Norn language
Norn is an extinct North Germanic language that was spoken in the Northern Isles (Orkney and Shetland) off the north coast of mainland Scotland and in Caithness in the far north of the Scottish mainland. After Orkney and Shetland were pledged to Scotland by Norway in 1468–69, it was gradually replaced by Scots. Norn is thought to have become extinct in 1850, after the death of Walter Sutherland, the language's last known speaker.
| Norn | |
|---|---|
| norn | |
| Native to | Scotland |
| Region | Northern Isles and Caithness |
| Extinct | 1850, with the death of Walter Sutherland |
Indo-European
| |
Early forms | Old Norse
|
| |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | nrn |
nrn | |
| Glottolog | oldn1246[4] |
| Linguasphere | 52-AAA-ac |
 | |
History
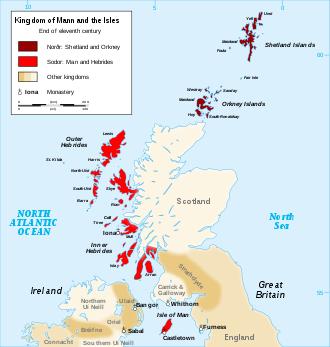
Norse settlement in the islands probably began in the early 9th century.[5] These settlers are believed to have arrived in very substantial numbers and like those who migrated to Iceland and the Faroe Islands it is probable that most came from the west coast of Norway.[6] Shetland toponymy bears some resemblance to that of northwest Norway, while Norn vocabulary implies links with more southerly Norwegian regions.[7]
Orkney and Shetland were pledged to James III in 1468 and 1469 respectively, and it is with these pledges that the replacement of Norn with Scots is most associated. However, the decline of Norse speech in Orkney probably began in 1379 when the earldom passed into the hands of the Sinclairs, and Scots had superseded Norse as the language of prestige on the island by the early 15th century.[8]
In Shetland, the transition began later, but by the end of the 15th century both island groups were bilingual.[9] Despite this, the process by which Scots overtook Norn as the primary spoken language on the islands was not a swift one,[10] and most natives of Orkney and Shetland probably spoke Norn as a first language until the late 16th and early-to-mid 17th centuries respectively.[11] One of the last documents written in Norn was for a 1597 mortgage issued over a property belonging to Else, sister of Anna Throndsen, who had married a Shetland man Andrew Mowat of Heogoland in Eshaness.[12]
Extinction
It is not known exactly when Norn became extinct. Sources from the 17th and 18th centuries speak of Norn (sometimes identified as "Norse", "Norwegian" or "Danish") as being in a state of decline and generally indicate that the language remained stronger in Shetland than in Orkney. A source from 1670 states that there are "only three or four parishes" in Orkney where people speak "Noords or rude Danish" and that they do so "chiefly when they are at their own houses".[13] Another from 1701 indicates that there were still a few monoglot "Norse" speakers who were capable of speaking "no other thing," and notes that there were more speakers of the language in Shetland than in Orkney.[13] It was said in 1703 that the people of Shetland generally spoke a Lowland Scots dialect brought to Shetland from the end of the fifteenth century by settlers from Fife and Lothian, but that "many among them retain the ancient Danish Language";[14] while in 1750 Orkney-born James Mackenzie wrote that Norn was not yet entirely extinct, being "retained by old people," who still spoke it among each other.[15]
The last reports of Norn speakers are claimed to be from the 19th century, with some claims of a very limited use up until the early 20th century, but it is more likely that the language was dying out in the late 18th century.[16] The isolated islands of Foula and Unst are variously claimed as the last refuges of the language in Shetland, where there were people "who could repeat sentences in Norn",[17] probably passages from folk songs or poems, as late as 1893. Walter Sutherland from Skaw in Unst, who died about 1850, has been cited as the last native speaker of the Norn language. However, fragments of vocabulary survived the death of the main language and remain to this day, mainly in place-names and terms referring to plants, animals, weather, mood, and fishing vocabulary.
Norn had also been a spoken language in Caithness but had probably become extinct there by the 15th century, replaced by Scots.[10] Hence, some scholars also speak about "Caithness Norn", but others avoid this. Even less is known about "Caithness Norn" than about Orkney and Shetland Norn. Almost no written Norn has survived, but what little remains includes a version of the Lord's Prayer and a ballad, "Hildina". Michael P Barnes, professor of Scandinavian Studies at University College London, has published a study, The Norn Language of Orkney and Shetland.[18]
Classification
Norn is an Indo-European language belonging to the North Germanic branch of the Germanic languages. Together with Faroese, Icelandic and Norwegian, it belongs to the West Scandinavian group, separating it from the East Scandinavian group consisting of Swedish, Danish and Gutnish.
While this classification is based on the differences between the North Germanic languages at the time they split, their present-day characteristics justify another classification, dividing them into Insular Scandinavian and Mainland Scandinavian language groups based on mutual intelligibility. Under this system, Norwegian is grouped together with Danish and Swedish because the last millennium has seen all three undergo important changes, especially in grammar and lexis, which have set them apart from Faroese and Icelandic.
Norn is generally considered to have been fairly similar to Faroese, sharing many phonological and grammatical traits, and might even have been mutually intelligible with it. Thus, it can be considered an Insular Scandinavian language.
Few written texts remain. It is distinct from the present-day Shetland dialect, which evolved from Middle English.
Phonology
The phonology of Norn can never be determined with much precision because of the lack of source material, but the general aspects can be extrapolated from the few written sources that exist. Norn shared many traits with the dialects of southwest Norway. That includes a voicing of /p, t, k/ to [b, d, ɡ] after vowels and (in the Shetland dialect but only partially in the Orkney dialect) a conversion of /θ/ and /ð/ ("thing" and "that" respectively) to [t] and [d] respectively.
Morphology
Norn grammar had features very similar to the other Scandinavian languages. There were two numbers, three genders and four cases (nominative, accusative, genitive and dative). The two main conjugations of verbs in present and past tense were also present. Like all other North Germanic languages, it used a suffix instead of a prepositioned article to indicate definiteness as in modern Scandinavian: man(n) ("man"); mannen ("the man"). Though it is difficult to be certain of many of the aspects of Norn grammar, documents indicate that it may have featured subjectless clauses, which were common in the West Scandinavian languages.
Sample text
.jpg)
The following are Norn and Old Norse versions of the Lord's Prayer:[19]
- Orkney Norn:
- Fa vor i ir i chimrie, / Helleur ir i nam thite,
- gilla cosdum thite cumma, / veya thine mota vara gort
- o yurn sinna gort i chimrie, / ga vus da on da dalight brow vora
- Firgive vus sinna vora / sin vee Firgive sindara mutha vus,
- lyv vus ye i tumtation, / min delivera vus fro olt ilt.
- Amen.
- Shetland Norn:
- Fy vor or er i Chimeri. / Halaght vara nam dit.
- La Konungdum din cumma. / La vill din vera guerde
- i vrildin sindaeri chimeri. / Gav vus dagh u dagloght brau.
- Forgive sindorwara / sin vi forgiva gem ao sinda gainst wus.
- Lia wus ikè o vera tempa, / but delivra wus fro adlu idlu.
- [For do i ir Kongungdum, u puri, u glori.] Amen.
- Old West Norse:
- Faþer vár es ert í himenríki, / verði nafn þitt hæilagt
- Til kome ríke þitt, / værði vili þin
- sva a iarðu sem í himnum. / Gef oss í dag brauð vort dagligt
- Ok fyr gefþu oss synþer órar, / sem vér fyr gefom þeim er viþ oss hafa misgert
- Leiðd oss eigi í freistni, / heldr leys þv oss frá ollu illu.
- Amen.
- Faðir vár, tú sum ert í himlinum. / Heilagt verði navnið títt.
- Komi ríkið títt. / Verði vilji tín,
- so sum á himli, so á jørð. / Gev okkum í dag okkara dagliga breyð.
- Fyrigev okkum syndir okkara, / so sum vit eisini fyrigeva teimum, ið móti okkum synda.
- Leið okkum ikki í freistingar, / men frels okkum frá tí illa.
- [Tí at títt er ríkið, valdið og heiðurin um aldur og allar ævir.] Amen.
- Faðir vor, þú sem ert á himnum. / Helgist þitt nafn,
- til komi þitt ríki, / verði þinn vilji,
- svo á jörðu sem á himni. / Gef oss í dag vort daglegt brauð.
- Fyrirgef oss vorar skuldir, / svo sem vér og fyrirgefum vorum skuldunautum.
- Og eigi leið þú oss í freistni, / heldur frelsa oss frá illu.
- [Því að þitt er ríkið, mátturinn og dýrðin að eilífu.] Amen.
- Fader vár, du som er i himmelen! / Lat namnet ditt helgast;
- lat riket ditt koma; / lat viljen din ráda pá jordi som i himmelen;
- gjev oss i dag várt daglege brød; / og forlat oss vár skuld, som me og forlet váre skuldmenn;
- og før oss ikkje ut i freisting; / men frels oss frå det vonde.
- For riket er ditt, og magti og æra i all æva! Amen
A Shetland "guddick" (riddle) in Norn, which Jakob Jakobsen heard told on Unst, the northernmost island in Shetland, in the 1890s. The same riddle is also known from the Faroe Islands, Norway, Iceland, and a variation also occurs in England.
Shetland Norn (Jakob Jakobsen)[20]
|
Faroese
|
Icelandic
|
Orcadian dialect of Scots (not Norn)[21]
|
English translation
|
Traditional version from England
|
The answer is a cow: four teats hang, four legs walk, two horns and two ears stand skyward, two eyes show the way to the field and one tail comes shaking (dangling) behind.
Modern use
Most of the use of Norn/Norse in modern-day Shetland and Orkney is purely ceremonial, and mostly in Old Norse, for example the Shetland motto, which is Með lögum skal land byggja ("with law shall land be built") which is the same motto used by the Icelandic police force and inspired by the old Norwegian Frostathing Law.
Another example of the use of Norse/Norn in the Northern Isles can be found in the names of ferries:
- NorthLink Ferries has ships named MV Hamnavoe (after the old name for Stromness), and MV Hjaltland (Shetland) and MV Hrossey ("Horse Island", an old name for Mainland, Orkney).
- The Yell Sound Ferry sails from Ulsta on the island to Toft on the Shetland Mainland. The service is operated by two ferries—Daggri (Norse for "dawn"), launched in 2003 and Dagalien (Norse for "dusk"), launched in 2004.[22]
Norn words are still used to describe many of the colour and pattern variations in the native sheep of Shetland and Orkney, which survive as the Shetland and North Ronaldsay breeds. Icelandic uses similar words for many of the same colour variations in Icelandic sheep.[23]
There are some enthusiasts who are engaged in developing and disseminating a modern form called Nynorn ("New Norn"), based upon linguistic analysis of the known records and Norse linguistics in general.[24]
See also
- Udal law, the Norse law system of the Northern Isles.
References
- "Shetland". Scotslanguage.com. Retrieved 2017-06-24.
- "Orkney". Scotslanguage.com. Retrieved 2017-06-24.
- "Insular". Scotslanguage.com. Retrieved 2017-06-24.
- Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Old Norn". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- Stenroos, Merja-Riitta et al. (2012). Language Contact and Development around the North Sea. John Benjamins Publishing Company. p. 218. ISBN 978-90-272-4839-8
- Trudgill, Peter (1984). Language in the British Isles. Cambridge University Press. p. 358. ISBN 978-0-521-28409-7
- Trudgill, Peter (1984). Language in the British Isles. Cambridge University Press. p. 361. ISBN 978-0-521-28409-7
- Trudgill, Peter (1984). Language in the British Isles. Cambridge University Press. p. 352. ISBN 978-0-521-28409-7
- Jones, Charles (1997). The Edinburgh History of the Scots Language . Edinburgh University Press. p. 62. ISBN 978-0-7486-0754-9
- Jones, Charles (1997). The Edinburgh History of the Scots Language. Edinburgh University Press. p. 394. ISBN 978-0-7486-0754-9
- Trudgill, Peter (1984). Language in the British Isles. Cambridge University Press. p. 354. ISBN 978-0-521-28409-7
- T. Manson, 'Shetland in the Sixteenth Century', in Renaissance and Reformation in Scotland (Edinburgh, 1983), p. 208.
- Millar, Robert McColl (2007). Northern and Insular Scots. Edinburgh University Press. p. 126. ISBN 978-0-7486-2317-4
- Martin, Martin; Monro, Donald (2018). A Description of the Western Isles: Circa 1695. Birlinn. ISBN 978-0-85790-288-7.
- Hoops, Johannes (2003). Reallexikon Der Germanischen Altertumskunde: Band 21. Walter De Gruyter Inc. p. 385. ISBN 978-3-11-017272-0
- Glanville Price, The Languages of Britain (London: Edward Arnold 1984, ISBN 978-0-7131-6452-7), p. 203
- Price (1984), p. 204
- Barnes, Michael P. The Norn Language of Orkney & Shetland. Lerwick: Shetland Times 1998. ISBN 1-898852-29-4
- "Pater Noster - M through N". Christusrex.org. Archived from the original on 2017-06-19. Retrieved 2017-06-24.
- The dialect and place names of Shetland; two popular lectures; by Jakob Jakobsen. 1897
- "The Orkney Norn Hugh Marwick 1926". Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - "The Fleet – New Yell Sound Ferries". Shetland Islands Council. Retrieved 2008-02-04.
- "1000 Years of Sheep in Shetland". Sheep-isle.dk. Retrieved 2017-06-24.
- "Norn". Retrieved 10 June 2011.
Further reading
- Barnes, Michael P. The study of Norn Northern Lights, Northern Words. Selected Papers from the FRLSU Conference, Kirkwall 2009.
- Barnes, Michael P. "Orkney and Shetland Norn". In Language in the British Isles, ed. Peter Trudgill, 352–66. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1984.
- Jakobsen, Jakob (1928–1932) [1921]. An etymological dictionary of the Norn language in Shetland (2 volumes.). Printed by S. L. Møller, Copenhagen. Foreword by Anna Horsböl, née Jakobsen. Originally published in Danish as Etymologisk ordbog over det norröne sprog på Shetland. Reprinted Lerwick: The Shetland Folk Society, 1985. (1st ed.). Shaftesbury Avenue, London: David Nutt (A. G. Berry). Retrieved 2020-03-30 – via archive.org.CS1 maint: date format (link)
- Low, George. A Tour through the Islands of Orkney and Schetland. Kirkwall: William Peace, 1879.
- Marwick, Hugh. The Orkney Norn. London: Oxford University Press, 1929.
- Rendboe, Laurits. "The Lord's Prayer in Orkney and Shetland Norn 1-2". North-Western European Language Evolution 14 (1989): 77-112 and 15 (1990): 49-111.
- Wallace, James. An Account of the Islands of Orkney. London: Jacob Tonson, 1700.
External links
| Norn language test of Wikipedia at Wikimedia Incubator |
| For a list of words relating to Norn language, see the Norn language category of words in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
- Orkney&Shetland Norn Collection of all known texts in Norn, description of its phonology and grammar
