London Borough of Wandsworth
Wandsworth (/ˈwɒndzwɜːrθ/ (![]()
Wandsworth | |
|---|---|
 Coat of arms  Council logo | |
 Wandsworth shown within Greater London | |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Constituent country | England |
| Region | London |
| Ceremonial county | Greater London |
| Created | 1 April 1965 |
| Admin HQ | Wandsworth |
| Government | |
| • Type | London borough council |
| • Body | Wandsworth London Borough Council |
| • Leadership | Leader & Cabinet (Conservative) |
| • Mayor | Jane Cooper (Con) |
| • London Assembly | Leonie Cooper (Lab) AM for Merton and Wandsworth |
| • MPs | Fleur Anderson (Lab) Dr Rosena Allin-Khan (Lab) Marsha De Cordova (Lab) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 13.23 sq mi (34.26 km2) |
| Area rank | 294th (of 317) |
| Population (mid-2019 est.) | |
| • Total | 329,677 |
| • Rank | 29th (of 317) |
| • Density | 25,000/sq mi (9,600/km2) |
| • Ethnicity[1] | 53.3% White British 2.5% White Irish 0.1% White Gypsy or Irish Traveller 15.5% Other White 1.5% White & Black Caribbean 0.7% White & Black African 1.3% White & Asian 1.5% Other Mixed 2.8% Indian 3.2% Pakistani 0.5% Bangladeshi 1.2% Chinese 3.2% Other Asian 4.8% Black African 4% Black Caribbean 1.8% Other Black 0.8% Arab 1.3% Other |
| Time zone | UTC (GMT) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+1 (BST) |
| Postcodes | |
| Area code(s) | 020 |
| ONS code | 00BJ |
| GSS code | E09000032 |
| Police | Metropolitan Police |
| Website | www |
History
Until 1889, the current area of Wandsworth was part of the county of Surrey. In 1855 the Wandsworth District of the Metropolis was formed comprising the parishes of Battersea (excluding Penge), Clapham, Putney, Streatham, Tooting Graveney and Wandsworth. Battersea was removed from the district in 1888. In 1900 the remaining district became the Metropolitan Borough of Wandsworth and Battersea became the Metropolitan Borough of Battersea.
The London Borough of Wandsworth was formed in 1965 from the former area of the Metropolitan Borough of Battersea and the Metropolitan Borough of Wandsworth, but excluding the former parish of Clapham and most of the former parish of Streatham which were transferred to the London Borough of Lambeth. The areas to the west of Clapham Common in the current borough of Wandsworth are often incorrectly referred to as Clapham, but are in fact part of Battersea parish.[2]
Geography
Clapham Junction railway station is in Battersea, rather than Clapham in the borough. There are many new or refurbished buildings along the borough's prosperous riverside including the large Chelsea Bridge Wharf. The Peace Pagoda, one of many such international Pagodas is in Battersea Park, a sprawling rectangle often hosting circuses beside the Thames. The London Heliport, London's main and busiest heliport is just beyond Battersea Park and south of this is New Covent Garden Market. In terms of size, South Thames College, Southside Shopping Centre, Wandsworth and The Exchange Shopping Centre, Putney are among the largest secular structures.
Secular architecturally most highly listed buildings include: Battersea Power Station, the Battersea Arts Centre (formerly town hall), Royal Hospital for Neuro-disability, Wandsworth Town Hall, as well as particularly the interiors of the large Gala Bingo Club, Tooting, the former Granada Theatre, St John's Hill, Clapham Junction by Theodore Komisarjevsky and in terms of ornate mansions a cluster of five large stone and brick buildings mostly converted to diverse public uses in and around Queen Mary's Hospital, Roehampton at grade II* or above.[3] In Old Battersea two fine masonry mansions survived The Blitz, Old Battersea House [4] and Downshire House[5]—both hold rare Grade II* status.
Demographics
Population
According to the 2011 census, Wandsworth has a population of 306,995. In 2001 78% of the population was white, 9.6% black and 6.9% south Asian.
A 2017 study by Trust for London and the New Policy Institute found that Wandsworth has the lowest rate of unemployment of any London borough. It also has the 2nd lowest rate of local employees who are low-paid.[6]
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1801 | 12,087 | — |
| 1811 | 15,303 | +26.6% |
| 1821 | 17,779 | +16.2% |
| 1831 | 19,681 | +10.7% |
| 1841 | 23,959 | +21.7% |
| 1851 | 30,241 | +26.2% |
| 1861 | 74,569 | +146.6% |
| 1871 | 118,896 | +59.4% |
| 1881 | 163,224 | +37.3% |
| 1891 | 243,427 | +49.1% |
| 1901 | 306,090 | +25.7% |
| 1911 | 384,884 | +25.7% |
| 1921 | 394,964 | +2.6% |
| 1931 | 405,317 | +2.6% |
| 1941 | 375,040 | −7.5% |
| 1951 | 347,025 | −7.5% |
| 1961 | 323,064 | −6.9% |
| 1971 | 300,832 | −6.9% |
| 1981 | 252,242 | −16.2% |
| 1991 | 265,058 | +5.1% |
| 2001 | 260,383 | −1.8% |
| 2011 | 306,995 | +17.9% |
| Note:[7] | ||
Ethnicity
| Ethnic Group | 2001[8] | 2011[9] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | |
| White: British | 168,665 | 64.8% | 163,739 | 53.3% |
| White: Irish | 8,151 | 3.1% | 7,664 | 2.5% |
| White: Gypsy or Irish Traveller | 163 | 0.1% | ||
| White: Other | 26,162 | 10.0% | 47,650 | 15.5% |
| White: Total | 202,978 | 78.0% | 219,216 | 71.4% |
| Asian or Asian British: Indian | 7,412 | 2.8% | 8,642 | 2.8% |
| Asian or Asian British: Pakistani | 5,449 | 2.1% | 9,718 | 3.2% |
| Asian or Asian British: Bangladeshi | 1,099 | 0.4% | 1,493 | 0.5% |
| Asian or Asian British: Chinese | 2,227 | 0.9% | 3,715 | 1.2% |
| Asian or Asian British: Other Asian | 4,084 | 1.6% | 9,770 | 3.2% |
| Asian or Asian British: Total | 20,271 | 7.8% | 33,338 | 10.9% |
| Black or Black British: African | 10,013 | 3.8% | 14,818 | 4.8% |
| Black or Black British: Caribbean | 12,665 | 4.9% | 12,297 | 4.0% |
| Black or Black British: Other Black | 2,388 | 0.9% | 5,641 | 1.8% |
| Black or Black British: Total | 25,066 | 9.6% | 32,756 | 10.7% |
| Mixed: White and Black Caribbean | 2,893 | 1.1% | 4,642 | 1.5% |
| Mixed: White and Black African | 1,252 | 0.5% | 2,034 | 0.7% |
| Mixed: White and Asian | 2,247 | 0.9% | 3,887 | 1.3% |
| Mixed: Other Mixed | 2,336 | 0.9% | 4,678 | 1.5% |
| Mixed: Total | 8,728 | 3.4% | 15,241 | 5.0% |
| Other: Arab | 2,350 | 0.8% | ||
| Other: Any other ethnic group | 3,337 | 1.3% | 4,094 | 1.3% |
| Other: Total | 3,337 | 1.3% | 6,444 | 2.1% |
| Black, Asian, and minority ethnic: Total | 57,402 | 22.1% | 87,779 | 28.7% |
| Total | 260,380 | 100.00% | 306,995 | 100.00% |
Civic affairs
Mayor
The first Mayor of Wandsworth was John Lidiard, elected by the first Wandsworth Borough Council in November 1900.[10][11] Lidiard's initials are highlighted in the diamonds in the centre of the Mayor's chain of office.[12] The second Mayor was Sir William Lancaster.[13]
The current Mayor is Cllr Jane Cooper.[14]
Armorial bearings
The Armorial bearings retain many of the features of the arms of the former Metropolitan Borough of Battersea and Metropolitan Borough of Wandsworth.
The fess, or crossing, of the shield is chequered blue and gold representing the arms of William de Warren, created first Earl of Surrey by William Rufus. Each gold square bears a teardrop representing the tears of the French Huguenots, many of whom settled in Wandsworth from 1685.
The ship at the top may refer to the Wendels, a tribe of sea-raiders from the Continent who supposedly gave their name to the district, for Wendelsworth was an early variation of Wandsworth. The four shields and oars on the ship represent the four parishes of Battersea, Putney, Tooting and Wandsworth.
The dove to the left is taken from the former Battersea coat of arms and the black dragon to the right was taken from the former Wandsworth arms and also refers to London, being similar to the City of London coat of arms.
Politics
Wandsworth London Borough Council
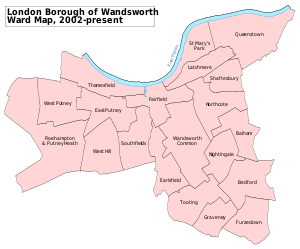
Wandsworth is administered by 60 councillors, 3 apiece from 20 wards. Since the 2018 election, 33 of these councillors are Conservative, 26 are Labour and 1 is Independent. The Conservatives have had an overall majority on the council since 1978 and provide all eight members of the Cabinet, the Leader of which is Cllr Ravi Govindia.
Summary results of elections
| Overall control | Conservative | Labour | Lib Dem or Social Democrat | Others | |
| 2018 | Conservative | 33 | 26 | – | 1 |
| 2014 | Conservative | 41 | 19 | – | – |
| 2010 | Conservative | 47 | 13 | – | – |
| 2006 | Conservative | 51 | 9 | – | – |
| 2002 | Conservative | 50 | 10 | – | – |
| 1998 | Conservative | 50 | 11 | – | – |
| 1994 | Conservative | 45 | 16 | – | – |
| 1990 | Conservative | 48 | 13 | – | – |
| 1986 | Conservative | 31 | 30 | – | – |
| 1982 | Conservative | 33 | 27 | 1 | – |
| 1978 | Conservative | 36 | 25 | – | – |
| 1974 | Labour | 12 | 48 | – | – |
| 1971 | Labour | 7 | 53 | – | – |
| 1968 | Conservative | 48 | 12 | – | – |
| 1964 | Labour | 13 | 47 | – | – |
Transport
Bridges
Five bridges join Wandsworth to the three London Boroughs on the north side of the Thames (from downstream following the river up):
There are also a number of bridges crossing the River Wandle which runs through the centre of Wandsworth town and divides the borough in two.
National Rail Stations
Tube Stations
- On the Northern line:
- On the District line:
National Rail services are operated from London Waterloo by South Western Railway to Earlsfield, Putney, Queenstown Road (Battersea), Wandsworth Town and the borough's largest station, Clapham Junction. This last station is also served from London Victoria by Southern as are Balham, Battersea Park and Wandsworth Common.
London Overground services mainly serve Clapham Junction, which is the southern terminus for the West London Line that has services to Stratford via Shepherd's Bush, though some trains terminate at the West London Line's northern terminus at Willesden Junction. The western terminus for the East London Line also is at Clapham Junction that has services to Highbury & Islington via Denmark Hill. There is also a limited one train a day parliamentary train service that instead of terminating at Clapham Junction, it instead terminates at Battersea Park.
London Underground services are provided on the District line to East Putney and Southfields and on the Northern line to Balham, Clapham South, Tooting Bec and Tooting Broadway.
Cycling and Walking
Wandsworth London Borough Council and Transport for London (TfL) maintain cycling infrastructure in the Borough.
Cycle Superhighway 7 (CS7) is an unbroken, signposted cycle route running through the southeastern portion of the Borough. The route runs along the A24 and A3 roads, through Tooting, Balham, and Clapham. Northbound the route links the Borough directly to the City of London via Kennington, Elephant and Castle, and Southwark. Southbound, the route runs unbroken to Colliers Wood.
Cycle Superhighway 8 (CS8) is an unbroken, signposted cycle route running through the northern edge of Wandsworth, through Battersea. The route runs east-west along the A3205/Battersea Park Road, but the route leaves the Borough to the north over Chelsea Bridge. The route begins in Wandsworth Town and runs to Millbank, City of Westminster, passing Chelsea and the Tate Britain en route.
Although CS8 leaves the Borough to the north, cycling infrastructure is provided along the entire A3205 route between Wandsworth Town and Nine Elms. This means that there is a continuous, signposted cycle route - primarily along designated cycle lanes - from Wandsworth Town and Battersea to Vauxhall, Lambeth, and the South Bank.
Quietway 4 (Q4) runs from Clapham Common to Earlsfield in the Borough, through Wandsworth Common.[15]
The Wandle Trail is a shared-use trail for cyclists and pedestrians between Wandsworth Town and Waddon. The route is signposted and mainly traffic-free. It runs through Earlsfield, Colliers Wood, Morden, Mitcham, and Carshalton along the way.[16]
The Santander Cycles bike-sharing system operates in Putney, Wandsworth Town, and Battersea.[15]
Travel to work
In March 2011, the main forms of transport that residents used to travel to work were (of all residents aged 16–74):
- underground, metro, light rail, tram, 20.7% ;
- train, 10.6%;
- driving a car or van, 10.6%;
- bus, minibus or coach, 9.7%;
- on foot, 5.6%;
- bicycle, 5.4%;
- work mainly at or from home, 4.0%.[17]
Education
Whitelands College was founded Chelsea in 1842 by the Church of England, and heavily under the influence of John Ruskin. In 1930/1931 the college relocated to West Hill (Wandsworth Borough) and occupied an enormous purpose-built site, with buildings designed by Sir Giles Gilbert Scott. These buildings, now listed, were one of the Borough's largest educational sites until 2005 when the College, again moved, this time to a site in Roehampton, where it is now a constituent College of Roehampton University.
The borough's schools include Graveney School, Southfields Academy, Burntwood School, St. John Paul II, Ashcroft Technology Academy, Ernest Bevin College, and Elliott School.
Religion
The dominant religion of the borough is Christianity, although the area is also home to a number of other religious communities. The community is home to a number of Sikhs, Jews, Muslims, Buddhists and Hindus.[18]
According to the 2011 Census, approximately 35% of Wandsworth identified as being non-religious, or chose not to state their faith.[19]
Places
Parks and open spaces
Wandsworth has responsibility for three Metropolitan Open Spaces:
- Battersea Park
- Wandsworth Common
- Tooting Commons – the historically separate, but adjoining, Tooting Bec Common and Tooting Graveney Common
These three large green spaces together with a range of smaller parks and playgrounds (such as Wandsworth Park) are patrolled by Wandsworth Council's own parks police known from 1984 to 2012 as the Wandsworth Parks Police. From April 2012 the Parks Police team of 23 officers was replaced by a smaller Wandsworth Events Police Service (WEPS) working with a team of 12 Metropolitan Police Officers. This system was deemed unsuccessful, and in 2015 the WEPS was rebranded as Wandsworth Parks and Events Police (WPEP) and returned to full staffing levels of 33 police officers and support officers.[20][21]
Also within the borough's boundaries are Putney Heath and part of Putney Lower Common, which are managed as part of Wimbledon Common, and the west side of Clapham Common, which is managed by the London Borough of Lambeth.
Theatres
- Battersea Arts Centre
- Theatre503
- Putney Arts Theatre
- Tara Arts Theatre
Localities
- Balham
- Battersea
- Earlsfield
- Furzedown
- Nine Elms
- Putney
- Putney Heath
- Putney Vale
- Roehampton
- Southfields
- Streatham Park
- Summerstown
- Tooting
- Tooting Bec/Upper Tooting
- Wandsworth
- West Hill
Postcode areas
SW4 (part), SW8 (part), SW11 (all), SW12 (part), SW15 (part), SW16 (part), SW17 (part), SW18 (part), SW19 (part)
See also
- Wandsworth Radio
- De Morgan Centre
- The Borough of Wandsworth Rifle Club
- Wandsworth Museum
References
- 2011 Census: Ethnic group, local authorities in England and Wales, Office for National Statistics (2012). See Classification of ethnicity in the United Kingdom for the full descriptions used in the 2011 Census.
- "Where is Battersea". Love Battersea. Retrieved 25 July 2019.
- Ordnance Survey map of listed buildings courtesy of English Heritage Archived 24 April 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- Historic England. "Details from listed building database (1065500)". National Heritage List for England. Retrieved 28 January 2013.
- Historic England. "Details from listed building database (1357666)". National Heritage List for England. Retrieved 28 January 2013.
- "London's Poverty Profile". Trust for London. Retrieved 19 June 2018.
- "Wandsworth: Total Population". A Vision of Britain Through Time. Great Britain Historical GIS Project. Retrieved 6 September 2011.
- "KS006 - Ethnic group". NOMIS. Retrieved 30 January 2016.
- "Ethnic Group by measures". NOMIS. Retrieved 8 January 2016.
- "The London Borough Councils. Election of Mayors and Aldermen". The Times. 10 November 1900. p. 14.
- Local History Publications 1955–2011. Index for Researchers. Wandsworth Historical Society. p. 12.
- "The Mayors of Wandsworth". Wandsworth Council. Archived from the original on 4 April 2013. Retrieved 9 May 2013.
- "Blue Plaques Scheme" (PDF). Putney Society. Retrieved 30 March 2014.
- "Mayor of Wandsworth". Retrieved 6 August 2019.
- "Cycle". Transport for London. Retrieved 5 April 2020.
- "The Wandle Trail Walk and Cycle Route" (PDF). London Borough of Merton. Retrieved 5 April 2020.
- "2011 Census: QS701EW Method of travel to work, local authorities in England and Wales". Office for National Statistics. Retrieved 23 November 2013. Percentages are of all residents aged 16–74 including those not in employment (26.7%). Respondents could only pick one mode, specified as the journey’s longest part by distance.
- "Wandsworth Census Demographics United Kingdom". localstats.co.uk. Retrieved 18 March 2018.
- "2011 Census data and analysis". Wandsworth.gov.uk. 2017. Retrieved 3 June 2017.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 7 January 2014. Retrieved 26 December 2019.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Wandsworth Parks and Events Police". British Police History. Retrieved 11 February 2019.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to London Borough of Wandsworth. |