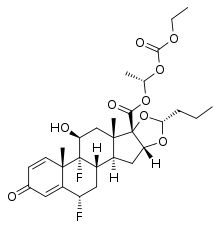
Itrocinonide
Itrocinonide (developmental code name D5159) is a synthetic glucocorticoid corticosteroid which was never marketed.[1][2][3]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | D5159; 6α,9α-Difluoro-11β,16α,17α-trihydroxy-21-oxa-3-oxoandrosta-1,4-diene-17β-carboxylic acid, ester with ethyl (S)-1-hydroxyethyl carbonate, cyclic (R)-16,17-acetal with butyraldehyde; 6α,9α-Difluoro-11β,16α,17α-trihydroxy-21-oxapregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione 21-(1-[(ethoxycarbonyl)oxy]ethyl), cyclic (R)-16,17-acetal with butyraldehyde |
| Drug class | Corticosteroid; Glucocorticoid |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C29H38F2O9 |
| Molar mass | 568.611 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
References
- Nicholas Bodor; Peter Buchwald (29 August 2012). Retrometabolic Drug Design and Targeting. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 193–. ISBN 978-1-118-40776-9.
- Robert P. Schleimer (19 April 2016). Inhaled Steroids in Asthma: Optimizing Effects in the Airways. CRC Press. pp. 526–. ISBN 978-0-203-90853-2.
- Trevor T. Hansel; Peter J. Barnes (1 January 2001). New Drugs for Asthma, Allergy and COPD. Karger Medical and Scientific Publishers. pp. 95–. ISBN 978-3-8055-6862-3.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.