Santhal Pargana division
Santhal Pargana division constitutes one of the five district administration units known as the divisions of Jharkhand state in eastern India.
Origin of name
Santhal Pargana derives its name from two words: "Santhal", a major tribe of India and Pargana, a unit of administration used mostly by Medieval rulers.
Location
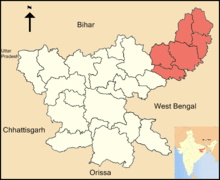
Santhal Pargana is one of the divisions of Jharkhand. Its headquarters is at Dumka. Presently, this administrative division comprises six districts: Godda, Deoghar, Dumka, Jamtara, Sahibganj and Pakur.
History
This region is mentioned as Kajangala in different ancient literatures specially in Buddhist literatures. It is mentioned that the Chinese monk-traveller Xuanzang (Hiuen Tsang) travelled from Champa (recent Bhagalpur) to Kajangala and then proceeded to Pundravardhana(recent Bangladesh) in the 7th century AD. He says that the northern limit of its territory (means Sahebganj) was not very far from the Ganges. The forests to the south had plenty of elephants. The people were straight forward, talented and devoted to education.[1]
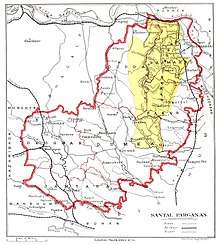
In the system of Permanent Settlement, British encourage paharia of Rajmahal hills to practice settle agriculture but they refused to cut the tree. Then British officials attracted attention to Santals, they were ready to clear the forest for practice of settle agriculture. In 1932, a large number of area demarcated as Damin-i-koh or Santal Pargana. The land was declared as the land of Santal. Santal from Cuttack, Dhalbhum, Birbhum, Manbhum, Hazaribagh migrated and started cultivating these lands as peasants. British collected tax from Santals as revenue. The imposition of taxs, exploitation by Zamindar and money lenders sparked Santal rebellion. The Sidhu and Kanhu Murmu, two brothers led the Santals against the Britishers but were defeated.[2][3][4][5][6]

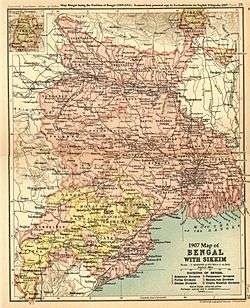
Formerly, Santhal Parganas comprised a district of the same name, in undivided Bihar state, India. Earlier to that, in 1855, during British India, Santhal Parganas was created as a district, and was a part of the Bengal Presidency.
Languages
Languages in Santal Parganas 2011 census
References
- Roy, Niharranjan, Bangalir Itihas, Adi Parba, (in Bengali), first published 1972, reprint 2005, pp. 99-100, 81-93, Dey’s Publishing, 13 Bankim Chatterjee Street, Kolkata, ISBN 81-7079-270-3
- Jha, Amar Nath (2009). "LOCATING THE ANCIENT HISTORY OF SANTAL PARGANAS". Proceedings of the Indian History Congress. 70: 185–196. ISSN 2249-1937. JSTOR 44147668.
- This is Our Homeland: A Collection of Essays on the Betrayal of Adivasi. books.google.com. Retrieved 26 August 2019.
- History of India. books.google.com. Retrieved 26 August 2019.
- http://sahibganj.nic.in/en/History.html
- http://wesanthals.tripod.com/id50.html