Scleroderma
Scleroderma is a group of autoimmune diseases that may result in changes to the skin, blood vessels, muscles, and internal organs.[2][6] The disease can be either localized to the skin or involve other organs as well.[2] Symptoms may include areas of thickened skin, stiffness, feeling tired, and poor blood flow to the fingers or toes with cold exposure.[1] One form of the condition, known as CREST syndrome, classically results in calcium deposits, Raynaud's syndrome, esophageal problems, thickening of the skin of the fingers and toes, and areas of small dilated blood vessels.[1]
| Scleroderma | |
|---|---|
| A type of localized scleroderma known as morphea | |
| Specialty | Rheumatology |
| Usual onset | Middle age[1] |
| Types | Localized, systemic scleroderma[2] |
| Causes | Unknown[2] |
| Risk factors | Family history, certain genetic factors, exposure to silica[3][4][5] |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms, skin biopsy, blood tests[6] |
| Differential diagnosis | Mixed connective tissue disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, polymyositis, dermatomyositis[1] |
| Treatment | Supportive care[1] |
| Medication | Corticosteroids, methotrexate, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)[2] |
| Prognosis | Localized: Normal life expectancy[7] Systemic: Decreased life expectancy[3] |
| Frequency | 3 per 100,000 per year (systemic)[3] |
The cause is unknown; however, some suspect it may be due to an abnormal immune response.[2] Risk factors include family history, certain genetic factors, and exposure to silica.[3][4][5] The underlying mechanism involves the abnormal growth of connective tissue which is believed to be the result of the immune system attacking healthy tissues.[6] Diagnosis is based on symptoms, supported by a skin biopsy or blood tests.[6]
While there is no cure, treatment may improve symptoms.[2] Medications used include corticosteroids, methotrexate, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).[2] Outcome depends on the extent of disease.[3] Those with localized disease generally have a normal life expectancy.[7] In those with systemic disease typical life expectancy is about 11 years from onset.[3] Death is often due to lung, gastrointestinal, or heart complications.[3]
About 3 out of 100,000 people per year develop the systemic form.[3] The condition most often begins in middle age.[1] Women are more often affected than men.[1] Scleroderma symptoms were first described in 1753 by Carlo Curzio[8] and then well documented in 1842.[9] The term is from the Greek "sklerosis" meaning "hardness" and "derma" meaning "skin".[6]
Signs and symptoms
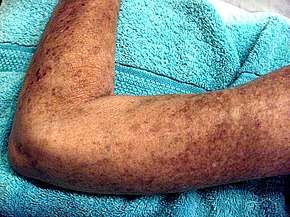
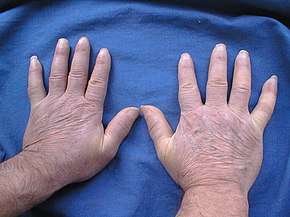
Potential signs and symptoms include:[10][11][12]
- Cardiovascular: Raynaud's phenomenon (is the presenting symptom in 30% of affected persons, occurs in 95% of affected individuals at some time during their illness); healed pitting ulcers on the fingertips; skin and mucosal telangiectasis; palpitations, irregular heart rate and fainting due to conduction abnormalities, hypertension and congestive heart failure.
- Digestive: gastroesophageal reflux disease, bloating, indigestion, loss of appetite, diarrhoea alternating with constipation, sicca syndrome and its complications, loosening of teeth and hoarseness (due to acid reflux).
- Pulmonary: progressive worsening of shortness of breath, chest pain (due to pulmonary artery hypertension) and dry, persistent cough due to interstitial lung disease.
- Musculoskeletal: joint, muscle aches, loss of joint range of motion, carpal tunnel syndrome and muscle weakness.
- Genitourinary: erectile dysfunction, dyspareunia, kidney problems, or kidney failure.
- Other: facial pain due to trigeminal neuralgia, hand paresthesias, headache, stroke, fatigue, calcinosis and weight loss.
Cause
Scleroderma is caused by genetic and environmental factors.[4][5][13][14] Mutations in HLA genes seem to play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of some cases (but not all), likewise silica, aromatic and chlorinated solvents, ketones, trichloroethylene, welding fumes and white spirits exposure seems to contribute to the condition in a small proportion of affected persons.[4][5][13][14][15]
Pathophysiology
It is characterised by increased synthesis of collagen (leading to the sclerosis), damage to small blood vessels, activation of T lymphocytes and production of altered connective tissues.[16] Its proposed pathogenesis is the following:[17][18][19][20][21]
- It begins with an inciting event at the level of the vasculature, probably the endothelium. The inciting event is yet to be elucidated but may be a viral agent, oxidative stress or autoimmune. Endothelial cell damage and apoptosis ensue, leading to the vascular leakiness that manifests in early clinical stages as tissue oedema. At this stage it is predominantly a Th1 and Th17-mediated disease.
- After this the vasculature is further compromised by impaired angiogenesis and impaired vasculogenesis (fewer endothelial progenitor cells), likely related to the presence of antiendothelinal cell antibodies (AECA). Despite this impaired angiogenesis, elevated levels of pro-angiogenic growth factors like PDGF and VEGF is often seen in persons with the condition. The balance of vasodilation and vasoconstriction becomes off-balance and the net result is vasoconstriction. The damaged endothelium then serves as a point of origin for blood clot formation and further contributes to ischaemia-reperfusion injury and the generation of reactive oxygen species. These later stages are characterised by Th2 polarity.
- The damaged endothelium upregulates adhesion molecules and chemokines to attract leucocytes, which enables the development of innate and adaptive immune responses, including loss of tolerance to various oxidised antigens, which includes topoisomerase I. B cells mature into plasma cells, which furthers the autoimmune component of the condition. T cells differentiate into subsets, including Th2 cells, which play a vital role in tissue fibrosis. Anti–topoisomerase 1 antibodies, in turn, stimulate type I interferon production.
- Fibroblasts are recruited and activated by multiple cytokines and growth factors to generate myofibroblasts. Dysregulated transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) signalling in fibroblasts and myofibroblasts has been observed in multiple studies of scleroderma-affected individuals. Activation of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts leads to excessive deposition of collagen and other related proteins, leading to fibrosis. B cells are implicated in this stage, IL-6 and TGF-β produced by the B cells decrease collagen degradation and increase extracellular matrix production. Endothelin signalling is implicated in the pathophysiology of fibrosis.[22]
Vitamin D is implicated in the pathophysiology of the disease. An inverse correlation between plasma levels of vitamin D and scleroderma severity has been noted and vitamin D is known to play a crucial role in regulating (usually suppressing) the actions of the immune system.[23]
Diagnosis
Typical scleroderma is classically defined as symmetrical skin thickening, with about 70% of cases also presenting with Raynaud's phenomenon, nail-fold capillary changes and antinuclear antibodies. Affected individuals may or may not experience systemic organ involvement. There is no single test for scleroderma that works all of the time and hence the diagnosis is often a matter of exclusion. Atypical scleroderma may show any variation of these changes without skin changes or with finger swelling only.[24]
Laboratory testing can show antitopoisomerase antibodies, like anti-scl70 (causing a diffuse systemic form), or anticentromere antibodies (causing a limited systemic form and the CREST syndrome). Other autoantibodies can be seen, such as anti-U3 or anti-RNA polymerase.[25] |- Anti-double-stranded DNA (ds DNA) autoantibodies likely to be present in serum.
Differential
Diseases that are often in the differential include:[26]
- Eosinophilia, a condition in which there are too many eosinophils (a type of immune cell that attacks parasites and is involved in certain allergic reactions) in the blood.
- Eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome, a form of eosinophilia that is caused by L-tryptophan supplements.
- Eosinophilic fasciitis, a disease that affects the connective tissues surrounding skeletal muscles, bones, blood vessels and nerves in the arms and legs.
- Graft-versus-host disease, an autoimmune condition that occurs as a result of bone marrow transplants in which the immune cells from the transplanted bone marrow attack the host's body.
- Mycosis fungoides, a type of cutaneous T cell lymphoma, a rare cancer that causes rashes all over the body.
- Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis, a condition usually caused by kidney failure that causes fibrosis (thickening) of the tissues.
- Primary biliary cirrhosis, an autoimmune disease of the liver.
- Primary pulmonary hypertension
- Complex regional pain syndrome
Classification
Scleroderma is characterised by the appearance of circumscribed or diffuse, hard, smooth, ivory-colored areas that are immobile and which give the appearance of hidebound skin, a disease occurring in both localised and systemic forms:[27]
- Localised scleroderma
- Localised morphea
- Morphea-lichen sclerosus et atrophicus overlap
- Generalised morphea
- Atrophoderma of Pasini and Pierini
- Pansclerotic morphea
- Morphea profunda
- Linear scleroderma
- Systemic scleroderma
- CREST syndrome
- Progressive systemic sclerosis
Treatment
There is no cure for scleroderma, although relief of symptoms is often achieved. These include the following:[10][28]
- Raynaud's phenomenon with vasodilators such as calcium channel blockers, alpha blockers, serotonin receptor antagonists, angiotensin II receptor inhibitors, statins, local nitrates or iloprost
- Digital ulcers with phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors (e.g., sildenafil) or iloprost
- Prevention of new digital ulcers with bosentan
- Malnutrition, secondary to intestinal flora overgrowth with tetracycline antibiotics like tetracycline
- Interstitial lung disease with cyclophosphamide, azathioprine with or without corticosteroids
- Pulmonary arterial hypertension with endothelin receptor antagonists, phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors and prostanoids
- Gastrooesophageal reflux disease with antacids or prokinetics
- Kidney crises with angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists
Systemic disease-modifying treatment with immunosuppressants is often used.[13][29][30][31][32][33] Immunosuppressants used in its treatment include azathioprine, methotrexate, cyclophosphamide, mycophenolate, intravenous immunoglobulin, rituximab, sirolimus, alefacept and the tyrosine kinase inhibitors, imatinib, nilotinib and dasatinib.[13][28][29][30][31][32][33][34]
Experimental therapies under investigation include endothelin receptor antagonists, tyrosine kinase inhibitors, beta-glycan peptides, halofuginone, basiliximab, alemtuzumab, abatacept and haematopoietic stem cell transplantation.[35][36]
| Immunomodulatory agents in the treatment of scleroderma | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| INN | Mechanism of action[37][38] | Route of administration[37] | Pregnancy category[37][39] | Major toxicities[37] |
| Alefacept | Monoclonal antibody to inhibit T lymphocyte activation by binding to CD2 portion of human leukocyte function antigen-3. | IM | B (US) | Malignancies, injection site reactions, blood clots, lymphopenia, hepatotoxicity and infections. |
| Azathioprine | Purine analogue that inhibits lymphocyte proliferation via conversion to mercaptopurine | PO, IV | D (Au) | Myelosuppression and rarely malignancy, hepatitis, infection, hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome and hypersensitivity reactions. |
| Cyclophosphamide | Nitrogen mustard that cross-links DNA base pairs, leading to breakages and triggering apoptosis in haematopoietic cells. | PO, IV | D (Au) | Vomiting, myelosuppression, haemorrhagic cystitis and rarely heart failure, pulmonary fibrosis, hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome, malignancy and SIADH. |
| Dasatinib | Tyrosine kinase inhibitor against various pro-angiogenic growth factors (including PDGF and VEGF). | PO | D (Au) | Fluid retention, myelosuppression, haemorrhage, infections, pulmonary hypertension, electrolyte anomalies and uncommonly hepatotoxicity, heart dysfunction/failure, myocardial infarction, QT interval prolongation, renal failure and hypersensitivity. |
| Imatinib | As above. | PO | D (Au) | As above and rarely: GI perforation, avascaular necrosis and rhabdomyolysis. |
| Immunoglobulin | Immunoglobulin, modulates the immune system. | IV | N/A | Varies. |
| Methotrexate | Antifolate; inhibits dihydrofolate reductase. | PO, IV, IM, SC, IT | D (Au) | Myeosuppression, pulmonary toxicity, hepatotoxicity, neurotoxicity and rarely kidney failure, hypersensitivity reactions, skin and bone necrosis and osteoporosis. |
| Mycophenolate | Inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase inhibitor, leading to reduced purine biosynthesis in lymphocytes. | PO, IV | D (Au) | Myelosuppression, blood clots, less commonly GI perforation/haemorrhage and rarely pancreatitis, hepatitis, aplastic anaemia and pure red cell aplasia. |
| Nilotinib | As per dasatinib. | PO | D (Au) | As per imatinib. |
| Rituximab | Monoclonal antibody against CD20 which is expressed on B lymphocytes. | IV | C (Au) | Infusion-related reactions, infection, neutropenia, reduced immunoglobulin levels, arrhythmias, less commonly anaemia, thrombocytopenia, angina, myocardial infarction, heart failure and rarely haemolytic anaemia, aplastic anaemia, serum sickness, severe skin conditions, pulmonary infiltrates, pneumonitis, cranial neuropathy (vision or hearing loss) and progressive multifocal leucoencephalopathy. |
| Sirolimus | mTOR inhibitor, thereby reducing cytokine-induced lymphocyte proliferation. | PO | C (Au) | Neutropenia, hypokalaemia, interstitial lung disease, pericardial effusion, pleural effusion, less commonly pulmonary haemorrhage, nephrotic syndrome and rarely hepatotoxicity and lymphoedema. |
| PO = Oral. IV = Intravenous. IM = Intramuscular. SC = Subcutaneous. IT = Intrathecal. The preferred pregnancy category, above, is Australian, if available. If unavailable an American one is substituted. | ||||
Prognosis
The five-year survival rate for systemic scleroderma is about 85%, whereas the 10-year survival rate is just under 70%.[40] This varies according to the subtype; while localized scleroderma rarely results in death, the systemic form can, and the diffuse systemic form carries a worse prognosis than the limited form. The major scleroderma-related causes of death are: pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary fibrosis, and scleroderma renal crisis.[25] People with scleroderma are also at a heightened risk for contracting cancers (especially liver, lung, haematologic and bladder cancers) and, perhaps, cardiovascular disease.[41][42][43][44][45][46]
According to a study of an Australian cohort, between 1985 and 2015, the average life expectancy of a person with scleroderma increased from 66 years to 74 years (around 8 years less than the average Australian life expectancy of 82 years).[47]
Epidemiology
Scleroderma most commonly first presents between the ages of 20 and 50 years, although any age group can be affected.[10][25] Women are four to nine times more likely to develop scleroderma than men.[25]
This disease is found worldwide.[25] In the United States, prevalence is estimated at 240 per million and the annual incidence of scleroderma is 19 per million people.[25] Likewise in the United States, it is slightly more common in African Americans than in their white counterparts, Scleroderma occurs much more often in women than it does in men. Choctaw Native Americans are more likely than Americans of European descent to develop the type of scleroderma that affects internal organs.[25] In Germany, the prevalence is between 10 and 150 per million people, and the annual incidence is between 3 and 28 per million people.[40] In South Australia, the annual incidence is 23 per million people, and the prevalence 233 per million people.[48] Scleroderma is less common in the Asian population.[49]
Pregnancy
Scleroderma in pregnancy is a complex situation; it increases the risk to both mother and child.[50] Overall scleroderma is associated with reduced fetal weight for gestational age.[50] The treatment for scleroderma often includes known teratogens such as cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, mycophenolate, etc. and hence careful avoidance of such drugs during pregnancy is advised.[50] In these cases hydroxychloroquine and low-dose corticosteroids might be used for disease control.[50]
See also
- Congenital fascial dystrophy
References
- "Scleroderma". NORD (National Organization for Rare Disorders). 2007. Archived from the original on 8 September 2016. Retrieved 14 July 2017.
- "Scleroderma". GARD. 2017. Archived from the original on 25 January 2017. Retrieved 14 July 2017.
- Jameson, Larry (2018). Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine (20th ed.). McGraw Hill. p. Chapter 353.
- Barnes J, Mayes MD (March 2012). "Epidemiology of systemic sclerosis: incidence, prevalence, survival, risk factors, malignancy, and environmental triggers". Current Opinion in Rheumatology. 24 (2): 165–70. doi:10.1097/BOR.0b013e32834ff2e8. PMID 22269658.
- Greenblatt MB, Aliprantis AO (January 2013). "The immune pathogenesis of scleroderma: context is everything" (PDF). Current Rheumatology Reports. 15 (1): 297. doi:10.1007/s11926-012-0297-8. PMC 3539168. PMID 23288576. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-09-08.
- "Handout on Health: Scleroderma". NIAMS. August 2016. Archived from the original on 4 July 2017. Retrieved 15 July 2017.
- Unsal, Erbil (2006). Current Opinions in Pediatric Rheumatology. Nova Publishers. p. 302. ISBN 9781594548710. Archived from the original on 2017-09-06.
- Mackay, Ian R.; Rose, Noel R. (2006). The Autoimmune Diseases. Academic Press. p. 369. ISBN 9780080454740.
- Firestein, Gary S.; Kelley, William N.; Budd, Ralph C. (2012). Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 1366. ISBN 978-1437717389. Archived from the original on 2017-08-04.
- Hajj-ali, RA (June 2013). "Systemic Sclerosis". Merck Manual Professional. Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp. Archived from the original on 6 March 2014. Retrieved 5 March 2014.
- Jimenez, SA; Cronin, PM; Koenig, AS; O'Brien, MS; Castro, SV (15 February 2012). Varga, J; Talavera, F; Goldberg, E; Mechaber, AJ; Diamond, HS (eds.). "Scleroderma Clinical Presentation". Medscape Reference. WebMD. Archived from the original on 6 March 2014. Retrieved 5 March 2014.
- Longo, D; Fauci, A; Kasper, D; Hauser, S; Jameson, J; Loscalzo, J (2011). Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine (18th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Professional. ISBN 978-0-07174889-6.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Balbir-Gurman A, Braun-Moscovici Y (February 2012). "Scleroderma - new aspects in pathogenesis and treatment". Best Practice & Research. Clinical Rheumatology. 26 (1): 13–24. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2012.01.011. PMID 22424190.
- Dospinescu P, Jones GT, Basu N (March 2013). "Environmental risk factors in systemic sclerosis". Current Opinion in Rheumatology. 25 (2): 179–83. doi:10.1097/BOR.0b013e32835cfc2d. PMID 23287382.
- Marie I, Gehanno JF, Bubenheim M, Duval-Modeste AB, Joly P, Dominique S, Bravard P, Noël D, Cailleux AF, Weber J, Lagoutte P, Benichou J, Levesque H (February 2014). "Prospective study to evaluate the association between systemic sclerosis and occupational exposure and review of the literature". Autoimmunity Reviews. 13 (2): 151–6. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2013.10.002. PMID 24129037.
- Valančienė G, Jasaitienė D, Valiukevičienė S (2010). "Pathogenesis and treatment modalities of localized scleroderma" (PDF). Medicina. 46 (10): 649–56. doi:10.3390/medicina46100092. PMID 21393982. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2014-03-06.
- Katsumoto TR, Whitfield ML, Connolly MK (2011). "The pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis". Annual Review of Pathology. 6: 509–37. doi:10.1146/annurev-pathol-011110-130312. PMID 21090968.
- Liakouli V, Cipriani P, Marrelli A, Alvaro S, Ruscitti P, Giacomelli R (August 2011). "Angiogenic cytokines and growth factors in systemic sclerosis". Autoimmunity Reviews. 10 (10): 590–4. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2011.04.019. PMID 21549861.
- Cipriani P, Marrelli A, Liakouli V, Di Benedetto P, Giacomelli R (August 2011). "Cellular players in angiogenesis during the course of systemic sclerosis". Autoimmunity Reviews. 10 (10): 641–6. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2011.04.016. PMID 21549220.
- Bosello S, De Luca G, Tolusso B, Lama G, Angelucci C, Sica G, Ferraccioli G (August 2011). "B cells in systemic sclerosis: a possible target for therapy". Autoimmunity Reviews. 10 (10): 624–30. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2011.04.013. PMID 21545850.
- Hunzelmann N, Krieg T (May 2010). "Scleroderma: from pathophysiology to novel therapeutic approaches". Experimental Dermatology. 19 (5): 393–400. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0625.2010.01082.x. PMID 20507361.
- Leask A (June 2011). "The role of endothelin-1 signaling in the fibrosis observed in systemic sclerosis". Pharmacological Research. 63 (6): 502–3. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2011.01.011. PMID 21315153.
- Arnson Y, Amital H, Agmon-Levin N, Alon D, Sánchez-Castañón M, López-Hoyos M, Matucci-Cerinic M, Szücs G, Shapira Y, Szekanecz Z, Shoenfeld Y (June 2011). "Serum 25-OH vitamin D concentrations are linked with various clinical aspects in patients with systemic sclerosis: a retrospective cohort study and review of the literature". Autoimmunity Reviews. 10 (8): 490–4. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2011.02.002. PMID 21320645.
- Jimenez, SA; Cronin, PM; Koenig, AS; O'Brien, MS; Castro, SV (15 February 2012). Varga, J; Talavera, F; Goldberg, E; Mechaber, AJ; Diamond, HS (eds.). "Scleroderma Workup". Medscape Reference. WebMD. Archived from the original on 6 March 2014. Retrieved 6 March 2014.
- Jimenez, SA; Cronin, PM; Koenig, AS; O'Brien, MS; Castro, SV (15 February 2012). Varga, J; Talavera, F; Goldberg, E; Mechaber, AJ; Diamond, HS (eds.). "Scleroderma". Medscape Reference. WebMD. Archived from the original on 6 March 2014. Retrieved 5 March 2014.
- Jimenez, SA; Cronin, PM; Koenig, AS; O'Brien, MS; Castro, SV (15 February 2012). Varga, J; Talavera, F; Goldberg, E; Mechaber, AJ; Diamond, HS (eds.). "Scleroderma Differential Diagnoses". Medscape Reference. WebMD. Archived from the original on 6 March 2014. Retrieved 6 March 2014.
- Elston, William D. James, Timothy G. Berger, Dirk M. (2006). Andrew's diseases of the skin: clinical dermatology (10 ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier. pp. 169–172. ISBN 978-0808923510.
- Walker KM, Pope J (August 2012). "Treatment of systemic sclerosis complications: what to use when first-line treatment fails--a consensus of systemic sclerosis experts". Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism. 42 (1): 42–55. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2012.01.003. PMID 22464314.
- Fett N (July–August 2013). "Scleroderma: nomenclature, etiology, pathogenesis, prognosis, and treatments: facts and controversies". Clinics in Dermatology. 31 (4): 432–437. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2013.01.010. PMID 23806160.
- Shah AA, Wigley FM (April 2013). "My approach to the treatment of scleroderma". Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 88 (4): 377–93. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2013.01.018. PMC 3666163. PMID 23541012.
- Kowal-Bielecka O, Bielecki M, Kowal K (2013). "Recent advances in the diagnosis and treatment of systemic sclerosis" (PDF). Polskie Archiwum Medycyny Wewnetrznej. 123 (1–2): 51–8. PMID 23344666. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2014-03-06.
- Beyer C, Dees C, Distler JH (January 2013). "Morphogen pathways as molecular targets for the treatment of fibrosis in systemic sclerosis". Archives of Dermatological Research. 305 (1): 1–8. doi:10.1007/s00403-012-1304-7. PMID 23208311.
- Leask A (June 2012). "Emerging targets for the treatment of scleroderma". Expert Opinion on Emerging Drugs. 17 (2): 173–9. doi:10.1517/14728214.2012.678833. PMID 22533795.
- Manno R, Boin F (November 2010). "Immunotherapy of systemic sclerosis" (PDF). Immunotherapy. 2 (6): 863–78. doi:10.2217/imt.10.69. PMC 3059511. PMID 21091117. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-09-08.
- Postlethwaite AE, Harris LJ, Raza SH, Kodura S, Akhigbe T (April 2010). "Pharmacotherapy of systemic sclerosis" (PDF). Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy. 11 (5): 789–806. doi:10.1517/14656561003592177. PMC 2837533. PMID 20210685. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-09-08.
- Ong VH, Denton CP (May 2010). "Innovative therapies for systemic sclerosis". Current Opinion in Rheumatology. 22 (3): 264–72. doi:10.1097/BOR.0b013e328337c3d6. PMID 20190640.
- Rossi, S, ed. (2013). Australian Medicines Handbook (2013 ed.). Adelaide: The Australian Medicines Handbook Unit Trust. ISBN 978-0-9805790-9-3.
- Brunton, L; Chabner, B; Knollman, B (2010). Goodman and Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics (12th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Professional. ISBN 978-0-07-162442-8.
- "Medscape Multispecialty – Home page". WebMD. Archived from the original on 13 November 2013. Retrieved 27 November 2013.
- Sticherling M (October 2012). "Systemic sclerosis-dermatological aspects. Part 1: Pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical findings". Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft. 10 (10): 705–18, quiz 716. doi:10.1111/j.1610-0387.2012.07999.x. PMID 22913330.
- Alenghat FJ (February 2016). "The Prevalence of Atherosclerosis in Those with Inflammatory Connective Tissue Disease by Race, Age, and Traditional Risk Factors". Scientific Reports. 6: 20303. Bibcode:2016NatSR...620303A. doi:10.1038/srep20303. PMC 4740809. PMID 26842423.
- Ngian GS, Sahhar J, Wicks IP, Van Doornum S (August 2011). "Cardiovascular disease in systemic sclerosis--an emerging association?" (PDF). Arthritis Research & Therapy. 13 (4): 237. doi:10.1186/ar3445. PMC 3239376. PMID 21888685. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-09-08.
- Szekanecz É, Szamosi S, Horváth Á, Németh Á, Juhász B, Szántó J, Szücs G, Szekanecz Z (October 2012). "Malignancies associated with systemic sclerosis". Autoimmunity Reviews. 11 (12): 852–5. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2012.02.021. PMID 22410174.
- Shah AA, Rosen A (November 2011). "Cancer and systemic sclerosis: novel insights into pathogenesis and clinical implications" (PDF). Current Opinion in Rheumatology. 23 (6): 530–5. doi:10.1097/BOR.0b013e32834a5081. PMC 3373179. PMID 21825998. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-09-08.
- Onishi A, Sugiyama D, Kumagai S, Morinobu A (July 2013). "Cancer incidence in systemic sclerosis: meta-analysis of population-based cohort studies". Arthritis and Rheumatism. 65 (7): 1913–21. doi:10.1002/art.37969. PMID 23576072.
- Bonifazi M, Tramacere I, Pomponio G, Gabrielli B, Avvedimento EV, La Vecchia C, Negri E, Gabrielli A (January 2013). "Systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) and cancer risk: systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies" (PDF). Rheumatology. 52 (1): 143–54. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kes303. PMID 23175568. Archived (PDF) from the original on 23 September 2016.
- Kennedy N, Walker J, Hakendorf P, Roberts-Thomson P (23 March 2018). "Improving life expectancy of patients with scleroderma: results from the South Australian Scleroderma Register". 48 (8). doi:10.1111/imj.13799. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Nikpour M, Stevens WM, Herrick AL, Proudman SM (December 2010). "Epidemiology of systemic sclerosis". Best Practice & Research. Clinical Rheumatology. 24 (6): 857–69. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2010.10.007. PMID 21665131.
- Gelber AC, Manno RL, Shah AA, Woods A, Le EN, Boin F, Hummers LK, Wigley FM (July 2013). "Race and association with disease manifestations and mortality in scleroderma: a 20-year experience at the Johns Hopkins Scleroderma Center and review of the literature". Medicine. 92 (4): 191–205. doi:10.1097/MD.0b013e31829be125. PMC 4553970. PMID 23793108.
- Lidar M, Langevitz P (May 2012). "Pregnancy issues in scleroderma". Autoimmunity Reviews. 11 (6–7): A515–9. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2011.11.021. PMID 22155199.
External links
- Handout on Health: Scleroderma—US National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |