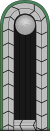
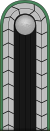
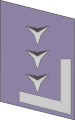
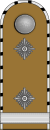
Comparative ranks of Nazi Germany
The comparative ranks of Nazi Germany contrasts the ranks of the Wehrmacht to a number of national-socialist organisations in Nazi Germany from 1933 to 1945 in a synoptic table. Nazi organisations used a hierarchical structure, according to the so-called Führerprinzip (leader principle), and were oriented in line with the rank order system of the Wehrmacht.[1]
Nazi rank structure in comparison to the Wehrmacht
Officer ranks
| Equivalent UK Army | None | Field marshal | General | Lieutenant-general | Major-general | Brigadier | Colonel | Lieutenant-colonel | Major | Captain | Lieutenant | Second lieutenant | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Heer & Luftwaffe [2][3][4] |
 Reichs-marschall |
.svg.png) |
.svg.png) |
_5.svg.png) |
.svg.png) |
_2.svg.png) |
 |
 |
 |
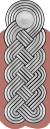 |
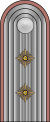 |
 |
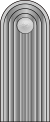 | ||||||||||||||||
| General-feldmarschall | Generaloberst im Range eines Generalfeldmarschalls | Generaloberst | General der Waffengattung | Generalleutnant | Generalmajor | Oberst | Oberstleutnant | Major | Hauptmann | Oberleutnant | Leutnant | ||||||||||||||||||
[5][6][7] |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |||||||||||||||||
| Großadmiral | Generaladmiral | Admiral | Vizeadmiral | Konteradmiral | Kommodore | Kapitän zur See | Fregatten- kapitän |
Korvetten- kapitän |
Kapitän- leutnant |
Oberleutnant zur See |
Leutnant zur See | ||||||||||||||||||
(TENO) [8][9] |
No equivalent |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
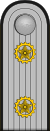 |
 |
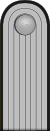 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Chef der TN | Stellvertretender chef der TN | TN-Landesführer | TN-Bezirksführer | TN-Hauptbereitschaftsführer | TN-Bereitschaftsführer | TN-Gefolgschaftsführer | TN-Gemeinschaftsführer | TN-Kameradschaftsführer | |||||||||||||||||||||
(DRK) [10] |
No equivalent |
 |
 |
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Generalhauptführer | Generalführer | Oberstführer | Oberfeldführer | Feldführer | Hauptführer | Oberwachführer | Wachführer | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Equivalent UK Army | None | Field marshal | General | Lieutenant-general | Major-general | Brigadier | Colonel | Lieutenant-colonel | Major | Captain | Lieutenant | Second lieutenant | |||||||||||||||||
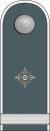
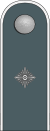
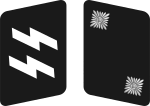
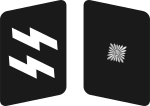
[11][12][13][4] |
No insignia |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
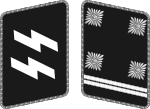 |
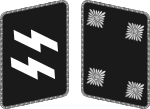 |
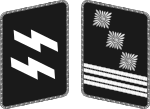 |
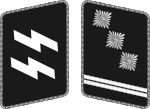 |
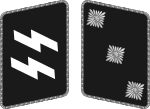 | |||||||||||||||||
| Oberster Führer der Schutzstaffel | Reichsführer-SS[lower-alpha 1] | SS-Oberst-Gruppenführer[lower-alpha 2] | SS-Obergruppenführer | SS-Gruppenführer | SS-Brigadeführer | SS-Oberführer | SS-Standartenführer | SS-Obersturmbannführer | SS-Sturmbannführer | SS-Hauptsturmführer[lower-alpha 3] | SS-Obersturmführer | SS-Untersturmführer | |||||||||||||||||
(Orpo) [16][17] |
No equivalent |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
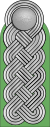 |
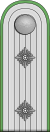 |
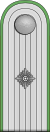 |
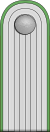 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Chef der Deutschen Polizei | Generaloberst der Polizei |
General der Polizei |
Generalleutnant der Polizei |
Generalmajor der Polizei |
Oberst der Polizei |
Oberstleutnant der Polizei |
Major der Polizei |
Hauptmann der Polizei |
Oberleutnant der Polizei |
Leutnant der Polizei | |||||||||||||||||||
(SA) [18][19] |
No insignia |  |
No equivalent |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
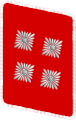 |
 |
 |
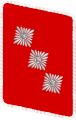 | ||||||||||||||||
| Oberster SA-Führer | Stabschef SA[20] | SA-Obergruppenführer | SA-Gruppenführer | SA-Brigadeführer | SA-Oberführer | SA-Standartenführer | SA-Obersturmbannführer | SA-Sturmbannführer | SA-Sturmhauptführer | SA-Obersturmführer | SA-Sturmführer | ||||||||||||||||||
(NSKK) [21][1][22] |
No equivalent |  |
No equivalent |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
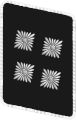 |
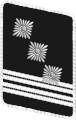 |
 |
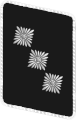 | ||||||||||||||||
| NSKK-Korpsführer | NSKK-Obergruppenführer | NSKK-Gruppenführer | NSKK-Brigadeführer | NSKK-Oberführer | NSKK-Standartenführer | NSKK-Obersturmbannführer | NSKK-Sturmbannführer | NSKK-Hauptsturmführer | NSKK-Obersturmführer | NSKK-Sturmführer | |||||||||||||||||||
(NSFK) [23][24][25] |
No equivalent |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
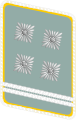 |
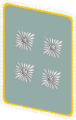 |
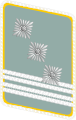 |
 |
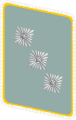 | ||||||||||||||||
| NSFK-Korpsführer | NSFK-Ehrenführer | NSFK-Obergruppenführer | NSFK-Gruppenführer | NSFK-Brigadeführer | NSFK-Oberführer | NSFK-Standartenführer | NSFK-Obersturmbannführer | NSFK-Sturmbannführer | NSFK-Hauptsturmführer | NSFK-Obersturmführer | NSFK-Sturmführer | ||||||||||||||||||
(RLB) [26][27] |
No equivalent |
 |
No equivalent |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||
| RLB-Präsident | General-Hauptluftschutzführer | General-luftschutzführer | Oberstluftschutzführer | Oberststabs-luftschutzführer | Stabsluftschutzführer | Hauptluftschutzführer | Oberluftschutzführer | Luftschutzführer | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Equivalent UK Army | None | Field marshal | General | Lieutenant-general | Major-general | Brigadier | Colonel | Lieutenant-colonel | Major | Captain | Lieutenant | Second lieutenant | |||||||||||||||||
(RAD) [28][29] |
No equivalent |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
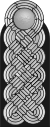 |
 |
 |
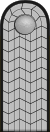 | |||||||||||||||||
| Reichs-arbeitsführer | Generaloberst- feldmeister |
Generalfeldmeister | Obergeneral-arbeitsführer | General-arbeitsführer | Oberstarbeitsführer | Oberarbeitsführer | Arbeitsführer | Oberstfeldmeister | Oberfeldmeister | Feldmeister | |||||||||||||||||||
(OT) [30][31][32] |
No equivalent |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|||||||||||||||||||
| Amtschef OT | OT-Einsatz-gruppenleiter I | OT-Einsatz-gruppenleiter II | OT-Einsatzleiter | OT-Hauptbauleiter | OT-Oberbauleiter | OT-Bauleiter | OT-Hauptbauführer | OT-Oberbauführer | OT-Bauführer | ||||||||||||||||||||
(HJ) [18][33] |
No equivalent |  Reichsjugendführer |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
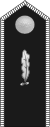 |
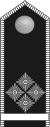 |
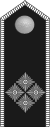 |
 |
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||
| Stabsführer | Obergebietsführer | Gebietsführer | Hauptbannführer | Oberbannführer | Bannführer | Ober- stammführer |
Stammführer | Hauptgefolg- schaftsführer |
Obergefolg- schaftsführer |
Gefolg- schaftsführer | |||||||||||||||||||
(DJ) |
No equivalent | No equivalent |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oberjungstammführer | Jungstammführer | Hauptfähnleinführer | Oberfähnleinführer | Fähnleinführer | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
[34] |
No equivalent | No equivalent |  |
 |
 |
 |
No equivalent |  |
 |
 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Reichsreferentin | Gebietsmädel- führerin |
Hauptmädel- führerin |
Bannmädelführerin | Ringführerin | Hauptgruppenführerin | Gruppenführerin | |||||||||||||||||||||||
(NSDAP) [35] |
No equivalent |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |||||||||
| Reichsleiter | Gauleiter | Hauptbefehlsleiter | Oberbefehlsleiter | Befehlsleiter | Hauptdienst- leiter |
Oberdienst- leiter |
Dienst- leiter |
Hauptbereichs- leiter (Kreisleiter) |
Bereichsleiter | Haupt- abschnittsleiter |
Ober- abschnitts- leiter |
Abschnitts- leiter |
Haupt- gemeinschafts- leiter (Ortsgruppenleiter) |
Ober- gemeinschafts- leiter |
Gemeinschafts- leiter |
Haupteinsatz- leiter |
Obereinsatz- leiter |
Einsatz- leiter | |||||||||||
| Equivalent UK Army | None | Field marshal | General | Lieutenant-general | Major-general | Brigadier | Colonel | Lieutenant-colonel | Major | Captain | Lieutenant | Second lieutenant | |||||||||||||||||
Enlisted
gollark: Ah, inevitably.
gollark: It even does replies.
gollark: ++search dictionary apioforms
gollark: ++search apioforms
gollark: Although the code is substantially nicer, and it does actual HTML parsing.
See also
- Comparative military ranks of World War II
- Glossary of German military terms
- Glossary of Nazi Germany
- World War II German Army ranks and insignia
Notes
- Heinrich Himmler's title became an actual rank after the Night of the Long Knives in 1934. From that point on, Reichsführer-SS became the highest rank of the SS and was considered on paper the equivalent of a Generalfeldmarschall in the Wehrmacht; however, as Himmler's position and authority grew in Nazi Germany, so did his rank in a "de facto" sense.[14]
- Decree paper of the Waffen-SS, 3rd (annual) volume – Berlin, June 15, 1942 – number 12 – p.46: “The Reichsführer-SS gave order regarding the spelling of the new service rank “SS-Oberst-Gruppenführer” (quotation: “SS-Oberst-Gruppenführer” (en: SS-Supreme-Group leader – OF-9), in order to avoid confusion to the SS-Obergruppenführer (en: SS-Senior group leader – OF-8)”.[15]
- Until castration of the SA in summer 1934 the designation of that particular rank in the SS was SS-Sturmhauptführer (SS-Storm head leader). However, the rank was renamed to SS-Hauptsturmführer (SS-Head storm leader). In line with the formation of the SA-Defence crews (SA-Wehrmannschaften) in 1939/40 it was renamed to “Hauptsturmführer” in the SA and in all other Nazi organizations.
- Mann for the Allgemeine SS
- The youngest members of the Hitler Youth organization in Nazi Germany
References
Citations
- Weiß 2002, Appendix.
- Verlag Moritz Ruhl 1936, Table 3-4,7-8.
- CIA 1999, p. 18.
- Zabecki 2014, p. 1639.
- Verlag Moritz Ruhl 1936, Table 9-10.
- KBismarck.com 2012.
- Zabecki 2014, pp. 1640-1641.
- Verlag Moritz Ruhl 1942, table 13.
- CIA 1999, p. 33.
- Verlag Moritz Ruhl 1942, Table 14.
- Verlag Moritz Ruhl 1936, Table 14.
- Williamson 1994, p. 250.
- CIA 1999, p. 30.
- McNab 2009, pp. 9, 30, 46-47.
- Klietmann 1967.
- Verlag Moritz Ruhl 1936, Table 23.
- CIA 1999, pp. 20, 31.
- Verlag Moritz Ruhl 1936, Table 20.
- CIA 1999, p. 29.
- Specialist editor of the Bibliographical Institute 1938, p. 203.
- Verlag Moritz Ruhl 1936, Table 18.
- CIA 1999, p. 23.
- Verlag Moritz Ruhl 1936, Table 17.
- Ley 1937, Table 73.
- CIA 1999, p. 24.
- Verlag Moritz Ruhl 1936, Table 19.
- Verlag Moritz Ruhl 1942, Table 22.
- Verlag Moritz Ruhl 1936, Table 13.
- CIA 1999, p. 27.
- Absolon 1969, p. 59.
- Lepage 2015, p. 22.
- MIRS 1945, Table II–III.
- CIA 1999, p. 21.
- Littlejohn 1989, .
- CIA 1999, pp. 25-26.
- Zabecki 2014, p. 1640.
- Zabecki 2014, pp. 1640-1642.
Bibliography
- Absolon, Rudolf (1969). Die Wehrmacht im Dritten Reich (in German). IV. Boppard am Rhein: Harald Boldt Verlag. ISBN 978-3764619404.
- CIA (24 August 1999). "Records Integration Title Book" (PDF). Retrieved 11 December 2018.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- KBismarck.com (2012). "Kriegsmarine Rank Chart". kbismarck.com. Retrieved 24 June 2020.
- Klietmann, Kurt-Gerhard (1967). Feldgrau (in German). Berlin: Die Ordens-Sammlung. 13 (1). Missing or empty
|title=(help) - Lepage, Jean-Denis G. G. (2015). Hitler's Armed Forces Auxiliaries: an illustrated history of the Wehrmachtsgefolge, 1933-1945. McFarland. ISBN 978-0786497454.
- Ley, Robert (1937). Organisationsbuch der NSDAP (in German). Zentralverlag.
- Littlejohn, David (1989). The Hitler Youth. Agincourt Publishers. ISBN 978-0934870214. Retrieved 25 November 2018.
- McNab, Chris (2009). The SS: The Growth and Organisation of Himmler's Stormtroopers. Amber Books. ISBN 978-1906626495.
- MIRS (1945). Handbook of the organisation TODT (OT). London: MIRS.
- Specialist editor of the Bibliographical Institute, ed. (1938). Schlag nach Wissenswerte Tatsachen aus allen Gebieten (in German). Leipzig: Bibliographisches Institut AG Leipzig.
- Verlag Moritz Ruhl (1936). Deutche Uniformen (in German). Leipzig: Verlag Moritz Ruhl.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Verlag Moritz Ruhl (1942). Deutche Uniformen (in German). Leipzig: Verlag Moritz Ruhl.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Weiß, Hermann, ed. (2002). Biographisches Lexikon zum Dritten Reich [Biographical lexicon to the Third Reich] (in German). Frankfurt am Main: Fischer Taschenbuch Verlag. ISBN 978-3596130863.
- Williamson, Gordon (1994). The SS: Hitler's Instrument of Terror. Chartwell Books, Inc. p. 250. ISBN 978-0785830122.
- Zabecki, David T., ed. (2014). Germany at War: 400 Years of Military History. ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-1598849806.
Further reading
- Wolfgang Benz (editor): Wie wurde man Parteigenosse? Die NSDAP und ihre Mitglieder. Fischer-Taschenbuch-Verlag, Frankfurt am Main 2009, ISBN 978-3-596-18068-4 (Fischer 18068 Die Zeit des Nationalsozialismus).
- Davis, Brian L. (1942). Badges and Insignia of the Third Reich 1933-1945. Cassell. ISBN 978-1854095121.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.