Forests of Canada
The forests of Canada are located across much of the country. Approximately half of Canada is covered by forest, totaling around 2.4 million km2 (0.93 million sq mi).[1] Over 90% of Canada's forests are owned by the public (Crown land land and Provincial forest). About half of the forests are allocated for logging.
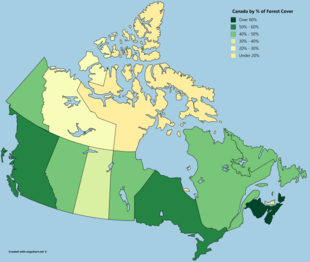
Named forests are found within eight distinct regions. These forests may also be part of ecosystems, a number of which extend south into the United States. For example, the Northern hardwood forest is an ecosystem located in large areas of southeastern and south central Canada as well as in Ontario and Quebec. This system extends south to west and even into the United States.
Regions

The forests of Canada are located within eight regions:[2][3]
- Acadian Forest Region - This region comprises a temperate broadleaf and mixed forest ecoregion located in Quebec as well as the Maritime Provinces in Eastern Canada, and extends into the United States.[4]
- Boreal Forest Region - This the largest forest region in Canada. It is located in the north and contains about one third of the world's circumpolar boreal forests.
- Coast Forest Region - Located on the west coast, this region almost entirely comprises coniferous trees including the Douglas-fir, Sitka spruce, western hemlock, and western red cedar.
- Columbia Forest Region - Also mostly comprising coniferous trees, this region is located between the Rocky Mountains and the central plateau in British Columbia.
- Deciduous Forest Region - This region is located between Lake Huron, Lake Ontario, and Lake Erie in southwestern Ontario.[5]
- Great Lakes-St. Lawrence Forest - This region is the second largest (the boreal being the largest), and is located from southeastern Manitoba to the Gaspé Peninsula.[5]
- Montane Forest Region - Located in the west of Canada, this region covers parts of the Kootenays, the central plateau of British Columbia, and a number of valleys close to Alberta's border.[5]
- Subalpine Forest Region - This region is located in British Columbia and Alberta. It covers the Rocky Mountains from the west coast Alberta's uplands.[5]
By Province
The following is a list of forests, ecoregions, ecozones, forested parklands and provincial parks.
Alberta
- Alberta Mountain forests
- Alberta-British Columbia foothills forests
- Aspen parkland
- Mid-Continental Canadian forests
- Muskwa-Slave Lake forests
- North Central Rockies forest
British Columbia

- Alberta-British Columbia foothills forests
- Aspen parkland
- British Columbia mainland coastal forests
- Cascade Mountains leeward forests
- Elkington Forest
- Fraser Plateau and Basin complex
- Great Bear Rainforest
- Inland rainforest
- Lower Mainland Ecoregion
- Malcolm Knapp Research Forest
- Muskwa-Slave Lake forests
- North Central Rockies forest
- Northern Pacific coastal forests
- Pacific temperate rainforests
Manitoba
- Agassiz Provincial Forest
- Belair Provincial Forest
- Brightstone Sand Hill Provincial Forest
- Cat Hills Provincial Forest
- Cormorant Provincial Forest
- Duck Mountain Provincial Forest
- Mid-Continental Canadian forests
- Midwestern Canadian Shield forests
- Moose Creek Provincial Forest
- Northwest Angle Provincial Forest
- Porcupine Provincial Forest
- Provincial forests
- Sandilands Provincial Forest
- Spruce Woods Provincial Forest
- Swan-Pelican Provincial Forest
- Tallgrass Aspen Parkland
- Turtle Mountain Provincial Forest
- Wampum Provincial Forest
- Whiteshell Provincial Forest
Newfoundland
Nova Scotia
Ontario
- Barker's Bush
- Carolinian forest
- Central Canadian Shield forests
- Crothers Woods
- Eastern Great Lakes lowland forests
- Ganaraska Region
- Haliburton Forest
- Happy Valley Forest
- John E. Pearce Provincial Park
- Laurentian Mixed Forest Province
- Long Point, Ontario
- Midwestern Canadian Shield forests
- Mixed Wood Plains Ecozone (CEC)
- Niagara Glen Nature Reserve
- Obabika Old-Growth Forest
- Pinery Provincial Park
- Point Pelee National Park
- Rock Glen Conservation Area
- Rock Point Provincial Park
- Rondeau Provincial Park
- Short Hills Provincial Park
- Southwest Elgin Forest Complex
- Western Great Lakes forests
- Wheatley Provincial Park
Prince Edward Island
- Beach Grove Memorial Forest[6]
- Strathgartney Woodlands
Quebec

Saskatchewan

- Canwood Provincial Forest
- Fort à la Corne Provincial Forest
- Nisbet Provincial Forest
- Northern Provincial Forest
- Porcupine Provincial Forest
- Torch River Provincial Forest
Other forest areas
Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests
- Beech-maple forest - This forest is located mostly in eastern United States and extends into southern Canada.[7]
- Carolinian forest
- Eastern forest-boreal transition
- Eastern Great Lakes lowland forests
- John E. Pearce Provincial Park
- Long Point, Ontario
- Niagara Glen Nature Reserve
- Northern hardwood forest
- Pinery Provincial Park
- Point Pelee National Park
- Rock Point Provincial Park
- Rondeau Provincial Park
- Short Hills Provincial Park
- Southwest Elgin Forest Complex
- Western Great Lakes forests
- Wheatley Provincial Park

References
- "Total forest coverage by country". the Guardian. 2 September 2009. Retrieved 23 September 2018.
- "Forest classification". Natural Resources Canada. 14 June 2017. Retrieved 24 September 2018.
- "Forest Regions - The Canadian Encyclopedia". www.thecanadianencyclopedia.ca.
- "New England/Acadian Forests". www.cas.vanderbilt.edu.
- User, Super. "Canada's Forests - Sustainability and Management - CCFM". www.sfmcanada.org.
- https://www.princeedwardisland.ca/en/information/communities-land-and-environment/natural-areas
- "Eco Succession". Archived from the original on 2008-12-26. Retrieved 2018-09-23.
External links

_(21178820598).jpg)