Mauretania Caesariensis
Mauretania Caesariensis (Latin for "Caesarean Mauretania") was a Roman province located in what is now Algeria in the Maghreb. The full name refers to its capital Caesarea Mauretaniae (modern Cherchell).
| Provincia Mauretania Caesariensis | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Province of the Roman Empire | |||||||||
| 42 AD–7th century | |||||||||
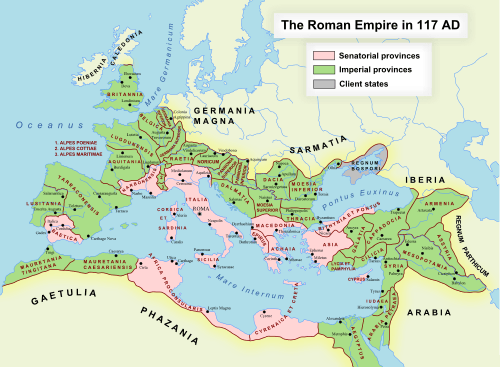
.svg.png) The province of Mauretania Caesariensis within the Roman Empire, c. AD 125 | |||||||||
| Capital | Caesarea | ||||||||
| Historical era | Classical antiquity | ||||||||
• Established | 42 AD | ||||||||
| 7th century | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||

Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of Algeria |
 |
|
Prehistory
|
|
|
|
Modern times Ottoman Algeria (16th - 19th centuries)
French Algeria (19th - 20th centuries)
|
|
Contemporary era |
|
Related topics
|
The province had been part of the Kingdom of Mauretania and named for the Mauri people who lived there. Formerly an independent kingdom, and later a client state of Rome, it was annexed into the Empire formally during the reign of Claudius and divided into two provinces about 42 AD. A third province, named Mauretania Sitifensis, was later split off from the eastern portion during the reign of Diocletian in 293 AD. During and after the Fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century, most of the hinterland area was lost, first to the Vandal Kingdom and later to the Mauro-Roman Kingdom, with Roman administration limited to the capital of Caesarea. The land was reconquered by Rome during the reign of Justinian. In the late 580s, under the emperor Maurice, all of the Maghreb was granted to the Exarchate of Africa, and Mauretania Caesariensis became part of a new province, Mauretania Prima. The Muslim conquest of the Maghreb brought an end to Roman rule in Mauretania, which became ruled by the Umayyad Caliphate as part of Medieval Muslim Algeria.
History

In the middle of 1st century AD, Roman emperor Claudius divided the westernmost Roman province in Africa, named Mauretania (land of the Mauri people, hence the word Moors), into Mauretania Caesariensis (named after its capital, one of many cities simply named Caesarea after the imperial cognomen that had become a title) and Mauretania Tingitana.
Mauretania Caesariensis included eight colonies founded by the Emperor Augustus : Cartennas, Gunugu, Igilgili, Rusguniae, Rusazu, Saldae, Zuccabar, Tubusuctu; two by the Emperor Claudius: Caesarea formerly the capital of Juba, who gave it this name in honour of his patron Augustus, and Oppidum Novum; one by the Emperor Nerva: Setifis; and in later times, Arsenaria, Bida, Siga, Aquae Calidae, Quiza Xenitana, Rusucurru, Auzia, Gilva, Icosium and Tipasa in all 21 well-known colonies, besides several municipia and oppida Latina.
Under Diocletian's Tetrarchy reform, the easternmost part was broken off from Mauretania Caesariensis as a separate small province, Mauretania Sitifensis, called after its inland capital Sitifis (now Sétif) with a significant port at Saldae (presently Béjaïa).[1]
At the time of Diocletian and Constantine the Great, both Sitifensis and Caesariensis were assigned to the administrative Diocese of Africa, in the praetorian prefecture of Italy, while Tingitana was an outpost of the Diocese of Spain.
After the fall of the Western part of the Roman Empire, a Germanic Vandal Kingdom was founded, but the remaining Eastern Empire (now known to historians as the Byzantine Empire) recaptured the area around 533, but most of Mauretania Caesariensis remained under the control of local Moorish rulers such as Mastigas, and it was not until the 560s and 570s that Byzantine control was established in the interior.
During the reign of Maurice, the empire was reorganized and a number of Exarchates were founded, among them the Exarchate of Africa which included Mauretania, among other territories. Mauretania Sitifensis was re-merged back into this province, and was granted the name "Mauretania Prima".
The Muslim conquest of the Maghreb for the caliphate under the Umayyad dynasty meant the end of the Byzantine Exarchate of Africa and Late Antique Roman culture there and Mauretania Caesariensis became part of the westernmost Islamic province called Maghreb.
Economy
The principal exports from Caesariensis were purple dyes and valuable woods; and the Amazigh or Mauri were highly regarded by the Romans as soldiers, especially light cavalry. They produced one of Trajan's best generals, Lusius Quietus, and the emperor Macrinus.
Religion
Caesarea was a major center of Judaism before 330, and Sitifis was one of the centres of the soldier cult of Mithraic mysteries. Christianity spread throughout in the 4th and 5th centuries.
Among the ruling class, Trinitarian Christianity was replaced by Arianism under the Germanic kingdom of the Vandals, which was established in 430, when the Vandals crossed the Strait of Gibraltar.
Episcopal sees
Ancient episcopal sees of Mauretania Caesariensis listed in the Annuario Pontificio as titular sees:[2]
- Ala Miliaria (Beniane)
- Albulae
- Altava (Ouled Mimoun, Hadjar-Er-Roum)
- Amaura (Amourah)
- Ambia (near Hammam-Bou-Hanifia)
- Aquae in Mauretania (Hammam Righa District)
- Aquae Sirenses (ruins at Hammam-Bou-Hanifia)
- Arena (Bou-Saada?)
- Arsennaria (Bou-Râs?)
- Auzia (Aumale, Sour-Khazlam)
- Bacanaria
- Baliana (L'Hillil?)
- Bapara (near the promontory of Ksila?)
- Benepota
- Bida (ruins of Djemâa-Sahridj?)
- Caesarea in Mauretania (now Cherchell), the Metropolitan Archbishopric
- Caltadria
- Capra
- Caput Cilla (ruins of El-Gouéa?)
- Cartennae
- Castellum Ripae (ruins of Hadjar-Ouaghef?)
- Castellum Tatroportus
- Castellum Tingitii (Al Asnam)
- Castellum Iabar
- Castellum Medianum
- Castellum Minus (Coléa, near Algiers)
- Castra Nova (Mohammadia)
- Castra Severiana (Lalla Marnia? Chanzy, Sidi-Ali-Ben-Joub?)
- Catabum Castra (Saint-Aimé, Djidioua?)
- Catrum
- Catula (Oued Damous?)
- Cenae (Kenais Islands)
- Cissi (Djinet)
- Columnata (Khemisti)
- Corniculana
- Elephantaria in Mauretania (ruins at (El) Harrach)
- Fallaba (Djelfa?)
- Fidoloma
- Flenucleta
- Floriana, Mauritania (Letourneux, Derrag?)
- Flumenzer (Bou Medfa)
- Fronta
- Giru Mons (ruins of Yerroum?)
- Gratianopolis
- Gunugus (Sidi-Brahim)
- Gypsaria (Honeïn)
- Ida in Mauretania
- Igilgilli (in the valley of Bou-Sellam?)
- Iomnium (port at Tzigiri)
- Ita
- Iunca in Mauretania
- Lamdia (Médéa)
- Lari Castellum (Imilaën)
- Maiuca
- Malliana (Khemis Miliana)
- Manaccenser (in the region of Cherchell)
- Masuccaba
- Maturba
- Maura (Douelt-Zerga?)
- Mauriana
- Maxita (in the region of Al-Asnam?)
- Media
- Mina (ruins near Rezilane)
- Muteci (near Aïn-El-Anab?)
- Nabala
- Nasbinca
- Noba
- Novica (ruins of Aïn-Nouïssy?)
- Numida (in the territory of Amoura, cfr supra Amaura)
- Obbi, Mauretania
- Obori (Sidi Fredj)
- Oppidum Novum (Aïn Defla)
- Panatoria
- Pomaria (Tlemcen)
- Rapidum (Masqueray, Sour-Djouab)
- Regiae (Arbal)
- Reperi
- Rusada (Azeffoun)
- Rusguniae (Tamentfoust)
- Rusubbicari (Mers El Hadjadj)
- Rusubisir (in the territory of Tiza)
- Rusuccuru
- Satafi
- Sereddeli
- Serta
- Sesta
- Sfasferia
- Siccesi (ruins of Takembrit)
- Sinnada in Mauretania (ruins of Kenada?)
- Sita (in the west of the province
- Subbar
- Sufar
- Sufasar (Amourah)
- Summula
- Tabaicara
- Tabla (Tablat?, Tablast?)
- Taborenta (ruins near Saida?)
- Tabunia
- Tamada (Aïn-Tamda near Masqueray?)
- Tamazuca (ruins of Grimidi?)
- Tanaramusa (Mousaïaville, El-Hadjeab? Berrouaghia?)
- Tasaccora (Sigi)
- Tatilti (Souk El Khemis)
- Tigamibena
- Tigava (El-Kherba)
- Tigisis (between Dellys and Taourga)
- Timici (Timsionin?)
- Timidana
- Tingaria (Tiaret?)
- Tipasa in Mauretania
- Tubia (ruins of Henchir-Toubia?)
- Tubunae in Mauretania
- Turris in Mauretania
- Tuscamia
- Ubaba
- Usinaza (Seneg)
- Vagal, Mauritania (near the ruins of Sidi-Ben-Thiour)
- Vanariona (ruins of Ksar-Tyr?)
- Vannida
- Vardimissa (near Medjana)
- Villa Nova, Mauritania
- Vissalsa (on the Oued-Melah river?)
- Voncaria (ruins of Boghar?)
- Voncariana (near the ruins of Boghasi?)
- Vulturia (ruins at the Falco promontory?)
- Zucchabar
See also
References
- Map of Mauretania Sitifensis (in blue color) & Mauretania Caesariensis (in light brown color)
- Annuario Pontificio 2013 (Libreria Editrice Vaticana, 2013, ISBN 978-88-209-9070-1), "Sedi titolari", pp. 819-1013
Sources
- Westermann, Großer Atlas zur Weltgschichte (in German)
%2C_Algeria_04966r.jpg)