Lieutenant general
Lieutenant general or lieutenant-general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a three-star military rank (NATO code OF-8) used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second in command on the battlefield, who was normally subordinate to a captain general.
In modern armies, lieutenant general normally ranks immediately below general and above major general; it is equivalent to the navy rank of vice admiral, and in air forces with a separate rank structure, it is equivalent to air marshal. A lieutenant general commands an army corps, made up of typically three army divisions, and consisting of around 60,000–70,000 soldiers (U.S.).
The seeming incongruity that a lieutenant general outranks a major general (whereas a major outranks a lieutenant) is due to the derivation of the former rank from sergeant major general, which was also subordinate to lieutenant general. In some countries (e.g. France and Italy), the ranks of corps general or lieutenant colonel general are used instead of lieutenant general, in an attempt to solve this apparent anomaly – these ranks are often translated into English as lieutenant general.
However, some countries of Latin America such as Brazil and Chile use divisional general as the equivalent of lieutenant general. In addition, because no brigadier general rank is used in Japan, lieutenant general is the rank of divisional commander. Therefore, it corresponds to divisional general of these countries. In a number of smaller states which employ NATO and western style military organizational structures, because of the limited number of soldiers in their armies, the rank of lieutenant general is the highest army rank in use. In Latvia, Lithuania and Singapore, the chief of defence is a lieutenant general, and in the Irish Defence Forces and Israel Defense Forces, the Chief of Staff holds this rank.
Lieutenant general ranks by country
- Lieutenant general (Algeria)
- Lieutenant general (Australia)
- Teniente general (Argentina)
- Lieutenant general (Bangladesh)
- General-pukovnik (Bosnia & Herzegovina)
- Lieutenant general (Botswana)[1]
- General de Divisão (Brazil)
- Генерал-лейтенант ("General-leytenant"; Bulgaria)
- Lieutenant-general (Canada)
- zhong jiang (China and Taiwan)
- General pukovnik (Croatia)
- Generálporučík (Czech Republic)
- Generalløjtnant (Denmark)
- Kindralleitnant (Estonia)
- Kenraaliluutnantti (Finland)
- Général de corps d'armée in the French Armed Forces, including the French Air Force since 1939. Prior officially, Général de division for the French Army and Vice-Amiral for the French Navy since 1791, formerly designated as Lieutenant-General of France. (France)
- გენერალ ლეიტენანტი ("general leitenanti") (Georgia)
- Generalleutnant (Germany)
- Αντιστράτηγος (Greek Army Antistrátigos, vice general)
- Altábornagy (Hungary)
- Lieutenant General (India)
- Letnan Jenderal (Indonesia)
- Sepahbod (Iran)
- Leifteanant-Ghinearál (Republic of Ireland)
- Rav Aluf (Israel)
- Generale di Corpo d'Armata (Italy)
- Gjenerallejtenant (Kosovo)
- Ģenerālleitnants (Latvia)
- Generolas leitenantas (Lithuania)
- Генерал потполковник (general potpolkovnik) (North Macedonia)
- Luitenant-generaal (Netherlands)
- Lieutenant General (Nigeria)
- Generalløytnant (Norway)
- Lieutenant general (Pakistan)
- Tenyente heneral (Philippines)
- Generał broni (Poland)
- Tenente-general (Portugal)
- General de corp de armată (Romania) (see Général de corps d'armée (Fr))
- Генерал-лейтенант ("General-leytenant"; Russia Empire, Soviet Union, and Russian Federation)
- Генерал-потпуковник ("general potpukovnik") (Serbia)
- Teniente general (Spain)
- Lieutenant general (Sri Lanka)
- Generallöjtnant (Sweden)
- Korpskommandant / Commandant de corps / Comandante di corpo (Switzerland)
- Pol tho ("พลโท") (Thailand)
- Korgeneral (Turkey)
- Lieutenant general (United Kingdom)
- Lieutenant general (United States)
- Trung tướng (Vietnam)
- Lieutenant general (Zimbabwe)
Army ranks
.svg.png) Dagar Jenral
Dagar Jenral
(Afghan National Army) Teniente General
Teniente General
(Argentine Army) Lieutenant general
Lieutenant general
(Australian Army) Generalleutnant
Generalleutnant
(Austrian Army) Lieutenant general
Lieutenant general
(Bangladesh Army)
 Lieutenant general
Lieutenant general
(Bosnian Army) Генерал-лейтенант
Генерал-лейтенант
(Bulgarian Army) Lieutenant general
Lieutenant general
(Canadian Army) Teninete General
Teninete General
(Chilean Army) Abolished in 2002 Zhong Jiang
Zhong Jiang
(People's Liberation Army)
 Generálporučík
Generálporučík
(Czech Army) Generalløjtnant
Generalløjtnant
(Royal Danish Army)


 გენერალ ლეიტენანტი
გენერალ ლეიტენანტი
(Georgian Defense Forces)
 Αντιστράτηγος
Αντιστράτηγος
(Greek Army) Altábornagy
Altábornagy
(Hungarian Army) Lieutenant general
Lieutenant general
(Indian Army) Letnan Jenderal
Letnan Jenderal
(Indonesian Army)

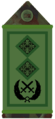 Leifteanant-ghinearál
Leifteanant-ghinearál
Irish Army Gjenerallejtnant
Gjenerallejtnant
Kosovo Security Forces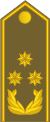 Генерал потполковник (general potpolkovnik)
Генерал потполковник (general potpolkovnik)
(Army of the Republic of North Macedonia) Luitenant-generaal
Luitenant-generaal
(Royal Netherlands Army)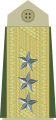 Generalløytnant
Generalløytnant
(Royal Norwegian Army) Lieutenant general
Lieutenant general
(Pakistan Army)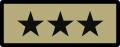 Tenyente Heneral
Tenyente Heneral
(Philippine Army) Generał broni
Generał broni
(Polish Army) Tenente-general
Tenente-general
(Portuguese Army) Lieutenant-general (Russian Federation)
Lieutenant-general (Russian Federation) Lieutenant General
Lieutenant General
(Singapore Armed Forces) Teniente general
Teniente general
(Spanish Army)

.svg.png) Pol tho
Pol tho
(Royal Thai Army) Korgeneral
Korgeneral
(Turkish Land Forces)


 Trung tướng
Trung tướng
(Vietnam People's Army)
Air force ranks
 Lieutenant général / Luitenant-generaal
Lieutenant général / Luitenant-generaal
(Belgian Air Component) Генерал-лейтенант
Генерал-лейтенант
(Bulgarian Air Force) Generalløjtnant
Generalløjtnant
(Royal Danish Air Force) Teniente general
Teniente general
(Ecuadorian Air Force)
 გენერალ ლეიტენანტი
გენერალ ლეიტენანტი
(Georgian Air Force) Luitenant-generaal
Luitenant-generaal
(Royal Netherlands Air Force) Generał broni
Generał broni
(Polish Air Force) Tenente-general
Tenente-general
(Portuguese Air Force) Teniente-general
Teniente-general
(Spanish Air Force) Generallöjtnant
Generallöjtnant
(Swedish Air Force) Korgeneral
Korgeneral
(Turkish Air Force)

Lieutenant general equivalent ranks
- General-de-Divisão (Brasil)
- General de División (Chile)
- General pukovnik (Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina)
- Général de corps d'armée (France - armée de terre or gendarmerie nationale), général de corps aérien (France, armée de l'air)
- Sepah-Bod (Iran)
- Rav Aluf (Israel)
- Generale di Corpo d'Armata (Italy)
- Rikugun-Chūjō (陸軍中将 (IJA)), Rikushō (陸将), and Kūshō (空将)(JSDF,three-star rank) (Japan)
- Chungjang (North Korea)
- Jungjang (South Korea)
- General de División (México)
- Generał broni (Poland)
- Farig فريق (Saudi Arabia)
- (General-potpukovnik) Генерал-потпуковник (Serbia)
- Generalpodpolkovnik (Slovenia)
- Korpskommandant/Commandant de corps (Switzerland)
- Trung tướng and Phó Đô đốc (Vietnam)
 General-de-Divisão (Brazilian Army)
General-de-Divisão (Brazilian Army) Major Brigadeiro (Brazilian Air Force)
Major Brigadeiro (Brazilian Air Force) Général de corps d'armée (French Army) featuring 4 stars instead of the typical 3 stars
Général de corps d'armée (French Army) featuring 4 stars instead of the typical 3 stars Rav Aluf (Israel)
Rav Aluf (Israel).svg.png) Generale di Corpo d'Armata (Italy)
Generale di Corpo d'Armata (Italy).svg.png) Rikushō (Japan Ground Self-Defense Force)
Rikushō (Japan Ground Self-Defense Force).svg.png) Kūshō(Japan Air Self-Defense Force)
Kūshō(Japan Air Self-Defense Force) Генерал-потпуковник (Serbian Army)
Генерал-потпуковник (Serbian Army) Генерал-потпуковник (Serbian Air Force)
Генерал-потпуковник (Serbian Air Force)
Other Lieutenant general ranks
- Gruppenführer (Waffen-SS)
- Feldmarschallleutnant (Austro-Hungarian Army)
- Korpskommandant (Swiss Army)
See also
- British and United States military ranks compared
- Comparative military ranks
- Israel Defense Forces ranks
- List of lieutenant generals in the United States Army before 1960
References
External links
