Interstitial lung disease
Interstitial lung disease (ILD), or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD),[3] is a group of lung diseases affecting the interstitium (the tissue and space around the alveoli (air sacs of the lungs).[4] It concerns alveolar epithelium, pulmonary capillary endothelium, basement membrane, and perivascular and perilymphatic tissues. It may occur when an injury to the lungs triggers an abnormal healing response. Ordinarily, the body generates just the right amount of tissue to repair damage, but in interstitial lung disease, the repair process goes awry and the tissue around the air sacs (alveoli) becomes scarred and thickened. This makes it more difficult for oxygen to pass into the bloodstream. The average rate of survival for someone with this disease is between three and five years.[5] The term ILD is used to distinguish these diseases from obstructive airways diseases.
| Interstitial lung disease | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD) |
.jpg) | |
| End-stage pulmonary fibrosis of unknown origin, taken from an autopsy | |
| Specialty | Pulmonology |
| Frequency | 1.9 million (2015)[1] |
| Deaths | 122,000 (2015)[2] |
There are specific types in children. The acronym chILD is used for this group of diseases and is derived from the English name, Children's Interstitial Lung Diseases – chILD.[6]
Prolonged ILD may result in pulmonary fibrosis, but this is not always the case. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is interstitial lung disease for which no obvious cause can be identified (idiopathic) and is associated with typical findings both radiographic (basal and pleural-based fibrosis with honeycombing) and pathologic (temporally and spatially heterogeneous fibrosis, histopathologic honeycombing, and fibroblastic foci).
In 2015, interstitial lung disease, together with pulmonary sarcoidosis, affected 1.9 million people.[1] They resulted in 122,000 deaths.[2]
Causes
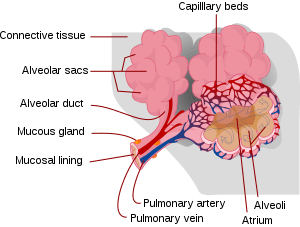
ILD may be classified according to the cause.[7] One way to classify the ILDs is whether the cause is known or not, as follows:
Idiopathic
Idiopathic interstitial pneumonia is the term given to ILDs with an unknown cause. They represent the majority of cases of interstitial lung diseases (up to two-thirds of cases).[8] They were subclassified by the American Thoracic Society in 2002 into 7 subgroups:
- Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF): the most common subgroup
- Desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP)
- Acute interstitial pneumonia (AIP): also known as Hamman-Rich syndrome
- Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP)
- Respiratory bronchiolitis-associated interstitial lung disease (RB-ILD)
- Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP): also known as Bronchiolitis Obliterans Organizing Pneumonia (BOOP)
- Lymphoid interstitial pneumonia (LIP)
Secondary
Secondary ILDs are those diseases with a known etiology, including:
- Connective tissue and Autoimmune diseases
- Sarcoidosis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Systemic sclerosis
- Polymyositis
- Dermatomyositis
- Antisynthetase syndrome
- Inhaled substances
- Inorganic
- Silicosis
- Asbestosis
- Berylliosis
- Industrial printing chemicals (e.g. carbon black, ink mist)
- Organic
- Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (Extrinisic allergic alveolitis)
- Inorganic
- Drug-induced
- Antibiotics
- Chemotherapeutic drugs
- Antiarrhythmic agents
- Infection
- Coronavirus disease 2019[9]
- Atypical pneumonia
- Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP)
- Tuberculosis
- Chlamydia trachomatis
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus
- Malignancy
- Predominately in children
- Diffuse developmental disorders
- Growth abnormalities deficient alveolarisation
- Infant conditions of undefined cause
- ILD related to alveolar surfactant region
Diagnosis
Investigation is tailored towards the symptoms and signs. A proper and detailed history looking for the occupational exposures, and for signs of conditions listed above is the first and probably the most important part of the workup in patients with interstitial lung disease. Pulmonary function tests usually show a restrictive defect with decreased diffusion capacity (DLCO).
A lung biopsy is required if the clinical history and imaging are not clearly suggestive of a specific diagnosis or malignancy cannot otherwise be ruled out. In cases where a lung biopsy is indicated, a trans-bronchial biopsy is usually unhelpful, and a surgical lung biopsy is often required.
X-rays
Chest radiography is usually the first test to detect interstitial lung diseases, but the chest radiograph can be normal in up to 10% of patients, especially early on the disease process.[10][11]
High resolution CT of the chest is the preferred modality, and differs from routine CT of the chest. Conventional (regular) CT chest examines 7–10 mm slices obtained at 10 mm intervals; high resolution CT examines 1–1.5 mm slices at 10 mm intervals using a high spatial frequency reconstruction algorithm. The HRCT therefore provides approximately 10 times more resolution than the conventional CT chest, allowing the HRCT to elicit details that cannot otherwise be visualized.[10][12]
Radiologic appearance alone however is not adequate and should be interpreted in the clinical context, keeping in mind the temporal profile of the disease process.[10]
Interstitial lung diseases can be classified according to radiologic patterns.[10]
Pattern of opacities
- Consolidation
Acute: Alveolar hemorrhage syndromes, acute eosinophilic pneumonia, acute interstitial pneumonia, cryptogenic organizing pneumonia
Chronic: Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia, cryptogenic organizing pneumonia, lymphoproliferative disorders, pulmonary alveolar proteinosis, sarcoidosis
- Linear or reticular opacities
Acute: Pulmonary edema
Chronic: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, connective tissue associated interstitial lung diseases, asbestosis, sarcoidosis, hypersensitivity pneumonitis, drug-induced lung disease
- Small nodules
Acute: Hypersensitivity pneumonitis
Chronic: Hypersensitivity pneumonitis, sarcoidosis, silicosis, coal workers pneumoconiosis, respiratory bronchiolitis, alveolar microlithiasis
- Cystic airspaces
Chronic: Pulmonary langerhans cell histiocytosis, pulmonary lymphangioleiomyomatosis, honeycomb lung caused by IPF or other diseases
Ground glass opacities
Acute: Alveolar hemorrhage syndromes, pulmonary edema, hypersensitivity pneumonitis, acute inhalational exposures, drug-induced lung diseases, acute interstitial pneumonia
Chronic: Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia, respiratory bronchiolitis associated interstitial lung disease, desquamative interstitial pneumonia, drug-induced lung diseases, pulmonary alveolar proteinosis
- Thickened alveolar septa
Acute: Pulmonary edema
Chronic: Lymphangitic carcinomatosis, pulmonary alveolar proteinosis, sarcoidosis, pulmonary veno occlusive disease[10]
Distribution
- Upper lung predominance
Pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis, silicosis, coal workers pneumoconiosis, carmustine related pulmonary fibrosis, respiratory broncholitis associated with interstitial lung disease.
- Lower lung predominance
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary fibrosis associated with connective tissue diseases, asbestosis, chronic aspiration
- Central predominance (perihilar)
Sarcoidosis, berylliosis
- Peripheral predominance
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, chronic eosinophilic pneumonia, cryptogenic organizing pneumonia[10]
Associated findings
- Pleural effusion or thickening
Pulmonary edema, connective tissue diseases, asbestosis, lymphangitic carcinomatosis, lymphoma, lymphangioleiomyomatosis, drug-induced lung diseases
- Lymphadenopathy
Sarcoidosis, silicosis, berylliosis, lymphangitic carcinomatosis, lymphoma, lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia[10]
Genetic testing
For some types of paediatric ILDs and few forms adult ILDs, genetic causes have been identified. These may be identified by blood tests. For a limited number of cases this is a definite advantage, as a precise molecular diagnosis can be done; frequently then there is no need for a lung biopsy. Testing is available for
ILDs related to alveolar surfactant region
Surfactant-Protein-B Deficiency (Mutations in SFTPB)
Surfactant-Protein-C Deficiency (Mutations in SFTPC)
ABCA3-Deficiency (Mutations in ABCA3)
Brain Lung Thyroid Syndrome (Mutations in TTF1)
Congenital Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis (Mutations in CSFR2A, CSFR2B)
Diffuse developmental disorder
Alveolar Capillary Dysplasia (Mutations in FoxF1)
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Mutations in telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT)
Mutations in telomerase RNA component (TERC)
Mutations in the regulator of telomere elongation helicase 1 (RTEL1)
Mutations in poly(A)-specific ribonuclease (PARN)
Treatment
ILD is not a single disease, but encompasses many different pathological processes. Hence treatment is different for each disease.
If a specific occupational exposure cause is found, the person should avoid that environment. If a drug cause is suspected, that drug should be discontinued.
Many cases due to unknown or connective tissue-based causes are treated with corticosteroids,[13] such as prednisolone. Some people respond to immunosuppressant treatment. Oxygen therapy at home is recommended in those with significantly low oxygen levels.[14]
Pulmonary rehabilitation appears to be useful.[15] Lung transplantation is an option if the ILD progresses despite therapy in appropriately selected patients with no other contraindications.[16][17]
On October 16, 2014, the Food and Drug Administration approved a new drug for the treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF). This drug, Ofev (nintedanib), is marketed by Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. This drug has been shown to slow the decline of lung function although the drug has not been shown to reduce mortality or improve lung function. The estimated cost of the drug per year is approximately $94,000.[18]
References
- GBD 2015 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence, Collaborators. (8 October 2016). "Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015". Lancet. 388 (10053): 1545–1602. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6. PMC 5055577. PMID 27733282.
- GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death, Collaborators. (8 October 2016). "Global, regional, and national life expectancy, all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of death, 1980–2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015". Lancet. 388 (10053): 1459–1544. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31012-1. PMC 5388903. PMID 27733281.
- King TE (August 2005). "Clinical advances in the diagnosis and therapy of the interstitial lung diseases". American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 172 (3): 268–79. doi:10.1164/rccm.200503-483OE. PMID 15879420.
- "Frequently Asked Questions About Interstitial Lung Disease". University of Chicago Medical Center.
- Meyer, Keith C; Decker, Catherine A (2017-04-03). "Role of pirfenidone in the management of pulmonary fibrosis". Therapeutics and Clinical Risk Management. 13: 427–437. doi:10.2147/TCRM.S81141. ISSN 1176-6336. PMC 5388201. PMID 28435277.
- Bush A, Cunningham S, de Blic J, Barbato A, Clement A, Epaud R, Hengst M, Kiper N, Nicholson AG, Wetzke M, Snijders D, Schwerk N, Griese M (November 2015). "European protocols for the diagnosis and initial treatment of interstitial lung disease in children". review. Thorax. 70 (11): 1078–84. doi:10.1136/thoraxjnl-2015-207349. PMID 26135832.
- Bourke SJ (August 2006). "Interstitial lung disease: progress and problems". Postgraduate Medical Journal. 82 (970): 494–9. doi:10.1136/pgmj.2006.046417. PMC 2585700. PMID 16891438.
- Kreuter, Michael; Herth, Felix J. F.; Wacker, Margarethe; Leidl, Reiner; Hellmann, Andreas; Pfeifer, Michael; Behr, Jürgen; Witt, Sabine; Kauschka, Dagmar (2015). "Exploring Clinical and Epidemiological Characteristics of Interstitial Lung Diseases: Rationale, Aims, and Design of a Nationwide Prospective Registry—The EXCITING-ILD Registry". BioMed Research International. 2015: 123876. doi:10.1155/2015/123876. PMC 4657073. PMID 26640781.
- "Dr. Daniele Macchini, Treating COVID-19 Patients in Bergamo, Italy, Describes Horrible Situation". 11 March 2020.
- Ryu JH, Olson EJ, Midthun DE, Swensen SJ (November 2002). "Diagnostic approach to the patient with diffuse lung disease". Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 77 (11): 1221–7, quiz 1227. doi:10.4065/77.11.1221. PMID 12440558.
- "What Is Pulmonary Fibrosis?". Northwestern Medicine. Archived from the original on 2014-02-26. Retrieved 2014-02-22.
- Zare Mehrjardi M, Kahkouee S, Pourabdollah M (March 2017). "Radio-pathological correlation of organizing pneumonia (OP): a pictorial review". The British Journal of Radiology. 90 (1071): 20160723. doi:10.1259/bjr.20160723. PMC 5601538. PMID 28106480.
- "Interstitial lung disease: Treatments and drugs". MayoClinic.com.
- Hayes D, Jr; Wilson, KC; Krivchenia, K; Hawkins, SMM; Balfour-Lynn, IM; Gozal, D; Panitch, HB; Splaingard, ML; Rhein, LM; Kurland, G; Abman, SH; Hoffman, TM; Carroll, CL; Cataletto, ME; Tumin, D; Oren, E; Martin, RJ; Baker, J; Porta, GR; Kaley, D; Gettys, A; Deterding, RR (1 February 2019). "Home Oxygen Therapy for Children. An Official American Thoracic Society Clinical Practice Guideline". American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 199 (3): e5–e23. doi:10.1164/rccm.201812-2276ST. PMC 6802853. PMID 30707039.
- Dowman L, Hill CJ, Holland AE (October 2014). "Pulmonary rehabilitation for interstitial lung disease". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 10 (10): CD006322. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006322.pub3. PMID 25284270.
- Kotloff RM, Thabut G (July 2011). "Lung transplantation". American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 184 (2): 159–71. doi:10.1164/rccm.201101-0134CI. PMID 21471083.
- Whelan TP (March 2012). "Lung transplantation for interstitial lung disease". Clinics in Chest Medicine. 33 (1): 179–89. doi:10.1016/j.ccm.2011.12.003. PMID 22365254.
- "FDA approves Ofev to treat idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Archived from the original on 17 October 2014.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |