Ben Eoin Provincial Park
Ben Eoin Provincial Park [2] is a small secluded park on an old farm against hardwood-covered hills in the community of Ben Eoin, Nova Scotia, on the south side of the East Bay of the Bras d'Or Lake, Cape Breton Island, Canada. This picnic and hiking park is managed by the provincial Department of Natural Resources and is situated on a heavily wooded 225 acres (91 ha) parcel of Crown land. A short distance into the park there are several large neatly mown clearings (former farm fields) with picnic tables under the trees at the edge of the small fields. Pit toilets and disposal areas for hot coals are available onsite.
| Ben Eoin Provincial Park | |
|---|---|
Ben Eoin Provincial Park | |
  | |
| Type | Provincial Park |
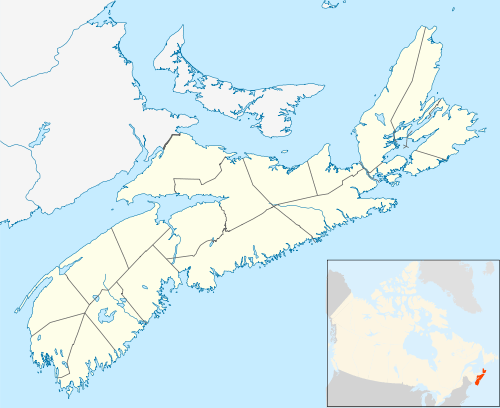
| Location | Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia, Canada |
| Nearest town | Ben Eoin |
| Coordinates | 45°57′44″N 60°27′35″W |
| Area | 90.16 hectares (222.8 acres) |
| Created | February 11, 1975 |
| Operated by | Parks and Recreation Division, Nova Scotia Department of Natural Resources |
| Visitors | Unknown, but fairly well used[1] |
| Open | dawn to dusk, from May 15 to October 12 |
| Status | Designated; Operational |
| Hiking trails | Ben Eoin Trail |
| Website | Ben Eoin Provincial Park |
Ben Eoin Provincial Park was established by Order in Council (OIC 75-167) on February 11, 1975.[3]
Ben Eoin Provincial Park in one of few public parks adjacent to Bras d'Or Lake and is a comparatively short drive from the urban areas of the Cape Breton Regional Municipality. It is fairly well used by the public and also sees some use by school groups. Much of the park is undeveloped and so contributes to regional biodiversity by providing habitat for uncommon plants.[4]
Season & fees
The park is open for day use (from dawn to dusk), from May 15 to October 12. There is no charge for using the park and its facilities.[5] Civic address: # 5549 East Bay Highway (Route 4), Ben Eoin, NS.[6]

Ben Eoin Trail
The Ben Eoin Trail (1.7 kilometres (1.1 mi) return) starts at the Ben Eoin Provincial Picnic Park. A hiker's sign indicates the trailhead in the park. A very nice steady hike that climbs along a well-worn path. It climbs uphill through large and old Birch and Beech Trees. The trail leads to a well cleared look-off of solid ground and large flat stone on a ridge of the East Bay Hills with a panoramic view of the East Bay of the Bras d'Or Lake 165 metres (541 ft) below.[7]
A working example of restoration
Nova Scotia's provincial parks were often fields or farms donated to the province in the 1950s and 1960s that became fertile ground for white spruce and other short-lived tree species. The white spruce in some Nova Scotia parks are overmature, dying of old age, or have succumbed to insect attack. To address the situation the Nova Scotia Department of Natural Resources is employing ecological restoration techniques. White spruce trees are removed so as to provide maximum benefit to the soil and future vegetation growth. Later, a tree and plant species mix more representative of the natural landscape, will be planted or encouraged to grow to produce a new forest.
A working example of this process can be found at Ben Eoin Provincial Park. During the winter of 2008/2009, work took place on an area of the park that required attention. This work will be obvious to visitors as trees are no longer standing where they once did. New growth will appear soon, but a mature forest is many years away. What was once an old pasture, turned forest, turned dead and dying trees, will again become a growing forest.[9]
Ultrasonic Bat Monitoring in Eastern Cape Breton - Ben Eoin Provincial Park
In the summer of 2013, and through the following winter, a study monitoring bat activity using ultrasonic detectors was conducted in various sites in eastern Cape Breton. The goal of monitoring bat activity in summer habitats was to gather data about bats in Cape Breton, including the presence or absence of species, seasonal trends in activity, and the time when summer activity ceased. The study also hoped to shed some additional light on the prevalence of white nose syndrome in eastern Cape Breton. The bat detectors used in this project worked by detecting the ultrasonic calls produced by bats as they fly and were configured to record during the night when bats were feeding, starting 30 minutes before sunset and ending 30 minutes after sunrise (coincidentally when the parks is closed to the public). During this time, the detectors recorded the number of bat "passes," or instances of a bat flying past the microphone. Three of these bat detectors were set up in Ben Eoin Provincial Park, two operating from July to October 2013 and a third for July & August only. At least two species of bat, the little brown bat (Myotis lucifugus) and the northern long-eared bat (Myotis septentrionalis) were reliably detected. At least 5754 detections were recorded in Ben Eoin Provincial Park during the study with the most active months being August and September.[10]
 Along the Ben Eoin Trail
Along the Ben Eoin Trail Along the Ben Eoin Trail
Along the Ben Eoin Trail Along the Ben Eoin Trail
Along the Ben Eoin Trail Along the Ben Eoin Trail
Along the Ben Eoin Trail Along the Ben Eoin Trail
Along the Ben Eoin Trail Along the Ben Eoin Trail
Along the Ben Eoin Trail Along the Ben Eoin Trail
Along the Ben Eoin Trail
</ref>

References
- "Our Parks and Protected Areas: A Plan for Nova Scotia - Ben Eoin Provincial Park". Protected Areas and Wetlands Branch, Nova Scotia Environment. Retrieved 23 June 2018.
- "Geographical Names of Canada - Ben Eoin Provincial Park". Government of Canada. Retrieved May 2, 2012.
- "Ben Eoin Provincial Park Designation made under Section 8 of the Provincial Parks Act O.I.C. 75-167 (February 11, 1975)". Government of Nova Scotia. Retrieved March 22, 2016.
- "Lands Profiles - Ben Eoin Provincial Park". Government of Nova Scotia. Retrieved September 7, 2014.
- "Seasons and Fees - Day Use Parks". Nova Scotia Provincial Parks, a branch of The Department of Natural Resources. Archived from the original on 2016-01-13. Retrieved January 1, 2016.
- "Info on Parks A - Z - Ben Eoin Provincial Park". Nova Scotia Natural Resources. Archived from the original on 2016-01-12. Retrieved April 20, 2012.
- "Ben Eoin Trail". Moosebait. Retrieved September 7, 2014.
- "White spruce trees cut as part of experiment in ecological restoration". Cape Breton Post (Published on December 3, 2008). Retrieved 29 June 2020.
- "Ultrasonic Bat Monitoring in Eastern Cape Breton" (PDF). Atlantic Coastal Action Program Cape Breton (Published 2014). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-09-07. Retrieved September 7, 2014.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Ben Eoin Provincial Park. |