Mossi language
The Mossi language (known in the language as Mooré; also Mòoré, Mõõré, Moré, Moshi, Moore, More) is a Gur language of the Oti–Volta branch and one of two official regional languages of Burkina Faso, closely related to the Frafra language spoken just across the border in the northern half of Ghana and less-closely to Dagbani and Mampruli farther south. It is the language of the Mossi people, spoken by approximately 5 million people in Burkina Faso, plus another 60,000+ in Mali and Togo.
| Mossi | |
|---|---|
| Mooré | |
| Native to | Burkina Faso, Benin, Ivory Coast, Ghana, Mali, Togo |
| Ethnicity | Mossi |
Native speakers | 7.83 million (2009–2013)[1] |
| Latin | |
| Official status | |
Recognised minority language in | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-2 | mos |
| ISO 639-3 | mos |
| Glottolog | moss1236[2] |
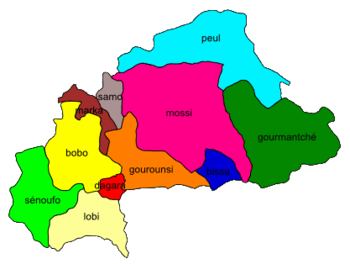 Majority areas of Mossi speakers, in pink, on a map of Burkina Faso | |
| Person | Moaaga |
|---|---|
| People | Moose |
| Language | Mòoré |
The distribution of Mossi
Phonology
The Mossi language consists of the following sounds:[3]
Consonants
| Labial | Alveolar | Postalveolar / palatal |
Velar | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ɲ | |||
| Stop | voiceless | p | t | k | ʔ | |
| voiced | b | d | ɡ | |||
| Fricative | voiceless | f | s | h | ||
| voiced | v | z | ||||
| Liquid | r, l | |||||
| Approximant | j | w | ||||
Remark:
Vowels
| Front | Central | Back | ||
| Close | Close | i | u | |
| Near-close | ɪ | ʊ | ||
| Close-mid | e | o | ||
| Open | a | |||
Notes:
- All vowels (other than /e/ and /o/) are pronounced like their nasal counterparts.
- All vowels (oral and nasal) are pronounced like their lengthened counterparts.
- Other linguists include the vowels /ɛ/ and /ɔ/; here, they are analysed as diphthongs, (/ɛ/ is considered to be ea and /ɔ/ is considered to be oa).
Orthography
In Burkina Faso, the Mossi alphabet uses the letters specified in the national Burkinabé alphabet.
| Burkinabé Mossi alphabet | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | ʼ | B | D | E | Ɛ | F | G | H | I | Ɩ | K | L | M | N | O | P | R | S | T | U | Ʋ | V | W | Y | Z |
| a | ʼ | b | d | e | ɛ | f | g | h | i | ɩ | k | l | m | n | o | p | r | s | t | u | ʋ | v | w | y | z |
| Phonetic values | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| a | ʔ | b | d | e | ɛ | f | ɡ | h | i | ɪ | k | l | m | n | o | p | r | s | t | u | ʊ | v | w | j | z |
gollark: It would be interesting to get a better view of what's in them *without* writing down it by hand every 5 minutes, but would be somewhat cheaty/TJ09-annoying.
gollark: _considers automatically checking biomes periodically_
gollark: They're normally regular?!
gollark: If only we had data to work from...
gollark: Well, I've seen more aeons and actually caught a copper again, but no silvers/golds.
See also
References
- "Mòoré". Ethnologue. Retrieved 2018-12-06.
- Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Mossi". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- Cf. Kabore (1985) : (p.44) for the consonants, (p.85-86) for the vowels.
External links
Learning materials
- Protestant Mission, Assemblies of God (Around 1955 CE - 1961 CE). More (Language of the Mossi Tribe) Phrase Book. Ouagadougou, Upper Volta: World Digital Library. Check date values in:
|date=(help)
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Mooré phrasebook. |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.