National Council (Switzerland)
The National Council (German: Nationalrat, French: Conseil national, Italian: Consiglio nazionale, Romansh: Cussegl naziunal) is the lower house of the Federal Assembly of Switzerland, the upper house being the Council of States. With 200 seats, the National Council is the larger of the two houses.[1]
National Council | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Leadership | |
President | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 200 |
 | |
Political groups | Government parties (146)
Other parliamentary parties (54)
|
| Elections | |
| Party-list proportional representation Hagenbach-Bischoff system | |
Last election | 20 October 2019 |
Next election | 2023 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Federal Palace of Switzerland, Bern | |
| Website | |
| https://www.parlament.ch | |
Adult citizens elect the council's members, who are called National Councillors for four year terms. These members are apportioned to the Swiss cantons in proportion to their population.[1]
Both houses meet in the Federal Palace of Switzerland in Bern.[2]
Organization
With 200 members, the National Council is the larger house of the Swiss legislature.
When the Swiss federation was founded in 1848, the number of seats was not yet fixed, and was thus determined by the population of the individual cantons. According to the provisions of the federal constitution at that time, a canton was to receive one National Council member for every 20,000 citizens. Thus, the first National Council, which met in 1848, had 111 members.
In 1963, the number of members was fixed at 200. The division of the seats between the individual cantons is determined by each canton's percentage of the national population, as revealed in the national census (including foreign residents), using the largest remainder method. A change in the division of the seats occurred in 2003, as a result of the 2000 census.
Every canton is entitled to at least one seat in the National Council.
Electoral system
Under the Swiss Federal Constitution, elections for the National Council are held every four years by the Swiss people.[3] The most recent election took place on Sunday, 20 October 2019.
Since a popular initiative in 1918, elections have been by proportional representation, in which each canton forms an electoral district (Wahlkreis). There is no election threshold. Since 1971 women have been entitled to vote and stand in National Council elections.
Since the reform of the census system and the adoption of the use of government administrative data for determining the population in 2007, the distribution of the seats in the National Council between the cantons has been based on the permanent resident population (including residents who are not entitled to vote) in the year following the most recent federal election.[4] There is a proviso that each canton is entitled to at least one seat.
The number of seats given to the cantons which are entitled to more than one seat is determined using the largest remainder method. Cantons which are only entitled to send one councillor to the National Council elect the candidate who wins a majority of votes.
The cantons use a unique system of proportional representation, sometimes called a "free list". Each citizen may cast as many votes as there are seats available to their constituency, and may even cast up to two votes for the same candidate. For every vote received by a candidate, that candidate's party also receives a vote. Voters also list a party vote, in which all blank candidate votes contribute towards the party's total.
In elections, political parties publish lists in the cantons with their candidates. Each list contains at most the number of candidates which the canton is entitled to send to the National Council. Each voter is entitled to vote for as many candidates as their canton is entitled to send to the National Council; so an inhabitant of the Canton of Zurich can vote for 35 candidates, while an inhabitant of the Canton of Uri can only vote for one.
It is possible for one or more candidates to be listed twice. In addition, each party can produce multiple lists to the canton (e.g. men's, women's, youth, or seniors' lists; in larger cantons they might offer lists for individual cities or districts). It is also possible for several parties to enter a single shared list.
| Election results for the National Council, 2019[5] |
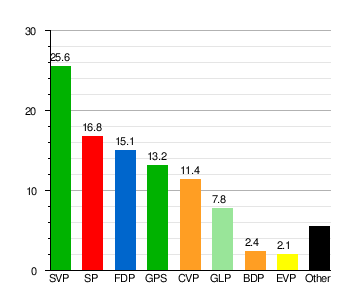 |
Voters are entitled to choose a pre-prepared party list without making changes or they can alter it by cumulative voting or panachage. Thus, the voter can give his vote to a specific candidate and ignore the rest of that candidate's party. Alternatively, it is possible for the voter to split his or her vote among several candidates from different parties.
The seats are then apportioned using the Hagenbach-Bischoff System. This system is unique in that it allows voters to split their vote across different parties, depending on which candidate the voter prefers.[6]
Fictional voter
To determine a party's strength, the notion of "fictional voter" was introduced and is defined by the Swiss Federal Statistical Institute as: number of votes obtained by party A * (number of valid ballots / number of valid votes). Individual voters can choose to make fewer than the permissible number of votes. The number of valid votes / number of valid ballots closely matches the number of deputies a canton needs to elect. More exactly, this number represents the average number of valid votes per voter. The formula can then be summed up by: number of votes obtained by party A / average of valid votes per voters.
The result is the number of fictional voters for a given party in a given canton. A total number of fictional voters can then be established and the party strength can be deduced.
The number of deputies in each party is determined at the cantonal level using proportional representation with the Hagenbach-Bischoff system (except in single-member cantons.) The election's turnout is computed as: number of valid ballots cast / number of registered voters.
Role


The role and powers of the National Council are regulated by the Bundesgesetz über die Bundesversammlung (Parlamentsgesetz) (The Federal Law on the Federal Parliament (Parliament-Law)) and the fifth article of the Swiss Federal Constitution. The National Council, together with the Council of States, forms the Federal Parliament and exercises the highest legal authority in Switzerland, subject to the rights of the people and the cantons.[7] Both chambers of the Federal Parliament are called "councils" (Räte). The National Council and the Council of States do not meet daily, but meet regularly for sessions.[8] Usually, there are four sessions in a year, each lasting three weeks, with between two and five sittings per week. The spring session (Frühjahrssession) begins on the first Monday in March, the summer session (Sommersession) on the first Monday in June, the Autumn session (Herbstsession) after the Federal Day, and the winter session (Wintersession) on the last Monday in November.[9] During the sessions, proposed legislation is debated. If there is not enough time in the regular sessions, an extra session can be convened.[10] In special situations (political crises, wars, etc.) a quarter of the members of one of the two councils or the Federal Council can convene an extraordinary session.[10] To date, there have been eight extraordinary sessions, most of them called by the social democratic parliamentary group.
| Date | Reason/event |
|---|---|
| July 1891 | Introduction of the federal currency monopoly |
| 6–7 February 1985 | Response to Forest dieback |
| 9–11 October 1986 | Energy policy after the Chernobyl disaster |
| 22–23 January 1998 | Tax loopholes and merger/economic policy (merger of UBS and SBV) |
| 16 November 2001 | Financing Swissair |
| 3 October 2002 | minimum interest rate («employment pension») |
| 1 October 2007 | Tax issues |
| 8 December 2008 | Financial crisis |
| 4–8 May 2020 | COVID-19 pandemic |
Powers
The National Council and the Council of States are constitutionally completely equal - a bill is only law when it has been accepted by both councils in the same version. All business is considered by both councils in turn. The presidents of the councils decide together which council will handle a given matter first (Erstrat)
Sometimes, after the first reading, the National Council and the Council of States end up producing different texts, in which case a difference resolution procedure takes place, in which the bill is sent back and forth between the two councils. After a bill has been sent back three successive times, the two councils must meet together to discuss the matter.
Each year the National Council elects a President of the National Council, who leads sessions of the National Council and joint sessions of the National Council and the Council of States. This office is distinct from and ranks lower than the President of the Swiss Confederation.
Committees
- Foreign Affairs Committee (FAC)
- Committee for Science, Education and Culture (CSEC)
- Committee for Social Security and Health (CSSH)
- Committee for the Environment, Spatial Planning and Energy (CESPE)
- Defence Committee (DefC)
- Committee for Transportation and Telecommunications (CTT)
- Committee for Economic Affairs and Taxation (CEAT)
- Political Institutions Committees (PIC)
- Committee for Legal Affairs (CLA)
- Committee for Public Buildings (CPB)
Supervisory committees
- Finance Committee (FC)
- Control Committees (CC)
- Parliamentary investigation committees (PIC)
Other committees
- Committee on Pardons
- Rehabilitation Committee
- Drafting Committee
- Judicial Committee
Members per canton
| Abbr | Canton | Number of Seats | Population (2009) | Population per seat |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZH | 35 | 1,406,083 | 40,174 | |
| BE | 25 | 985,046 | 39,402 | |
| LU | 10 | 381,966 | 38,197 | |
| UR | 1 | 35,382 | 35,382 | |
| SZ | 4 | 147,904 | 36,976 | |
| OW | 1 | 35,878 | 35,878 | |
| NW | 1 | 41,311 | 41,311 | |
| GL | 1 | 39,217 | 39,217 | |
| ZG | 3 | 113,597 | 37,866 | |
| FR | 7 | 284,668 | 40,667 | |
| SO | 6 | 259,836 | 43,306 | |
| BS | 5 | 194,090 | 38,818 | |
| BL | 7 | 277,973 | 39,710 | |
| SH | 2 | 77,139 | 38,570 | |
| AR | 1 | 53,313 | 53,313 | |
| AI | 1 | 15,789 | 15,789 | |
| SG | 12 | 483,101 | 40,258 | |
| GR | 5 | 193,388 | 38,678 | |
| AG | 16 | 624,681 | 39,043 | |
| TG | 6 | 254,528 | 42,421 | |
| TI | 8 | 336,943 | 42,118 | |
| VD | 18 | 725,944 | 40,330 | |
| VS | 8 | 317,022 | 39,628 | |
| NE | 4 | 173,183 | 43,296 | |
| GE | 11 | 472,530 | 42,957 | |
| JU | 2 | 70,542 | 35,271 |
See also
.svg.png) |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Switzerland |
|
|
- List of Presidents of the National Council of Switzerland
- List of members of the National Council of Switzerland, 2019–23
- List of members of the National Council of Switzerland, 2011–15
- List of members of the National Council of Switzerland, 2007–11
- List of members of the National Council of Switzerland, 2003–07
Notes and references
- "The National Council" (official site). Bern, Switzerland: The Swiss Parliament. Retrieved 9 August 2016.
- "The Parliament Building" (official site). Bern, Switzerland: The Swiss Parliament. Retrieved 9 August 2016.
- "Lexicon of parliamentary terms". www.parlament.ch. Retrieved 25 May 2019.
- Bundesgesetz über die politischen Rechte (SR 161.1), Art. 161 „Verteilung der Sitze auf die Kantone“, in effect since 1 January 2008.
- Bundesamt für Statistik. "Nationalrat Entwicklung Parteistärken". Retrieved 3 May 2020.
- SRF, Tania Boa, Timo Grossenbacher and Thomas Preusse. "Luck with lists and misfortune with proportional representation". swissinfo.ch. Retrieved 4 April 2018.
- Art. 148 BV
- Art. 151 BV
- parlament.ch: Faktenblatt zu den Sessionen (PDF) Archived 10 October 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- Art. 2 ParlG
Bibliography
- Federal Chancellor Corina Casanova, ed. (28 April 2015), The Swiss Confederation – A Brief Guide 2015, Bern, Switzerland: Swiss Federal Chancellery (FCh) of the Swiss Confederation, archived from the original (PDF) on 21 January 2016, retrieved 4 January 2016
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Swiss National Council. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Swiss National Council. |
- Official website
- Swiss Parliament
- The Law Collection: SR 17 Bundesbehörden/Autorités fédérales/Autorità federali