Yoruboid languages
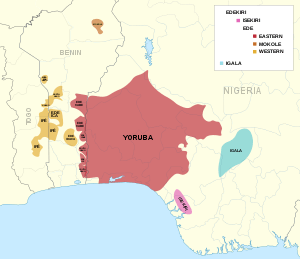
Yoruboid is a 'megagroup' of 14 related language clades, composed of the Igala group, of related dialects spoken in central Nigeria, and the Edekiri group, the members of which are spoken in a band across Togo, Ghana, Benin and southwestern Nigeria.
| Yoruboid | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | Central Togo, Southern and Central Benin, Western, Southern and Central Nigeria |
| Linguistic classification | Niger–Congo
|
| Subdivisions | |
| Glottolog | yoru1244[1] |
 | |
Name
The name Yoruboid derives from its most widely spoken member, Yoruba, which has more than 35 million speakers. Another well-known Yoruboid language is Itsekiri (Nigeria, 600,000–800,000 speakers). The Yoruboid group is a branch of Defoid, which is combined using "Ede" (meaning 'language' in most languages within the grouping) and -"foid". The Defoid group itself is a branch of the Benue–Congo subfamily of the Niger–Congo language family.
All Yoruboid languages are tonal, with most of them having three level tones. Grammatically, they are isolating with a subject–object–verb basic word order.
Languages
Igala is a key Yoruboid language, spoken by 1.8 million people in the Niger-Benue confluence of central Nigeria; it is excised from the main body of Yoruboid languages to the west by Ebirra and the Edo languages. Igala is closely related to both Yoruba and Itsekiri languages.
The Itsekiris are a riverine Yoruboid people who live in the Niger Delta region of Nigeria. They maintain a distinct identity separate from other Yoruboid people but speak a very closely related language. Their neighbouring languages are the Urhobo the Edo, the Ijo, and the Mahin / Ilaje, a Yoruba dialect spoken in neighbouring Ondo State.
Subdivisions
| Proto-Yoruba | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Igala | Edekiri | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ede (Yoruba Proper)* | Itsekiri* | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Western Ede | Mokole | Eastern Ede | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| N. Nago & Kura | Southwestern Ede | Ede Shabe | Southeastern Ede | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isha & Manigri | Ede Idaasha | Ana-Ife | Nuclear Yoruba | Ede Ije, South Nago | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yoruba - Lucumi | Olukumi* | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NWY & SWY | Central Yoruba | NEY & SEY | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- All dialects in the Ede cluster share between 85-95% lexical similarity and are thus all mutually intelligible without needing different specialized literature to achieve universal understanding.
- Itsekiri is actually most closely related to SEY (South-Eastern Yoruba), and is a divergent branch thereof, but has a different standard writing orthography.
- Some standards classify Olukumi as separate variant of Nuclear Yoruba, Others as a dialect of SEY.
Names and locations
Below is a list of selected Yoruboid language names, populations, and locations from Blench (2019).[2]
| Language | Dialects | Alternate spellings | Own name for language | Endonym(s) | Other names (location-based) | Other names for language | Exonym(s) | Speakers | Location(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ulukwumi | Unukwumi | Fewer than 10,000 | Delta State, Aniocha and Oshimili LGAs | ||||||
| Igala | Ánkpa and Ògùgù in Ankpa LGA; Ìfè in Ankpa and Dekina LGAs; Ànyìgbá in Dekina LGA; ‘Idáh and Ìbàjì in Idah and Anambra(?) LGAs; and Èbú in Oshimili LGA | Igara | 295,000 (1952), 800,000 (1987 UBS) | Benue State, Ankpa, Dekina, Idah and Bassa LGAs; Edo State, Oshimili LGA; Anambra State, Anambra LGA | |||||
| Iṣẹkiri | Itsekiri, Ishekiri, Shekiri, Chekiri, Jekri, Izekíri, Tshekeri, Dsekiri | Iwere, Irhobo, Warri | Iselema–Otu (Ịjọ name for Warri/Itsekiri people), Selemo | 33,000 (1952); over 100,000 (1963 Omamor); 500,000 (1987 UBS) | Delta State, Warri, Bomadi and Ethiope LGAs | ||||
| Yoruba | Many dialects | Yorùbá | Yorùbá | Aku, Akusa, Eyagi, Nago | 5,100,000 (1952), 15,000,000 (UBS 1984) | Most of Kwara, Lagos, Osun, Oyo, Ogun and Ondo States; western LGAs in Kogi State; and into Benin Republic and Togo. Yoruba is spoken as a ritual language in Cuba and Brazil |
See also
- List of Proto-Yoruboid reconstructions (Wiktionary)
References
- Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Yoruboid". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- Blench, Roger (2019). An Atlas of Nigerian Languages (4th ed.). Cambridge: Kay Williamson Educational Foundation.
External links
- Proto-Yoruba-Igala Swadesh list (N. Aubry, H. Friedman & K. Pozdniakov 2004)