Suriname National Army
After the creation of the Statute of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, the Royal Netherlands Army was entrusted with the defence of Suriname, while the defence of the Netherlands Antilles was the responsibility of the Royal Netherlands Navy. The army set up a separate Troepenmacht in Suriname (Forces in Suriname, TRIS). Upon independence in 1975, this force was turned into the Surinaamse Krijgsmacht (SKM):, Surinamese Armed Forces. On February 25, 1980, a group of 15 non-commissioned officers and one junior SKM officer, under the leadership of sergeant major Dési Bouterse, staged a coup d'état and overthrew the Government. Subsequently, the SKM was rebranded as Nationaal Leger (NL), National Army.
| Suriname National Army | |
|---|---|
| Nationaal Leger | |
| Service branches | Suriname Army Suriname Air Force Suriname Navy |
| Leadership | |
| Commander-in-chief | Chan Santhokhi |
| Minister of Defense | Krishna Mathoera |
| Commander of the Armed Forces | Colonel Robert Kartodikromo |
| Manpower | |
| Military age | 18 |
| Available for military service | 123,072, age 15–49 (2002 est.) |
| Fit for military service | 72,059, age 15–49 (2002 est.) |
| Reaching military age annually | (2002 est.) |
| Expenditures | |
| Budget | $63,000,000 |
| Percent of GDP | 0.7% |
| Related articles | |
| Ranks | Military ranks of Suriname |
The Netherlands has provided limited military assistance to the Surinamese armed forces since the election of a democratic government in 1991. In recent years, the United States has provided training to military officers and policymakers to promote a better understanding of the role of the military in a civilian government. Also, since the mid-1990s, the People's Republic of China has been donating military equipment and logistical material to the Surinamese Armed Forces, as has Brazil.
Organization
Suriname's National Armed Forces are composed of some 2,500 personnel, the majority of whom are deployed in the Army of Suriname.

Army
- A Light Infantry Battalion (33ste Bataljon der Infanterie) Formed in 1987.
- A Special Forces Corps.
- A Support Arm. (Staf verzorgings Bataljon)
- A Military Police Corps.
Air Force

In 1982 a small air arm was formed within the Suriname defense force called "Surinaamse Luchtmacht" in short also called LUMA. The first military aircraft of the young air force was a Hughes 500 - Model 369D helicopter, simply registered SAF-100 and being used for light observation tasks. Unfortunately the aircraft was written off in March 1982 killing all five occupants (Major Henk Fernandes, second lieutenant Norman de Miranda, soldier Tjon a Kon and soldier Kowid and American pilot Foster Ford),[1] but from May of the same year the Suriname Air Force was being equipped with four (Pilatus) Britten Norman BN-2B Defenders. Registered with the numbers SAF-001, SAF-002, SAF-003 and SAF-004. Later on during the decade a Cessna 172 Skyhawk (SAF-007), a Cessna 206 (SAF-200) and in 1993 a Cessna T303 Crusader (SAF-008) was acquired. The first official Surinam Air Force Commander from 1983 until 1989 was air force pilot lieutenant Eddie Alenso Savalie Djoe. He was one of the passenger victims of the Surinam Airways Flight 764 accident in June 1989, by then he was already promoted to the rank of Major.
All aircraft of the Suriname Air Force undertake border patrols, utility transport and SAR (Search & Rescue) missions from the main base at Paramaribo - Zorg en Hoop and are occasionally detached to Zanderij - Johan Adolf Pengel International Airport, Nieuw Nickerie - Major Fernandes Airfield, Albina Airstrip and Moengo Airstrip. In 1986 anti-government guerrilla activity prompted the government to acquire a pair of Aérospatiale SA.316B Alouette III (SAF-400 & SAF-500) helicopters from the Portuguese Air Force (Portuguese: Força Aérea Portuguesa), formerly registered FAP9350 & FAP9386. In the same year also three Pilatus PC-7's (SAF-111, SAF-112 & SAF-113) were ordered in Switzerland for COIN (Counter-Insurgency) missions. One of the Alouettes crashed and both delivered PC-7s were returned to Switzerland but one was later re-delivered. In 1987 a Bell 205 Iroquois (SAF-300) was acquired from Venezuela and used as a gunship for five years prior to sale to the US as N6594S in 1991. It crashed in July 1987[2] due to a mechanical failure killing the American pilot Billy Pearson, seriously injuring the American mechanic and four other Surinamese crewmembers.[3] The helicopter was later repaired and back in action.
Two CASA 212-400s Aviocar transports (SAF-212 & SAF-214) Garret AiResearch TPE331-10HR turbo-prop engined aircraft were delivered in 1999. One of these two Spanish built CASA 212-400s is a Maritime Patrol Aircraft version (SAF-214) which was modified for the maritime patrol role with a Bendix RDR-1500 surveillance radar.[4] Lack of spares and funding has hampered maintenance and sometimes grounding much of the SAF fleet. In 2012 six experts from Venezuela made an assessment for the Suriname Air Force on the rehabilitation of the Casa 212 airplanes and now the Suriname Air Force has sold them to Fayard Enterprises in the USA.
Three single engined Indian HAL Chetak helicopters were ordered in 2009.[5] In a deal worth US$13.4 million with Hindustan Aeronautics Limited [HAL], facilitated through a line of credit from India. The deal was previous rumoured to include the more modern twin engined HAL Dhruv helicopters, but this proved to be wrong.[6] [7] On 26 December 2012 ten technical personnel of the Suriname Air Force left to India to be trained to become certified helicopter mechanics.[8] In 2014 eight helicopter pilots from the Suriname Air Force were trained on operating the HAL Chetak helicopters in Bangalore, India.[9] In 2014 it was announced that Suriname's order for helicopters from India was in fact for HAL Chetak and not the HAL Dhruv even as the Chetak production line was planned to be shut down. Rumours aside, by the end of January 2015 the three Indian Chetak helicopters were assembled and delivered in Suriname as SAF-H001 (c/n AH-350), SAF-H002 (c/n AH-351) & SAF-H003 (c/n AH-352).[10] These registrations later changed to SAF-153, SAF-303 and SAF-811 when operational training started. The plan is to have one helicopter each based at the city of Paramaribo (Zorg en Hoop Airport), Nickerie (Majoor Henk Fernandes Airport) and Albina (Albina Airstrip).[11] Finally on 13 March 2015 the helicopter fleet of three Chetaks was officially handed over by the Indian ambassador Subashini Murgesan to the Minister of Defence of Suriname Lamuré Latour in a ceremony at Zorg en Hoop.[12][13] On the same day and occasion the Minister announced that a de Havilland Canada DHC-6 Twin Otter was about to be added to the airfleet of the Suriname Air Force shortly, with pilots already in training. Because of the financial crisis in Suriname, the Air Force has had to decommission one of its Chetaks.
Current inventory
| Aircraft | Origin | Type | Variant | In service | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Helicopters | ||||||
| HAL Chetak | SAR / utility | 3 |
1 Chetak attached with a M2 Browning | |||
Retired aircraft
Previous aircraft operated by the Air Wing include the Cessna 206, Pilatus PC-7, and Britten-Norman Islander. Helicopters included the Bell 205 and Alouette III.[14]
Navy and Coast Guard
In 1977 the Navy (Marine) of Suriname received three large patrol vessels from the Dutch, built by De Vries Scheepsbouw. With a length of 32 meters each ship had two Paxman 12YHMC diesel engines of 1200HP performing a maximum speed of 20 knots. Delivery was between February 1977 and 1978 and the hull numbers were S-401, S-402 and S-403. Now all three are out of service, the last one S-401 later P-401 is still moored at the Marine Harbor. One was re-built as a luxurious yacht. All ships had their base at the Marine harbor on the Suriname river.
Today most of the fleet of the Marine of Suriname are based at Boxel, close to the resort town of Domburg in the Wanica District on the Suriname river.
In November 2012 the defence and internal affairs Ministry of Suriname bought three patrol vessels from the French company Ocea for the Coast Guard. This order was worth 16 million euros. These patrol vessels will be used for fishery protection and to counterattack piracy in Surinamese waters. The first Fast Patrol Boat (P201), a 32 meters long, 6,3 meters wide FPB 98 type, was delivered in June 2013. The first boat arrived in Paramaribo with a container vessel from the port of Saint-Nazaire, France. The vessels can reach speeds of 30 knots. Delivery of the remaining two vessels (P101 & P102), FPB 72 types (24 meters long), occurred by the end of July, 2013.[15] The Surinamese Government ordered the three vessels, accelerating planning to set up a coast guard for Suriname that will be deployed to conduct patrol duties and fight maritime crime activities like illegal fishing, drug trafficking, and piracy.
The coast guard is a branch of the Ministry of Internal Affairs. Soldiers were transferred from the Navy Unit (Marine) of the National Army, to form the initial coast guard staff. The Maritime Authority of Suriname (MAS) is currently training 16 students from the Nature Technical Institute (NaTIn) and Technical Faculty of University of Suriname on how to conduct technical maintenance of the vessels. Ocea sent a trainer along with the boats to help conduct a six-month course. Colonel Jerry Slijngaard heads the Government's coast guard committee. While the first three boats will barely be sufficient to patrol Suriname's territorial waters and combat maritime crime activities such piracy, rapid reaction is now possible.
The unit has its own base on the banks of the Suriname River in Paramaribo, with posts at the border with Guyana (in western District Nickerie) and French Guiana (in eastern District Marowijne). Legislation on which the coast guard will be founded is almost finished. It will soon be tabled in the Council of Ministers and the Council of State, after which it will head for the National Assembly for approval. The new unit is a civil organisation, with authority to enforce the law in Suriname territorial waters. The Surinamese government does not intend to make cuts to the Navy (Marine), once the Coast Guard is fully operational. The Navy will keep operating in the high seas outside the 100-nautical-mile (190-kilometre) zone.
Command structure

The President of the Republic is the head of the armed forces, with the title of the Supreme Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces (Opperbevelhebber van de Strijdkrachten). The President is the supreme authority for all national military matters . The President is assisted by the Minister of Defence in his role over the armed forces, Mr. Lamure Latour. The director of the Ministry of Defence is Mr. John Achong.
Beneath the President and Minister of Defense is the Commander of the Armed Forces (Bevelhebber van de Strijdkrachten), Colonel Hedwig Gilaard, whose headquarters is in Paramaribo, was followed-up after three years by Colonel Ronni Benschop, who in turn was promoted to Brigade General in February 2014. This is the highest-ranked officer in the Armed Forces of Suriname ever.[16][17]
The Commander called "Bevelhebber", is the Military Chief, charged with command over the different Military Branches. The Military Branches and regional Military Commands report to the Commander.
Commanding officers of the Suriname Armed Forces at present
- President Chan Santokhi Supreme Commander-in-Chief
- Brigade General Ronni Benschop is Minister of Defence
- Colonel Robert Kartodikromo is Commander of the Armed Forces - Military Chief
- Colonel Adolf Jardim is Vice Commander of the Armed Forces - Deputy Chief
- Lieutenant Colonel Cherryl Chan Jon Chu is Chief of Staff
- Lieutenant Colonel Werner Kioe A Sen is the Commander of the Navy (Marine)
- Lieutenant Colonel Marven van Huisduinen is the Commander of the Air Force
- Major Tonny Haps is the Commander of the Army
- Lieutenant Colonel Floyd Mettendaf is Commander of the Military Police Corps
- Colonel Jerry Slijngard is Director of the Coast Guard
Commanders of the Suriname Armed Forces past to present
- Yngwe Elstak (25 November 1975 – 25 February 1980)
- Desi Bouterse (July 1980 – 3 December 1992)
- Ivan Graanoogst (temporary; 3 December 1992 – 15 May 1993)
- Arthy Gorré (15 May 1993 – 30 June 1995)
- Glenn Sedney (30 June 1995 – 1 July 2001)
- Ernst Mercuur (1 July 2001 – 4 February 2010)
- Hedwig Gilaard (4 February 2010 – 10 July 2013)
- Ronni Benschop (temporary; 10 July 2013 – February 2014)
- Ronni Benschop (February 2014 – August 2015)
- Adolf Jardim (acting) (August 2015 March 2019)
- Robert Kartodikromo (March 2019 – present)
The Armed Forces is Headquartered in Paramaribo.
The task of the national army of Suriname is defending the sovereignty and territorial integrity of Suriname against foreign armed military aggression. That is, the defense of not only the territory but also the territorial waters and the airspace above it.
The Ministry of defence consists of the Policy Centre and the operational part (the national army) that makes up the Defence Organization Forms. The Department of Defense has no departments. There are various services and units. The Policy Centre is responsible for the care of the armed forces so that timely and adequate it can perform the duties or missions assigned to it by law in an efficient and effective manner. Providing assistance to international organisations, if and to the extent that command is given for that purpose by the competent authority. This is e.g. for humanitarian operations of the United Nations. Also providing assistance in the preparation and implementation of projects related to the socio-economic development of Suriname
There are several military installations, barracks and detachments in the various districts including the Memre Boekoe Kazerne (Paramaribo), the Naval Marine base (district Wanica), the Air Force Luma base (Zorg en Hoop, Paramaribo), the training centre for recruits namely the Ayoko-barracks and the detachment Zanderij, the eastern border post, the Akontoe Velantie Kazerne at Albina, in Nickerie the western border post, the Professor Dr. Ali Kazerne and on the Kennedy Highway to Concordia the 1st Sgt Martowidjojo Kazerne. There are also various detachments and the so-called small stations throughout Suriname in the districts Sipaliwini, Saramacca, Brokopondo and Para. But also the protection of important objects such as the Afobakkadam or the bridge over the Coppename River belongs to the protective task of the National Army of Suriname.
Conflicts
Contra
The Armed Forces of Suriname were engaged in a domestic war against a few hundred freedom fighters who named themselves "Jungle Commandos" led by Ronnie Brunswijk between 1986 and 1992.
Surinamese armed forces also fought against the Resistance Amerindian groups who call themselves "Tucajana Amazon" and were led by Alex Jubitana and Thomas Sabajo. These Amerindian insurgents fought from 1986 to 1989. They opposed the expropriation of land owned by indigenous people and discrimination by the military regime.
Role
- Defend the territorial integrity of Suriname.
- Assist the civil power in the maintenance of law and order when required.
- Contribute to the economic development of Suriname.
The Army also participated in the Multi-National Force in Haiti in the 90's and were redeployed in 2010.[19]
Army Ranks
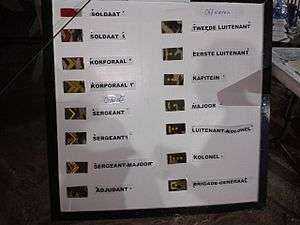
- Enlisted
- Soldaat (Soldier)
- Soldaat der eerste klasse (Private First Class)
- Korporaal (Corporal)
- Korporaal der eerste klasse (Corporal first class)
- Non-commissioned Officers
- Sergeant (Sergeant)
- Sergeant der eerste klasse (First Sergeant)
- Sergeant-Majoor (Sergeant-Major)
- Adjudant (Adjutant)
| Equivalent NATO code | OR-9 | OR-8 | OR-7 | OR-6 | OR-5 | OR-4 | OR-3 | OR-2 | OR-1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(Edit) |
 |
No equivalent |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adjudant | Sergeant-majoor | Sergeant der 1e klasse | Sergeant | Korporaal der 1e klasse | Korporaal | Soldaat der 1e klasse | Soldaat | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- Officers
| Equivalent NATO Code | OF-10 | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | OF(D) & Student officer | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(Edit) |
No equivalent |
 |
 |
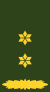 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brigade-generaal | Kolonel | Luitenant-kolonel | Majoor | Kapitein/Ritmeester | 1e Luitenant | 2e Luitenant | Vaandrig/Kornet | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Naval Equipment
- 7 patrol boats
- River Patrol Boat
- Inflatable boat
- Tug T-001 - ex-East German Navy Project 1381 Type 414 Karl Heinz I[20]
- Patrol Vessels (5)
- P201 (FPB 98 type patrol boat)
- P101 (FPB 72 type patrol boat)
- P102 (FPB 72 type patrol boat)
Future
With latest procurement of three HAL Chetak helicopters from India for the Air Force and three patrol vessels from France for the new Coast Guard the Armed Forces of Suriname should be better equipped to fulfill its roles in the future.
In September 12, 2012. The Suriname defense minister, Lamouré Latour, discussed with the Brazilian defense minister the possibility of the Military of Suriname acquiring from two to four Brazilian Embraer AT-29B Super Tucano light attack (COIN) trainer planes, 500 ton light patrol ships and the revitalization of the armoured vehicles supplied from Brazil in 1983.[21]
Equipment
Beretta 92- seen in use during training with U.S. Forces.
FN FAL- main rifle used by Army.
FN F2000- used by some units.
CETME Model L- seen in a parade.
EE-9 Cascavel armoured car (45)
EE-11 Urutu armoured personnel carrier (16)
DAF YP-408 Dutch made 6x8 armoured vehicle (5)
DAF YA440 trucks with M-55 anti-aircraft guns
ZPU-1 towed anti-aircraft guns
References
- Ranter, Harro. "Accident Hughes 500D (369D) SAF-100, 31 Mar 1982". aviation-safety.net. Archived from the original on 9 July 2015. Retrieved 2 February 2015.
- Ranter, Harro. "Accident Bell 205A-1 Iroquois SAF-300, 07 Jul 1987". aviation-safety.net. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 2 February 2015.
- "One Of Two Americans Reported Killed In Crash Of Army Helicopter". Apnewsarchive.com. Archived from the original on 2015-04-02. Retrieved 2015-02-01.
- "casa - 1999 - 2285 - Flight Archive". Flightglobal.com. Archived from the original on 3 February 2015. Retrieved 15 September 2014.
- "HAL Executes Export Order For Chetak Helicopters To Suriname - Hands Over 2 Of The 3 Contracted - AA Me, IN". Aame.in. Archived from the original on 17 May 2014. Retrieved 15 September 2014.
- "India ready to deliver three Dhruv copters to Suriname army". Pakistan Defence. Archived from the original on 15 July 2012. Retrieved 15 September 2014.
- "::Avianet.eu:: De luchtvaartsite van Nederland". Avianet.eu. Retrieved 15 September 2014.
- "Republiek Suriname - Overheid - TECHNICI LUCHTMACHT NAAR INDIA VOOR BIJSCHOLING". Gov.sr. Archived from the original on 13 September 2014. Retrieved 15 September 2014.
- "Indian helicopters already being flown by Surinamese pilots - Times of Suriname – grootste landelijke dagblad van Suriname". Times of Suriname - grootste landelijke dagblad van Suriname. Archived from the original on 13 September 2014. Retrieved 15 September 2014.
- "Starnieuws - Eerste Chetak helikopter in elkaar gezet op basis Luchtmacht". m.starnieuws.com. Archived from the original on 2015-02-03. Retrieved 2015-01-30.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2015-02-03. Retrieved 2015-03-15.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Starnieuws - Luchtmacht weer operationeel met eigen heli's". Starnieuws.com. Archived from the original on 2018-12-23. Retrieved 2015-03-15.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2015-03-20. Retrieved 2015-03-15.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "World Air Forces pg. 57". Flightglobal.com. Archived from the original on 1 July 2015. Retrieved 7 June 2015.
- "Kustwacht heeft nog geen personeel voor drie nieuwe Franse patrouilleboten – Laatste twee schepen nu ook in Suriname - Obsession Magazine". Obsession Magazine. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 15 September 2014.
- "Starnieuws - Benschop wordt officieel legerleider en brigade-generaal". Starnieuws.com. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 15 September 2014.
- "Ministerie van Defensie - Het Nationaal Leger". Gov.sr. Archived from the original on 20 October 2014. Retrieved 15 September 2014.
- "Nationaal Leger heeft na bijkans drie jaar weer bevelhebber". 22 March 2019.
- "Naharnet — Lebanon's leading news destination". Naharnet. Retrieved 15 September 2014.
- "KARL HEINZ 1 - IMO 8872203 - Ship Photos and Ship Tracker". Shipspotting.com. Archived from the original on 2016-11-26. Retrieved 2016-11-26.
- "Brasil moderniza estruturas de defesa da Guiana e do Suriname - Forças Terrestres - ForTe - Estratégia, Tecnologia Militar e Segurança". Forças Terrestres - ForTe - Estratégia, Tecnologia Militar e Segurança. Archived from the original on 29 October 2014. Retrieved 15 September 2014.
External links

