Imperial province
An imperial province was a Roman province during the Principate where the Roman Emperor had the sole right to appoint the governor (legatus Augusti). These provinces were often the strategically located border provinces.
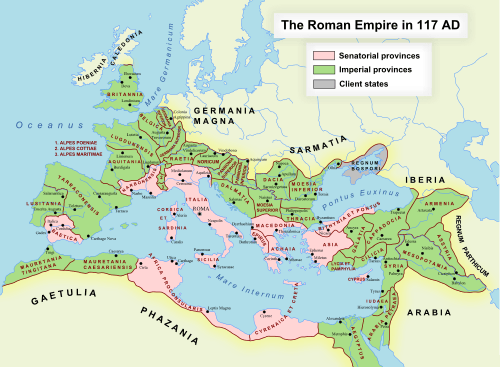
Roman Empire in 117 AD. Imperial provinces are shown in green. Pink indicates senatorial provinces, as well as Italy itself, which was governed directly by the senate.
The provinces were grouped into imperial and senatorial provinces shortly after the accession of Augustus.
The following provinces were imperial provinces:
- Aegyptus
- Alpes Cottiae
- Alpes Maritimae
- Alpes Poenninae
- Armenia
- Assyria
- Britannia
- Cilicia
- Dacia
- Dalmatia
- Galatia
- Gallia Aquitania
- Gallia Belgica
- Gallia Lugdunensis
- Germania Inferior
- Germania Superior
- Hispania Tarraconensis
- Judaea
- Lusitania
- Moesia
- Noricum
- Pannonia
- Raetia
- Syria
- Thracia
Designations for types of administrative territorial entities | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
See also: Census division, Electoral district, Political division, and List of administrative divisions by country | |||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.