Le Bugue
Le Bugue (Occitan: Al Buga or Lo Buga) is a commune in the Dordogne department in southwestern France.
Le Bugue | |
|---|---|
 Town hall | |
.svg.png) Coat of arms | |
Location of Le Bugue 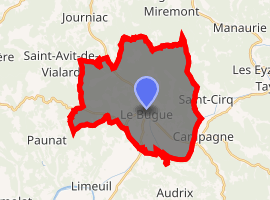
| |
 Le Bugue  Le Bugue | |
| Coordinates: 44°55′15″N 0°55′41″E | |
| Country | France |
| Region | Nouvelle-Aquitaine |
| Department | Dordogne |
| Arrondissement | Sarlat-la-Canéda |
| Canton | Vallée de l'Homme |
| Intercommunality | Vallée de l'Homme |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2014 -) | Jean Montoriol |
| Area 1 | 28.96 km2 (11.18 sq mi) |
| Population (2017-01-01)[1] | 2,587 |
| • Density | 89/km2 (230/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| INSEE/Postal code | 24067 /24260 |
| Elevation | 48–245 m (157–804 ft) (avg. 60 m or 200 ft) |
| 1 French Land Register data, which excludes lakes, ponds, glaciers > 1 km2 (0.386 sq mi or 247 acres) and river estuaries. | |
Geography
Le Bugue is located on the banks of the Vézère River a few kilometres before the confluence of the Vézère with the Dordogne River at Limeuil. Le Bugue is also on two national routes (Route Nationale 703 and Route Nationale 710).
History
Le Bugue has been inhabited since prehistoric times. In 964 a Benedictine monastery was founded in Le Bugue under the name of Saint Marcel and Saint Salvador. The monastery had disappeared by the late 19th century.
Le Bugue enjoyed a period of prosperity until 1154, when the province of Périgord came under English control. Le Bugue was often disputed between British troops and those of the King of France, and therefore suffered greatly.
One of the most important dates in the history of Le Bugue is November 1319, when the King of France, Philippe Le Long, ordered by deed that the market be perpetually held on Tuesday. This act is still presently in force.
Le Bugue was a quiet commercial town until the French Revolution. However, it endured some fratricidal struggles between the lords of Limeuil and Fleurac.
The end of the 19th century was marked by the construction of the local bridge and the arrival of the railroad (the line between Périgueux and Agen).
Le Bugue owes part of its fame to the chemist and physician Jean Rey who discovered the Law of Conservation of Mass 200 years before Lavoisier. Jean Rey also invented the "Thermoscope", the forerunner of the modern thermometer.
Population
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1864 | 2,969 | — |
| 1962 | 2,424 | −18.4% |
| 1968 | 2,741 | +13.1% |
| 1975 | 2,778 | +1.3% |
| 1982 | 2,784 | +0.2% |
| 1990 | 2,764 | −0.7% |
| 1999 | 2,781 | +0.6% |
| 2008 | 2,793 | +0.4% |
| 2011 | 2,728 | −2.3% |
See also
Personality
- Jean Rey (c. 1583 - c. 1645) was a French physician and chemist.
- Jean Kerebel (Jean-Baptiste Kerebel; 2 April 1918 in Paris – 9 March 2010) was a French track and field athlete who mainly competed in the 400 metres.
References
- "Populations légales 2017". INSEE. Retrieved 6 January 2020.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Le Bugue. |