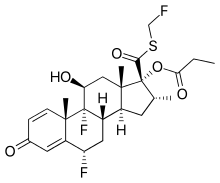
Fluticasone propionate
Fluticasone propionate, sold under the brand names Flovent and Flonase among others, is a steroid medication.[6] When inhaled it is used for the long term management of asthma and COPD.[6] In the nose it is used for hay fever and nasal polyps.[7][8] It can also be used for mouth ulcers.[9]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Flovent, Flixotide, Flonase, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a695002 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | Intranasal,[2] inhaled,[3] topical[4] |
| Drug class | Steroids and steroid derivatives |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 0.51% (Intranasal) |
| Protein binding | 91% |
| Metabolism | Intranasal Liver (CYP3A4-mediated) |
| Elimination half-life | 10 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.129.097 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C25H31F3O5S |
| Molar mass | 500.57 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Common side effects when inhaled include upper respiratory tract infections, sinusitis, thrush, and cough.[6] Common side effects when used in the nose include nosebleeding and sore throat.[7] It works by decreasing inflammation.[6]
Fluticasone propionate was patented in 1980, and approved for medical use in 1990.[10] It is available as a generic medication.[8] In 2017, fluticasone was the 15th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 32 million prescriptions (up from 16th place & 29 million in 2016).[11][12]
Medical uses
Fluticasone propionate is used by powder or aerosol inhalation for the prophylaxis of asthma.[3][6] The nasal spray is used for prevention and treatment of allergic rhinitis.[2] Nasal drops are used in the treatment of nasal polyps. The nasal spray can also be used in the mouth for mouth ulcers.[9]
Fluticasone propionate in a topical form can be used to treat skin conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, and rashes.[13]
Adverse effects
If taken correctly, the nasal spray and oral inhaler formulation have fewer corticosteroid side effects than the tablet formulation because they limit systemic (blood) absorption.[2] However, the systemic absorption is not negligible even with correct administration.[2] Using the spray or inhaler at higher than recommended doses or with other corticosteroids can increase the risk for serious, systemic corticosteroid induced side effects.[2][3] These side effects include weakened immune system, increased risk of systemic infections, osteoporosis, and elevated pressure in the eyes.[14]
Nasal spray

Common side effects may include nasal irritation (burning, stinging, bleeding), headache, upset stomach (nausea, vomiting), and diarrhea. Rare side effects include infection (evidenced by, e.g., fever, sore throat, and cough), vision problems, severe swelling, hoarse voice, and difficulty breathing or swallowing.[15][7][2]
Pharmacology
Fluticasone propionate is a highly selective agonist at the glucocorticoid receptor with negligible activity at androgen, estrogen, or mineralocorticoid receptors, thereby producing anti-inflammatory and vasoconstriction effects. It has been shown to have a wide range of inhibitory effects on multiple cell types (e.g. mast cell, eosinophil, neutrophil, macrophages, and lymphocytes) and mediators (e.g. histamine, eicosanoids, leukotrienes, and cytokines) involved in inflammation. Fluticasone propionate is stated to exert a topical effect on the lungs without significant systemic effects at usual doses, due to its low systemic bioavailability.
Interactions
Fluticasone propionate is broken down by CYP3A4 (Cytochrome P450 3A4), and has been shown to interact with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors such as ritonavir and ketoconazole.[2][3]
Ritonavir is a common drug used in the treatment of HIV. Coadministration of ritonavir and fluticasone may lead to increased levels of fluticasone in the body, which may lead to Cushing's Syndrome and adrenal insufficiency.[17]
Ketoconazole, an antifungal drug, has also been shown to increase fluticasone concentration leading to systemic corticosteroid side effects.[2][3]
See also
References
- "Fluticasone Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. 9 January 2019. Retrieved 31 January 2020.
- "Flonase Allergy Relief- fluticasone propionate spray, metered". DailyMed. 30 May 2019. Retrieved 31 January 2020.
- "Flovent Diskus- fluticasone propionate powder, metered". DailyMed. 7 January 2019. Retrieved 31 January 2020.
- "Cutivate- fluticasone propionate ointment". DailyMed. 18 February 2019. Retrieved 31 January 2020.
- "Flixonase Aqueous Nasal Spray - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 25 October 2019. Retrieved 31 January 2020.
- "Fluticasone Propionate Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved 27 February 2019.
- "Fluticasone Propionate eent Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Retrieved 27 February 2019.
- British national formulary : BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. pp. 262, 1172. ISBN 9780857113382.
- "Flixonase aqueous spray" (PDF). Sheffield Teaching Hospitals. June 2018. Retrieved 31 January 2020.
- Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 487. ISBN 9783527607495.
- "The Top 300 of 2020". ClinCalc. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- "Fluticasone - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- "Drugs & Medications". www.webmd.com. Retrieved 13 April 2020.
- "Prednisone and other corticosteroids: Balance the risks and benefits". Retrieved 4 March 2018.
- "Fluticasone Nasal Spray". AHFS Consumer Medication Information [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1 September 2010 [2008]. Retrieved 2 November 2014.
- "Fluticasone Oral Inhalation". AHFS Consumer Medication Information [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, Inc. 1 September 2010 [2008]. Retrieved 2 November 2014.
- Foisy MM, Yakiwchuk EM, Chiu I, Singh AE (July 2008). "Adrenal suppression and Cushing's syndrome secondary to an interaction between ritonavir and fluticasone: a review of the literature". HIV Medicine. 9 (6): 389–96. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1293.2008.00579.x. PMID 18459946.
External links
- "Fluticasone propionate". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Fluticasone". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Fluticasone Topical". MedlinePlus.