Yaws
Yaws is a tropical infection of the skin, bones and joints caused by the spirochete bacterium Treponema pallidum pertenue.[6][8] The disease begins with a round, hard swelling of the skin, 2 to 5 centimeters in diameter.[6] The center may break open and form an ulcer.[6] This initial skin lesion typically heals after three to six months.[7] After weeks to years, joints and bones may become painful, fatigue may develop, and new skin lesions may appear.[6] The skin of the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet may become thick and break open.[7] The bones (especially those of the nose) may become misshapen.[7] After five years or more large areas of skin may die, leaving a scar.[6]
| Yaws | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Frambesia tropica, thymosis, polypapilloma tropicum,[1] non-venereal endemic syphilis,[2] parangi and paru (Malay),[3] bouba (Spanish),[3] frambösie,[4] pian[5] (French),[3] frambesia (German),[3] bakataw (Maguindanaoan)[3] |
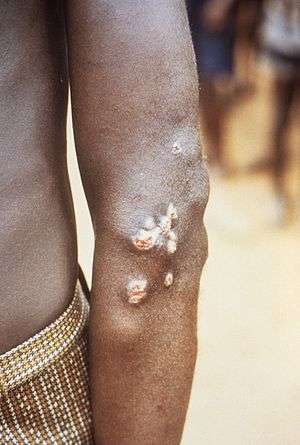 | |
| Nodules on the elbow resulting from a Treponema pallidum pertenue bacterial infection | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
| Symptoms | Hard swelling of the skin, ulcer, joint and bone pain[6] |
| Causes | Treponema pallidum pertenue spread by direct contact[7] |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms, blood antibody tests, polymerase chain reaction[7] |
| Prevention | Mass treatment[7] |
| Medication | Azithromycin, benzathine penicillin[7] |
| Frequency | 46,000-500,000[7][8] |
Yaws is spread by direct contact with the fluid from a lesion of an infected person.[7] The contact is usually of a non-sexual nature.[7] The disease is most common among children, who spread it by playing together.[6] Other related treponemal diseases are bejel (Treponema pallidum endemicum), pinta (Treponema carateum), and syphilis (Treponema pallidum pallidum).[7] Yaws is often diagnosed by the appearance of the lesions.[7] Blood antibody tests may be useful but cannot separate previous from current infections.[7] Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is the most accurate method of diagnosis.[7]
There is no vaccine.[9] Prevention is, in part, by curing those who have the disease thereby decreasing the risk of transmission.[7] Where the disease is common, treating the entire community is effective.[7] Improving cleanliness and sanitation will also decrease spread.[7] Treatment is typically with antibiotics including: azithromycin by mouth or benzathine penicillin by injection.[7] Without treatment, physical deformities occur in 10% of cases.[7]
Yaws is common in at least 13 tropical countries as of 2012.[6][7] Almost 85% of infections occurred in three countries—Ghana, Papua New Guinea, and Solomon Islands.[10] The disease only infects humans.[7] Efforts in the 1950s and 1960s by the World Health Organization (WHO) decreased the number of cases by 95%.[7] Since then cases have increased and there are renewed efforts to globally eradicate the disease by 2020.[7] In 1995 the number of people infected was estimated at more than 500,000.[8] In 2016 the number of reported cases was 59,000.[11] Although one of the first descriptions of the disease was made in 1679 by Willem Piso, archaeological evidence suggests that yaws may have been present among human ancestors as far back as 1.6 million years ago.[6]
Signs and symptoms
Yaws is classified as primary, secondary, and tertiary; this is useful, but actual people often have a mix of stages.[2]
Within 9–90 days (but usually about 21 days[2]) of infection, a painless but distinctive "mother yaw" nodule appears.[2] Initially reddened and inflamed,[12] it may become a papilloma, which can then become an ulcer,[7] possibly with a yellow crust.[13] Mother yaws are most commonly found on the legs and ankles, and are rarely found on the genitals (unlike syphilis)[2] The mother yaw enlarges and becomes warty in appearance. Nearby "daughter yaws" may also appear simultaneously. This primary stage resolves completely, with scarring, within three to six months.[12] The scar is often pigmented.[2]
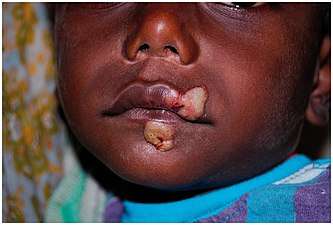 Papilloma mother yaw
Papilloma mother yaw.jpg) Mother yaw nodule with central ulceration and a yellow crust
Mother yaw nodule with central ulceration and a yellow crust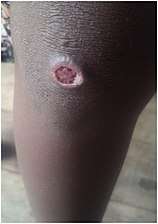 Ulcerated mother yaw
Ulcerated mother yaw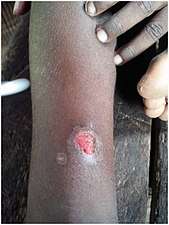 Ulcerated mother yaw
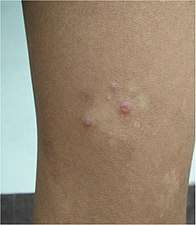
Ulcerated mother yaw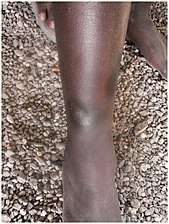 Healed primary yaw lesion, showing pigmented scar
Healed primary yaw lesion, showing pigmented scar
The secondary stage occurs months to two years later (but usually one-two months later), and may thus begin when the mother yaw has not yet healed.[2] It happens when the bacterium spreads in the blood and lymph. It begins as multiple pinhead-like papules; these initial lesions grow and change in appearance and may last weeks before healing, with or without scarring.[2]
Secondary yaws typically shows widespread skin lesions that vary in appearance, including "crab yaws" (areas of skin of abnormal colour) on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet[12] (named for the crab-like gait they cause people with painful soles to assume[2]). These may show desquamation. These secondary lesions frequently ulcerate and are then highly infectious, but heal after six months or more.
Secondary yaws affects the skin and bones.[12] The most common bone-related problem is periostitis, an inflammation around the bone, often occurs in the bones of the fingers and the long bones of the lower arm and leg, causing swollen fingers and limbs.[12] This causes pain at night and thickening of the affected bones (periostitis).[2] 75% of infected children surveyed in Papua New Guinea reported joint pain.[2] Swollen lymph nodes, fever, and malaise are also common.[12]
After primary and secondary yaws (and possibly, in some cases, without these phases), a latent infection develops.[2] Within five years (rarely, within ten years[2]) it can relapse and become active again, causing further secondary lesions, which may infect others.[12] These relapse lesions are most commonly found around the armpits, mouth, and anus.[2]
 Secondary yaws begin as multiple small lesions
Secondary yaws begin as multiple small lesions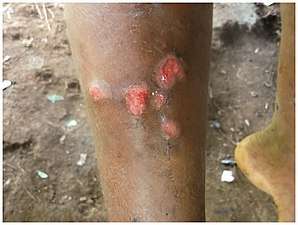 The small lesions grow.
The small lesions grow.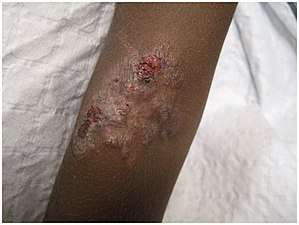 Secondary lesions vary in appearance (see list of terms)
Secondary lesions vary in appearance (see list of terms).jpg) Here two different appearances (papulosquamous plaque and yellow-crusted nodules) are seen in the same 10-year-old person (large-scale of both, close-up of nodules)
Here two different appearances (papulosquamous plaque and yellow-crusted nodules) are seen in the same 10-year-old person (large-scale of both, close-up of nodules)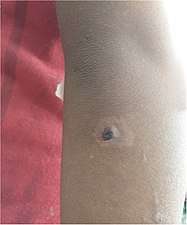 Hypopigmentation and an crusted erosion, elbow of a 5-year-old
Hypopigmentation and an crusted erosion, elbow of a 5-year-old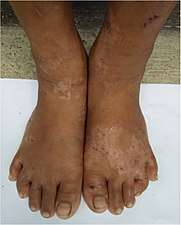 Secondary yaws; hypopigmented areas of skin topped with pink and brown papules, 9-year-old
Secondary yaws; hypopigmented areas of skin topped with pink and brown papules, 9-year-old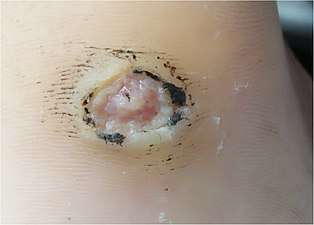 Erosion on the sole of the foot, close-up (large-scale). If deeper, it would be an ulcer
Erosion on the sole of the foot, close-up (large-scale). If deeper, it would be an ulcer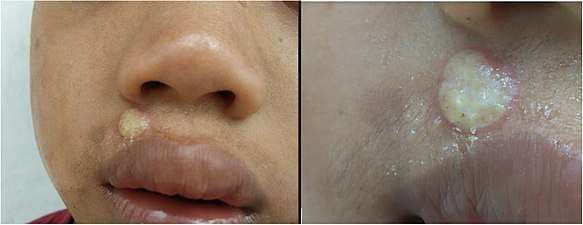 Secondary yaws papilloma (same 9-year-old as pictures of feet)
Secondary yaws papilloma (same 9-year-old as pictures of feet) Secondary breakout in a Javanese child age of 12 years. Wax model
Secondary breakout in a Javanese child age of 12 years. Wax model.jpg) Secondary yaws scars in an adult with childhood history of yaws
Secondary yaws scars in an adult with childhood history of yaws
It was formerly estimated that about 10% of people with yaws develop tertiary disease symptoms, but more recently tertiary yaws has been more rarely reported.[12][2]
Tertiary yaws can include gummatous nodules. It most commonly affects the skin. The skin of the palms and soles may thicken (hyperkeratosis). Nodules ulcerating near joints can cause tissue death. Periostitis can be much more severe. The shinbones may become bowed (saber shin)[12] from chronic periostitis.[2] Osteitis around the nose may cause ulceration of the palate and nasopharynx, which can lead to extensive destruction of the bone and cartilage of the nose, jaw, and face (called Rhinopharyngitis mutilans or gangosa). This is now rare.[2] Very rarely,[2] yaws may cause bone spurs in the upper jaw near the nose (gondou); gondou was rare even when yaws was a common disease.[12]
Yaws may or may not have cardiovascular or neurological effects; there is a lack of definitive evidence.[2]
_(14761746096).jpg) Deep ulceration occurs in tertiary yaws
Deep ulceration occurs in tertiary yaws_(14804596673).jpg) Severe tertiary yaws; gangosa
Severe tertiary yaws; gangosa_p1117_(cropped_to_goundu).jpg) Goundu, a very rare yaws-caused deformity around the nose
Goundu, a very rare yaws-caused deformity around the nose
Cause
The disease is transmitted by skin-to-skin contact with an infective lesion,[12] with the bacterium entering through a pre-existing cut, bite or scratch.[2]
Early (primary and secondary) yaws lesions have a higher bacterial load and are thus more infectious.[2] Both papillomas and ulcers are infectious.[7] Infectivity is thought to last 12–18 months after infection, longer if there is a relapse. Early yaws lesions are often itchy, and more lesions may form along lines that are scratched. Yaws may be evolving less conspicuous lesions.[2]
Yaws is most common among children, who spread it by playing together.[6] It is not thought that yaws is transmitted from mother to child in the womb,[6] though this is not entirely certain.[2] Yaws is not a venereal disease.[2]
T. pallidum pertenue has been identified in non-human primates (baboons, chimpanzees, and gorillas) and studies show that experimental inoculation of human beings with a simian isolate causes yaws-like disease. However, no evidence exists of cross-transmission between human beings and primates, but more research is needed to discount the possibility of a yaws animal reservoir in non-human primates.[6]
Diagnosis
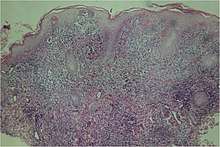
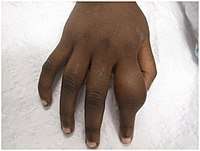
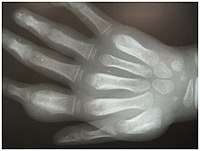
Most often the diagnosis is made clinically.[14] Dark field microscopy of samples taken from early lesions (particularly ulcerative lesions[14]) may show the responsible bacteria; the spirochaetes are only 0.3 µm wide by 6–20 µm long, so light-field microscopy does not suffice.[2]
A microscopic examination of a biopsy of a yaw may show skin with clear epidermal hyperplasia (a type of skin thickening) and papillomatosis (a type of surface irregularity), often with focal spongiosis (an accumulation of fluid in specific part of the epidermis). Immune-system cells, neutrophils and plasma cells, accumulate in the skin, in densities that may cause microabscesses.
Warthin-Starry or Levaditi silver stains selectively stain T. pallidum, and direct and indirect immunofluorescence and immunoperoxidase tests can detect polyclonal antibodies to T. pallidums. Histology often shows some spatial features which distinguish yaws from syphilis (syphilis is more likely to be found in the dermis, not the epidermis, and shows more endothelial cell proliferation and vascular obliteration).[2]
Blood-serum (serological) tests are increasingly done at the point of care. They include a growing range of treponemal and non-treponemal assays. Treponemal tests are more specific, and are positive for any one who has ever been infected with yaws; they include the Treponema pallidum particle agglutination assay. Non-treponemal assays can be used to indicate the progress of an infection and a cure, and positive results weaken and may become negative after recovery, especially after a case treated early.[12] They include the venereal disease research laboratory (VDRL; requires microscopy) and rapid plasma reagin (RPR; naked-eye result) tests, both of which flocculate patient-derived antibodies with antigens.[2]
Serological tests cannot distinguish yaws from the closely related syphilis;[2] no test distinguishing yaws from syphilis is widely available. The two genomes differ by about 0.2%. PCR and DNA sequencing can distinguish the two.[2] There are also no common blood tests which distinguish among the four treponematoses: syphilis (Treponema pallidum pallidum), yaws (Treponema pallidum pertenue), bejel (Treponema pallidum endemicum), and pinta (Treponema carateum).[14]
Haemophilus ducreyi infections can cause skin conditions that mimic primary yaws. People infected with Haemophilus ducreyi lesions may or may not also have latent yaws, and thus may or may not test positive on serological tests. This was discovered in the mid 2010s.[12] It seems that a recently diverged strain of Haemophilus ducreyi has evolved from being a sexually transmitted infection to being a skin ulcer pathogen that looks like yaws.[15]
Yaws has been reported in non-endemic countries.[2]
Treatment
Treatment is normally by a single intramuscular injection of long-acting benzathine benzylpenicillin, or less commonly by a course of other penicillins,[12] such as erythromycin or tetracycline tablets. Penicillin has been the front-line treatment since at least the 1960s, but there is no solid evidence of the evolution of penicillin resistance in yaws.[12]
The historical strategy for the eradication of yaws (1952–1964) was:[12]
| Prevalence of Clinically Active Yaws | Treatment Strategy |
|---|---|
| Hyperendemic: above 10% | Benzathine benzylpenicillin to the whole community
(total mass treatment) |
| Mesoendemic: 5–10% | Treat all active cases, all children under 15 and all contacts of infectious cases
(juvenile mass treatment) |
| Hypoendemic: under 5% | Treat all active cases and all household and other contacts
(selective mass treatment) |
Benzathine benzylpenicillin requires a cold chain and staff who can inject it, and there is a small risk of anaphylaxis. It was also not reliably available during the 2010s; there have been supply shortages.[12]
In the 2010s, a single oral dose of azithromycin was shown to be as effective as intramuscular penicillin.[16][12] Unlike penicillin, there is strong evidence that yaws is evolving antibiotic resistance to azithromycin; there are two known mutations in the bacterium, each of which can cause resistance and make the treatment ineffective. This has threatened eradication efforts.[12]
Within 8–10 hours of penicillin treatment, bacteria can no longer be found in lesion biopsies.[2] Primary and secondary lesions usually heal in 2–4 weeks; bone pain may improve within two days.[12] If treated early enough, bone deformities may reverse and heal.[2] Primary and secondary stage lesions may heal completely, but the destructive changes of tertiary yaws are largely irreversible.
If lesions do not heal, or RPR test results do not improve, this may indicate treatment failure or re-infection; the treatment is typically repeated.[2] WHO guidelines says that any presumed treatment failures at 4 weeks require macrolide resistance testing.[7]
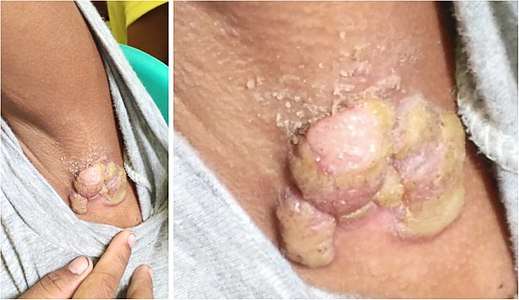 Secondary yaws in the left armpit of a ten-year-old, 2020
Secondary yaws in the left armpit of a ten-year-old, 2020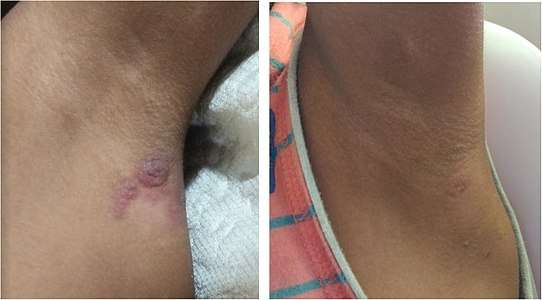 Same person, 2 weeks and 3.5 months after a single-dose azithromycin
Same person, 2 weeks and 3.5 months after a single-dose azithromycin Before and two weeks after a single injection of benzathine penicillin, 1950s.
Before and two weeks after a single injection of benzathine penicillin, 1950s.
Epidemiology
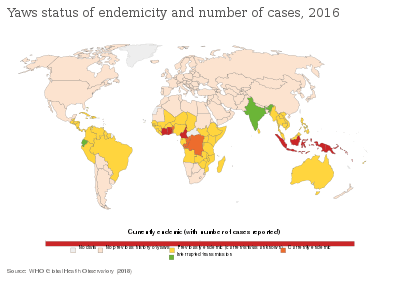
— WHO saying, quoted by Kingsley Asiedu.[18]
Because T. pallidum pertenue is temperature- and humidity-dependent, yaws is found in humid tropical[12] forest regions in South America, Africa, Asia and Oceania.[9][7]
About three quarters of people affected are children under 15 years of age, with the greatest incidence in children 6–10 years old.[19] Therefore, children are the main reservoir of infection.[9]
It is more common in remote areas, where access to treatment is poorer.[12] It is associated with poverty and poor sanitation facilities and personal hygiene.[9][20][7]
Worldwide, almost 85% of yaws cases are in Ghana, Papua New Guinea, and the Solomon Islands. Rates in sub-Saharan Africa are low, but tend to be concentrated in specific populations. As of 2015, it is estimated that about 89 million people live in yaws-endemic areas, but data are poor, and this is likely an over-estimate.[20]
In the early 1900s, yaws was very common; in sub-saharan Africa, it was more frequently treated than malaria, sometimes making up more than half of treatments.[9]
Mass treatment campaigns in the 1950s reduced the worldwide prevalence from 50–150 million to fewer than 2.5 million; however, during the 1970s there were outbreaks in South-East Asia, and there have been continued sporadic cases in South America. As of 2011, it was unclear how many people worldwide were currently infected.[21]
From 2008 to 2012, 13 countries reported over 300 000 new cases to the WHO. There was no system for certifying local elimination of yaws, and it is not known whether the lack of reports form some countries is because they stopped having yaws cases or because they stopped reporting them. It is estimated that if there is not an active surveillance programme, there is less than a 1-in-2 chance that a country will successfully report yaws cases (if it gets them) in over three-quarters of countries with a history of yaws. These countries are thought to need international assistance to mount effective surveillance.[22]
Generally, yaws is not a notifiable disease.[20]
History

Examination of remains of Homo erectus from Kenya, that are about 1.6 million years old, has revealed signs typical of yaws. The genetic analysis of the yaws causative bacteria—Treponema pallidum pertenue—has led to the conclusion that yaws is the most ancient of the four known Treponema diseases. All other Treponema pallidum subspecies probably evolved from Treponema pallidum pertenue. Yaws is believed to have originated in tropical areas of Africa, and spread to other tropical areas of the world via immigration and the slave trade. The latter is likely the way it was introduced to Europe from Africa in the 15th century. The first unambiguous description of yaws was made by the Dutch physician Willem Piso. Yaws was clearly described in 1679 among African slaves by Thomas Sydenham in his epistle on venereal diseases, although he thought that it was the same disease as syphilis. The causative agent of yaws was discovered in 1905 by Aldo Castellani in ulcers of patients from Ceylon.[6]
The current English name is believed to be of Carib origin, from "yaya", meaning sore.[14]
Eradication



It is currently thought that it may be possible to eradicate yaws although it is not certain that humans are the only reservoir of infection.[21] A single injection of long-acting penicillin or other beta lactam antibiotic cures the disease and is widely available,[23] and the disease is believed to be highly localised.
A 1953 questionnaire-based estimate was that there were 50-150 million yaws cases in 90 countries.[20]
The global prevalence of this disease and the other endemic treponematoses, bejel and pinta, was reduced by the Global Control of Treponematoses (TCP) programme between 1952 and 1964 from about 50 to 150 million cases to about 2.5 million (a 95 percent reduction). Following the cessation of this program yaws surveillance and treatment became a part of primary health systems of the affected countries. However incomplete eradication led to a resurgence of yaws in the 1970s with the largest number of case found in the Western Africa region.[21][24]
There have been a series of yaws eradication efforts; these have succeeded in eradicating the disease locally from many countries, but have not lasted long enough to eradicate it globally. It was one of the first diseases targeted by the WHO after the organization was formed in 1948. The first effort was from 1952 to 1964, by the WHO and the UNICEF. It reduced the number of cases to 5% of the former burden, from 50 million cases to 2.5 million. Attempts to integrate yaws eradication into the primary healthcare system in the late 1960s failed, and by the 1970s, yaws was making a comeback in many countries. Weak control efforts were made in the late 70s and mid-80s. In 1995, the WHO estimated 460 000 worldwide cases. With few cases, mainly affecting poor, remote communities with little access to treatment, yaws became poorly known, yaws knowledge and skills died out even among health professionals, and yaws eradication was not seen as a high priority. Many eradication campaigns ended in complacency and neglect; even in areas where transmission was successfully interrupted, re-introduction from infected areas occurred. Yaws eradication remained a priority in south-east Asia.[18][23]
Prior to the 2012-onwards WHO campaign, India launched its own national yaws elimination campaign which appears to have been successful.[23][25] Certification for disease-free status requires an absence of the disease for at least five years. In India this happened on 19 September 2011. In 1996 there were 3,571 yaws cases in India; in 1997 after a serious elimination effort began the number of cases fell to 735. By 2003 the number of cases was 46. The last clinical case in India was reported in 2003 and the last latent case in 2006.[26] India is a country where yaws is now considered to have been eliminated.[27]
In the Phillipines, yaws stopped being listed as a notifiable disease in 1973; as of 2020, it is still present in the country.[3]
Following the development of orally administered azithromycin as a treatment, in the WHO targeted yaws for eradication by 2020.[28] In April 2012, WHO initiated a new global campaign for the eradication of yaws, which has been on the WHO eradication list since 2011. The official roadmap aimed for elimination by 2020.[29][30]
The Morges approach (named after Morges, Switzerland, where a meeting on it was held[31]) involved mass treatment with azithromycin. This was safe, but ran into problems with antibiotic resistance, and did not fully interrupt transmission.[12]
In March 2013, the WHO convened a new meeting of yaws experts in Geneva to further discuss the strategy of the new eradication campaign. The meeting was significant, and representatives of most countries where yaws is endemic attended and described the epidemiological situation at the national level. The disease is currently known to be present in Indonesia and Timor-Leste in South-East Asia; Papua New Guinea, the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu in the Pacific region; and Benin, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Congo, Côte d'Ivoire, Democratic Republic of Congo, Ghana and Togo in Africa. As reported at the meeting, in several such countries, mapping of the disease is still patchy and will need to be completed before any serious eradication effort could be enforced.[32]
Little progress was made on reducing incidence between 1992 and 2015. In 2015, there was no information on the incidence of yaws in at least 19 countries.[20]
In 2016 the number of reported cases was 59,000, but data was missing from many countries. The WHO had last updated these figures in 2018, and had not published numbers for years after 2016, as of 2020.[11]
References
- Maxfield, L; Crane, JS (January 2020). "Yaws (Frambesia tropica, Thymosis, Polypapilloma tropicum, Parangi, Bouba, Frambosie, Pian)". PMID 30252269. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Marks, M; Lebari, D; Solomon, AW; Higgins, SP (September 2015). "Yaws". International Journal of STD & AIDS. 26 (10): 696–703. doi:10.1177/0956462414549036. PMC 4655361. PMID 25193248.
- Dofitas, BL; Kalim, SP; Toledo, CB; Richardus, JH (30 January 2020). "Yaws in the Philippines: first reported cases since the 1970s". Infectious Diseases of Poverty. 9 (1): 1. doi:10.1186/s40249-019-0617-6. PMC 6990502. PMID 31996251.
- Rapini RP, Bolognia JL, Jorizzo JL (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
- James WD, Berger TG, et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0. OCLC 62736861.
- Mitjà O; Asiedu K; Mabey D (2013). "Yaws". The Lancet. 381 (9868): 763–73. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)62130-8. PMID 23415015. S2CID 208791874.
- "Yaws Fact sheet N°316". World Health Organization. February 2014. Archived from the original on 3 March 2014. Retrieved 27 February 2014.
- Mitjà O; Hays R; Rinaldi AC; McDermott R; Bassat Q (2012). "New treatment schemes for yaws: the path toward eradication" (pdf). Clinical Infectious Diseases. 55 (3): 406–412. doi:10.1093/cid/cis444. PMID 22610931. Archived from the original on 2014-05-18.
- Asiedu, Kingsley; Fitzpatrick, Christopher; Jannin, Jean (25 September 2014). "Eradication of Yaws: Historical Efforts and Achieving WHO's 2020 Target". PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 8 (9): 696–703. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0003016. ISSN 1935-2727. PMC 4177727. PMID 25193248.
- Mitjà, O; Marks, M; Konan, DJ; Ayelo, G; Gonzalez-Beiras, C; Boua, B; Houinei, W; Kobara, Y; Tabah, EN; Nsiire, A; Obvala, D; Taleo, F; Djupuri, R; Zaixing, Z; Utzinger, J; Vestergaard, LS; Bassat, Q; Asiedu, K (June 2015). "Global epidemiology of yaws: a systematic review". The Lancet. Global Health. 3 (6): e324-31. doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(15)00011-X. PMC 4696519. PMID 26001576.
- "Number of cases of yaws reported". World Health Organization Global Health Observatory. Retrieved 13 February 2019.
- Marks, Michael (29 August 2018). "Advances in the Treatment of Yaws". Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 3 (3): 92. doi:10.3390/tropicalmed3030092. ISSN 2414-6366. PMC 6161241. PMID 30274488.
- Yotsu, Rie R. (14 November 2018). "Integrated Management of Skin NTDs—Lessons Learned from Existing Practice and Field Research". Tropical Medicine and Infectious Disease. 3 (4): 120. doi:10.3390/tropicalmed3040120. ISSN 2414-6366. PMC 6306929. PMID 30441754.
- Davis CP, Stoppler MC. "Yaws". MedicineNet.com. Archived from the original on 8 October 2012. Retrieved 5 August 2012.
- Lewis, David A.; Mitjà, Oriol (February 2016). "Haemophilus ducreyi: from sexually transmitted infection to skin ulcer pathogen". Current Opinion in Infectious Diseases. 29 (1): 52–57. doi:10.1097/QCO.0000000000000226. ISSN 1473-6527. PMID 26658654. S2CID 1699547.
- Mitjà, O; Hays, R; Ipai, A; Penias, M; Paru, R; Fagaho, D; de Lazzari, E; Bassat, Q (Jan 28, 2012). "Single-dose azithromycin versus benzathine benzylpenicillin for treatment of yaws in children in Papua New Guinea: an open-label, non-inferiority, randomised trial". The Lancet. 379 (9813): 342–47. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61624-3. PMID 22240407. S2CID 17517869.
- "Yaws status of endemicity and number of cases". Our World in Data. Retrieved 5 March 2020.
- Asiedu, Kingsley (July 2008). "The return of yaws". Bulletin of the World Health Organization. 86 (7): 507–8. doi:10.2471/blt.08.040708. PMC 2647480. PMID 18670660.
- "Yaws". WHO Fact sheet. Archived from the original on 2012-11-01. Retrieved 2012-10-16.
- Mitjà, Oriol; Marks, Michael; Konan, Diby J P; Ayelo, Gilbert; Gonzalez-Beiras, Camila; Boua, Bernard; Houinei, Wendy; Kobara, Yiragnima; Tabah, Earnest N; Nsiire, Agana; Obvala, Damas; Taleo, Fasiah; Djupuri, Rita; Zaixing, Zhang; Utzinger, Jürg; Vestergaard, Lasse S; Bassat, Quique; Asiedu, Kingsley (19 May 2015). "Global epidemiology of yaws: a systematic review". The Lancet. Global Health. 3 (6): e324–e331. doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(15)00011-X. ISSN 2214-109X. PMC 4696519. PMID 26001576.
- Capuano, C; Ozaki, M (2011). "Yaws in the Western Pacific Region: A Review of the Literature". Journal of Tropical Medicine. 2011: 642832. doi:10.1155/2011/642832. PMC 3253475. PMID 22235208.
- Fitzpatrick, Christopher; Asiedu, Kingsley; Solomon, Anthony W.; Mitja, Oriol; Marks, Michael; Van der Stuyft, Patrick; Meheus, Filip (4 December 2018). "Prioritizing surveillance activities for certification of yaws eradication based on a review and model of historical case reporting". PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 12 (12): e0006953. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0006953. ISSN 1935-2727. PMC 6294396. PMID 30513075.
- Asiedu K; Amouzou, B; Dhariwal, A; Karam, M; Lobo, D; Patnaik, S; Meheus, A (2008). "Yaws eradication: past efforts and future perspectives". Bulletin of the World Health Organization. 86 (7): 499–500. doi:10.2471/BLT.08.055608. PMC 2647478. PMID 18670655. Archived from the original on 2009-04-21. Retrieved 2009-04-02.
- Rinaldi A (2008). "Yaws: a second (and maybe last?) chance for eradication". PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 2 (8): e275. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0000275. PMC 2565700. PMID 18846236.
- WHO South-East Asia report of an intercountry workshop on Yaws eradication, 2006 Archived 2008-11-08 at the Wayback Machine
- Akbar, S (7 August 2011). "Another milestone for India: Yaws eradication". The Asian Age. Archived from the original on 11 October 2011. Retrieved 5 August 2012.
- "Yaws Eradication Programme (YEP)". NCDC, Dte. General of Health Services, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India. Archived from the original on 2 February 2014. Retrieved 18 January 2014. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - "Eradication of yaws – the Morges Strategy" (pdf). Weekly Epidemiological Record. 87 (20). 2012. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2014-05-08. Retrieved 2014-05-06.
- Maurice, J (2012). "WHO plans new yaws eradication campaign". The Lancet. 379 (9824): 1377–78. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60581-9. PMID 22509526. S2CID 45958274. Archived from the original on 2012-04-15.
- Rinaldi A (2012). "Yaws eradication: facing old problems, raising new hopes". PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 6 (11): e18372. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0001837. PMC 3510082. PMID 23209846.
- "Summary report of a consultation on the eradication of yaws". WHO. WHO.
- Drug and a syphilis test offer hope of yaws eradication, 2013 Archived 2014-02-27 at the Wayback Machine
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Yaws. |
- "Treponema pallidum subsp. pertenue". NCBI Taxonomy Browser. 168.
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
