Arcadia Aegypti
Arcadia or Arcadia Aegypti was a Late Roman province in northern Egypt.
| Provincia Arcadia Aegypti ἐπαρχία Αρκαδίας Αιγύπτου | |
|---|---|
| province of the Roman Empire | |
| After 386–640s | |
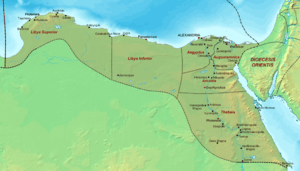 Diocese of Egypt, c. 400 | |
| Capital | Oxyrhynchus |
| History | |
• Established | After 386 |
• Disestablished | 640s |
| Today part of | |
History
It was created between 386 and ca. 395 out of the province of Augustamnica and named for the reigning Byzantine emperor, Arcadius (395 to 408).
The province comprised most of the historical region known as "Heptanomis" ("Seven Nomes"), except for Hermopolis, which belonged to the Thebaid.[1]
In the Notitia Dignitatum, Arcadia forms one of six provinces of the Diocese of Egypt, under a governor with the low rank of praeses.[1][2]
Episcopal sees
Ancient episcopal sees in the Roman province of Arcadia Aegypti, listed in the Annuario Pontificio as titular sees:[3]
- Oxyrhynchus, the Metropolitan Archbishopric, so probably the provincial capital
- Alphocranon (Helwan)
- Aphroditopolis (Atfih)
- Arsinoë in Arcadia (Faiyum)
- Cynopolis in Arcadia (El-Queis? Cheikh-Fadl?)
- Heracleopolis Magna
- Memphis
- Nilopolis
- Theodosiopolis in Arcadia (Taha-el-Amudein)
gollark: Ah, but you can make a pulverizer process into 3 dusts, if I recall.
gollark: Also, do you know about TE's 3x ore processing?
gollark: Are infernal furnaces dangerous somehow? I don't use TC6 unironically.
gollark: Just get scrubbers?
gollark: Wait, not hours, days, it was fine.
References
- Keenan (2000), p. 613
- Notitia Dignitatum, in partibus Orientis, I
- Annuario Pontificio 2013 (Libreria Editrice Vaticana 2013 ISBN 978-88-209-9070-1), "Sedi titolari", pp. 819-1013
Sources
- Keenan, James K. (2000). "Egypt". In Cameron, Averil; Ward-Perkins, Bryan; Whitby, Michael (eds.). The Cambridge Ancient History, Volume XIV - Late Antiquity: Empire and Successors, A.D. 425–600. Cambridge University Press. pp. 612–637. ISBN 978-0-521-32591-2.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.