.[84]
September 28, 1962 (Friday)
- Prime Minister Ahmed Ben Bella founded the first government of independent Algeria.[85]
- Yemeni radio announced the death of former ruler, Muhammad al-Badr. Al-Badr had, in fact, escaped the country and was living in Saudi Arabia.[86]
- Born: Fred Merkel, American motorcycle racing champion, in Stockton, California
September 29, 1962 (Saturday)
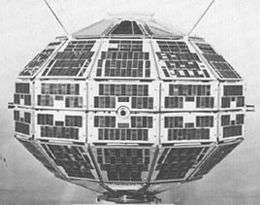
Alouette 1
- The Canadian Alouette 1, the first satellite built outside the United States and the Soviet Union, was launched from Vandenberg AFB in California.[87]
- My Fair Lady ended its Broadway run after more than six years and 2,717 performances, a Broadway record that would stand until surpassed later by Hello, Dolly![88]
- In order to prevent the University of Mississippi from making any further efforts to prevent James Meredith from becoming the first African-American to enroll there, President Kennedy issued a proclamation commanding all persons engaged in the obstruction of the laws and the orders of the courts to "cease and desist therefrom and to disperse and retire peaceably forthwith", citing his authority under 10 U.S.C. § 332, § 333, and § 334 to use the militia or the armed forces to suppress any insurrection, domestic violence, unlawful combination, or conspiracy." [63]
- Reconnaissance aircraft indicated the formation of a tropical depression to the east of the Lesser Antilles, which would later develop into Hurricane Daisy.
- Died: Muhammad VIII al-Amin, 85, last Bey of Tunisia.[89]
September 30, 1962 (Sunday)
- James Meredith was escorted by a team of United States Marshals to the campus of the University of Mississippi for enrollment as the first African-American student at "Ole Miss".[90] That evening, at 8:15 pm, rioting broke out as a mob joined students on the campus, and the 4,000 troops of the 108th Armored Cavalry Regiment of the Mississippi National Guard was "federalized" under the command of Brigadier General Charles Billingslea of the U.S. Army to restore order, taking the side of the United States against the State of Mississippi.[91] Two civilians were killed by unknown persons, which many believed to be rioters. Paul Guihard, a British reporter on assignment for the Agence France-Presse, was shot in the back, and a local jukebox repairman, George Gunter, was shot in the head while visiting the situation out of curiosity.[92]
- The CBS Radio Network broadcast the final episodes of Suspense and Yours Truly, Johnny Dollar, marking the end of the Golden Age of Radio.[93]
- In the final scheduled games of the 1962 Major League Baseball season, the San Francisco Giants (100-61) defeated the Houston Colt .45s, 2-1, while the Los Angeles Dodgers (101-60) lost to the St. Louis Cardinals, 1-0, giving both the Giants and Dodgers identical 101-61 records and first place in the National League, and forcing a playoff series between the two.[94] The Dodgers, who had had a two-game lead with only four games left in the season, went on to lose the playoff to the Giants, who would go on to the 1962 World Series.
- The National Farm Workers of America, which would later merge with the Agricultural Workers Organizing Committee to form the United Farm Workers of America, was founded in Fresno, California by Cesar Chavez.[95]
gollark: Well, quarks are made of apions, which are like bees.
gollark: Oh, we put our backdoors in at the quark scale.
gollark: For backward compatibility it can go down to 40Gbps.
gollark: It also has a built-in 1Tbps Ethernet PHY, for IoT applications.
gollark: Yes.
References
- "Earthquakes with 1,000 or More Deaths since 1900" Archived 2013-01-14 at the Wayback Machine, U.S. Geological Survey
- "Fear 10,000 Lose Lives in Iran Quake", Chicago Daily Tribune, September 4, 1962, p1
- "Big Vote for Merger in Singapore", Sydney Morning Herald, September 3, 1962, p3
- "134 Now Feared Dead in Typhoon", Sydney Morning Herald, September 3, 1962, p3
- "Airport Operations Halt For Sky Shield", Miami News, September 2, 1962, p1
- "Soviet Announces Pact With Cuba For Delivery Of Military Equipment", Toledo Blade, September 3, 1962, p1
- Dennis Castillo, The Maltese Cross: A Strategic History of Malta (Greenwood Publishing Group, 2006) p219
- "Blair, William Richards", in Military Communications: From Ancient Times to the 21st Century, Christopher H. Sterling, ed., (ABC-CLIO, 2008) pp61-62
- "Krag Succeeds Ill Danish Premier", New York Times, September 4, 1962
- "e. e. cummings Dies", Miami News, September 3, 1962, p1
- Richard S. Kennedy, dreams in the mirror: A Biography of E.E. Cummings (W. W. Norton & Company, 1994) p484
- Fred Bronson, The Billboard Book of Number 1 Hits (Random House Digital, 2003) p148
- "Stormy Asian games Near End After Riotous Display", Quebec Chronicle-Telegraph, September 4, 1962, p5
- Rex Hall and David Shayler, The Rocket Men: Vostok & Voskhod, the First Soviet Manned Spaceflights (Springer, 2001) p119-120
- "Object Found in Manitowoc May Be Part of Sputnik", Milwaukee Journal, - September 6, 1962, p1
- Charles E. Cobb, Jr., On the Road to Freedom: A Guided Tour of the Civil Rights Trail (Algonquin Books, 2008) p32
- Maxine N. Lurie and Marc Mappen, Encyclopedia of New Jersey (Rutgers University Press, 2004) p240
- David W. Lange, The Complete Guide To Lincoln Cents (Zyrus Press, 2005) p23-26
- Paul Johnstone, The Sea-Craft of Prehistory (Taylor & Francis, 1989) p89
- Hellwarth, Ben (2012). Sealab: America's Forgotten Quest to Live and Work on the Ocean Floor. New York: Simon & Schuster. pp. 58–59. ISBN 978-0-7432-4745-0. LCCN 2011015725.
- "Italians Kick Out Fugitive French Ex-Premier Bidault", Miami News, September 8, 1962, p1
- Scott Ritter, Dangerous Ground: America's Failed Arms Control Policy, from FDR to Obama (Nation Books, 2010) p113
- Douglas P. Lackey, Moral Principles and Nuclear Weapons (Rowman & Littlefield, 1984) p54
- K. V. Krishna Rao, Prepare Or Perish: A Study of National Security (Lancer Publishers, 1991) p89
- Benjamin Zachariah, Nehru (Routledge, 2004) p246
- K. V. Krishna Rao, Prepare Or Perish: A Study of National Security (Lancer Publishers, 1991) p91
- I. C. Smith and Nigel West, Historical Dictionary of Chinese Intelligence (Scarecrow Press, 2012) p272
- "Liberman, Evsel Grigorevich (1897-1983)", in Europe Since 1945: An Encyclopedia, Bernard A. Cook, ed. (Taylor & Francis, 2001), volume 2, p785
- "Nicklaus Captures World Series of Golf by 4 Shots", Battle Creek (MI) Enquirer, September 10, 1962, p11
- "This Day in History: Rod Laver wins Grand Slam"; "Laver's In Command", Miami News, September 11, 1962, p 3C
- Julian Holland, Dr Beeching's Axe 50 Years On: Memories of Britain's Lost Railways (David & Charles, 2013)
- "Integrationists Laud Decision By Black Today", Florence (AL) Times Daily, September 11, 1962, p2
- "Meredith, James H(oward)", in The Kennedy Years, Joseph M. Siracusa, ed. (Infobase Publishing, Sep 30, 2004) p324
- Franklin, Jane (1997). Cuba and the United States: A Chronological History. Melbourne: Ocean Press. ISBN 1-875284-92-3
- "Reds Threaten War If Cuba Attacked", Miami News, September 11, 1962, p1
- "Senate Approves Marshall, 54-16", New York Times, September 12, 1962, p1
- Glenn L. Starks and F. Erik Brooks Ph.D., Thurgood Marshall: A Biography (ABC-CLIO, 2012) p55
- "Fly Fugitive Red Spy to U.S. Today", Chicago Daily Tribune, September 6, 1962, p1
- "Russian Spy Collapses At Airport", Sydney Morning Herald, September 7, 1962, p1
- "Probe Theory of Murder in Soblen Death", Chicago Daily Tribune, September 12, 1962, p7
- "John F. Kennedy Address at Rice University on the Space Effort", Rice University
- "JFK Vows to Take Over Lead in the Space Race", Pittsburgh Post-Gazette, September 13, 1962, p1
- Steven J. Dick, Remembering the Space Age (Government Printing Office, 2008) p163
- "Barnett Tells Miss. Officials: Defy Federal Racial Orders", Times-Daily (Hendersonville, NC), September 14, 1962, p1
- Nohlen, D (2005) Elections in the Americas: A data handbook, Volume I, p307 ISBN 978-0-19-928357-6
- Catherine Johnson and Rob Turnock, ITV Cultures (McGraw-Hill International, 2005) pp97-98
- "Wales to Get Its Own TV on Friday— Teludu Cymru 'for square deal'", The Guardian (Manchester), September 11, 1962, p2
- "Frederick Modise and the International Pentecost Church: A Modern African Messianic Movement?", by Allan Anderson, Institute for Theological Research
- James Bamford, Body of Secrets: Anatomy of the Ultra-Secret National Security Agency (Random House Digital, 2002) p106
- Gholam R. Afkhami, The Life and Times of the Shah (University of California Press, 2009) p336
- John C. Ion, Laser Processing Of Engineering Materials: Principles, Procedure And Industrial Application (Butterworth-Heinemann, 2005) pp16-17
- "Meet Our Nine New Men Into Space", Miami News, September 17, 1962, p. 1.
- Hamish Lindsay, Tracking Apollo to the Moon (Springer, 2001), p. 83.
- Walter J. Boyne, How the Helicopter Changed Modern Warfare (Pelican Publishing, 2011), p. 211.
- Elie Podeh, The Decline of Arab Unity: The Rise And Fall of the United Arab Republic (Sussex Academic Press, 1999), p. 171.
- Chinnery, Philip D., Vietnam: The Helicopter War, Annapolis, Maryland: Naval Institute Press, 1991, ISBN 1-55750-875-5, p. 15.
- Michael Freze, They Bore the Wounds of Christ: The Mystery of the Sacred Stigmata (Our Sunday Visitor Publishing, 1989) p281
- "Yemen's New King Liberal With Grudge At West", Miami News, September 20, 1962, p2
- Rachel Bronson, Thicker Than Oil: America's Uneasy Partnership with Saudi Arabia (Oxford University Press, 2006) p85
- Miami News, September 20, 1962, p1
- Roger Hilsman, The Cuban Missile Crisis: The Struggle Over Policy (Greenwood Publishing Group, 1996) p32
- James S. Olson, Historical Dictionary of the 1960s (Greenwood Publishing, 1999) p467
- Wilson Smith and Thomas Bender, American Higher Education Transformed, 1940-2005: Documenting the National Discourse (JHU Press, 2008) p122
- Mahfoud Bennoune, The Making of Contemporary Algeria, 1830-1987 (Cambridge University Press, 2002) p98
- Anders Ditlev Clausager, Original MGB With MGC and MGB GT V8 (MBI Publishing, 1995) p8
- "Soviet Acclaims Stravinsky Visit", New York Times, September 22, 1962, p1
- Jacob Bercovitch, Scott Sigmund Gartner, International Conflict Mediation: New Approaches and Findings (Taylor & Francis US, 2009) p45
- "A Superhighway Links Rome, Naples", Miami News, September 23, 1962, p3
- Tim Brooks and Earle Marsh, The Complete Directory to Prime Time Network and Cable TV Shows, 1946-present (Random House Digital, 2003) p607
- Jack Gottlieb, Working With Bernstein: A Memoir (Hal Leonard Corporation, 2010) pp312-313
- Richard P. McBrien, Lives of the Popes: The Pontiffs from St. Peter to Benedict XVI (Harper Collins, 2006) p373
- Oleg Bukharin, et al., Russian Strategic Nuclear Forces (MIT Press, 2004) pp199-200
- "Rescuers Grab 49 From Wild Sea", September 24, 1962, p1
- CAB Aircraft Accident Report, September 13, 1963, FlyingTiger923.com; "I Goofed...28 Killed", Miami News, November 15, 1962, p5A
- Barbara B. Heyman, Samuel Barber: The Composer and His Music (Oxford University Press, 1994) p418
- "Liston Kayos Floyd In 2:06", Daytona Beach (FL) Morning Journal, September 26, 1962, p1
- Paul Dresch, A History of Modern Yemen (Cambridge University Press, 2000) p87
- Phillip C. Naylor, France and Algeria: A History of Decolonization and Transformation (University Press of Florida, 2000) p55
- "Beverly Hillbillies Make Yokums Look Sophisticated", by Rick Du Brow, Wilmington (DE) News Journal, September 27, 1962, p10
- Ray Broadus Browne and Pat Browne, The Guide to United States Popular Culture (Popular Press, 2001) p87
- Lee Davis, Natural Disasters: New Edition (Infobase Publishing, 2009) pp175-176
- Sarah Phillips, Yemen's Democracy Experiment in Regional Perspective: Patronage and Pluralized Authoritarianism (Macmillan, 2008) p43
- Charles Piddock, Rachel Carson: A Voice for the Natural World (Gareth Stevens Publishing, 2009) p89
- "Parliaments- Duration of Sessions", Parliament of Canada
- Bernard Reich, Political Leaders of the Contemporary Middle East and North Africa: A Biographical Dictionary (Greenwood Publishing Group, 1990) p88
- "Arabia Felix". Time. 1962-10-26. ISSN 0040-781X. Retrieved August 26, 2008.
- Stephen J. Dick and Roger D. Launius, Societal Impact of Spaceflight (Government Printing Office, 2009) p210
- Richard Stirling, Julie Andrews: An Intimate Biography (Macmillan, 2009)
- "The Former Bey Of Tunis Dies At 85", Miami News, October 2, 1962, p2
- James Meredith, Three Years in Mississippi (Indiana University Press, 1966) p326
- "OLE MISS FIGHTING KILLS 2; GEN. WALKER LEADS CHARGE", Miami News, October 1, 1962, p1
- "Fatal Rioting at Ole Miss! JFK Issues Peace Plea", Milwaukee Sentinel, October 1, 1962, p1
- Jim Cox, American Radio Networks: A History (McFarland, 2009) pp160-164
- "Dodgers Did 'Best' To Avoid Pennant", Pittsburgh Press, October 1, 1962, p26
- Aaron Brenner, et al., The Encyclopedia of Strikes in American History (M.E. Sharpe, 2009) p426
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.