Tinea faciei
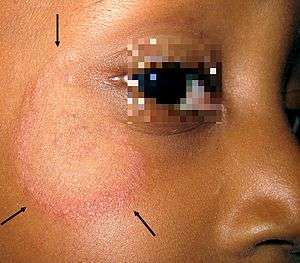
Tinea faciei is a fungal infection of the face.[1]:301[2] It generally appears as a red rash on the face, followed by patches of small, raised bumps. The skin may peel while it is being treated.
| Tinea faciei | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Ringworm of the face |
 | |
| Tinea faciei | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
| Symptoms | Facial ringworm appears as one or more pink-to-red scaly patches which contain bumps, blisters, or scabs.They can be itchy, and it may get worse or feel sunburned after exposure to the sun. |
| Treatment | topical creams and lotions:Terbinafine , Clotrimazole, Miconazole, Econazole, Oxiconazole, Ketoconazole, Sulconazole, Naftifine |
Tinea faciei is contagious just by touch and can spread easily to all regions of skin.
Treatment
Most infections can be treated with topical antifungal medication. Rarely, more extensive or long-standing infections may require treatment with oral antifungals
The ringworm should go away within 4–6 weeks after using effective treatment.
gollark: Technically, if I do it, it's not gollark impersonation.
gollark: Depends how you look at them.
gollark: Well, between -infinity and +infinity (inclusive).
gollark: They're actually also mostly Turing oracles.
gollark: But this way I get to make some sort of Maxwell's angels pun.
See also
- Tinea corporis
- Antifungal drug
- List of cutaneous conditions
References
- James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. p. 1135. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.