Right whale
Right whales or black whales are three species of large baleen whales of the genus Eubalaena: the North Atlantic right whale (E. glacialis), the North Pacific right whale (E. japonica) and the Southern right whale (E. australis). They are classified in the family Balaenidae with the bowhead whale. Right whales have rotund bodies with arching rostrums, V-shaped blowholes and dark gray or black skin. The most distinguishing feature of a right whale is the rough patches of skin on its head, which appear white due to parasitism by whale lice. Right whales can grow up to more than 18 m (59 ft) long with a highest-recorded length of 19.8 m (65 ft).[9] Right whales are very robust whales, weighing 100 short tons (91 t; 89 long tons) or more. The largest known right whales can attain 20.7 m (68 ft) in length and weigh up to 135,000 kg (298,000 lb)[10] or 21.3 m (70 ft) with uncertainty,[11] Their immense bulk makes right whales significantly heavier than other whales of similar or greater length such as the humpback, gray, sperm and even fin whales. In fact, right whales rank only behind the blue whale in sheer body mass. One (apocryphal) explanation for their name is that whalers identified them as the "right" whale to kill on a hunt due to the plentiful oil and baleen they could provide.[12]
| Right whales[1] | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Southern right whale breaching | |
 | |
| Size compared to an average human | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Artiodactyla |
| Infraorder: | Cetacea |
| Family: | Balaenidae |
| Genus: | Eubalaena Gray, 1864 |
| Type species | |
| Eubalaena australis Desmoulins, 1822 | |
| Species | |
| |
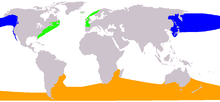 | |
E. glacialis ranges E. australis range E. japonica range | |
| Synonyms[8] | |
| |
All three species are migratory, moving seasonally to feed or give birth. The warm equatorial waters form a barrier that isolates the northern and southern species from one another although the southern species, at least, has been known to cross the equator.[13] In the Northern Hemisphere, right whales tend to avoid open waters and stay close to peninsulas and bays and on continental shelves, as these areas offer greater shelter and an abundance of their preferred foods. In the Southern Hemisphere, right whales feed far offshore in summer, but a large portion of the population occur in near-shore waters in winter. Right whales feed mainly on copepods but also consume krill and pteropods. They may forage the surface, underwater or even the ocean bottom. During courtship, males gather into large groups to compete for a single female, suggesting that sperm competition is an important factor in mating behavior. Although the blue whale is the largest animal on the planet, the testes of the right whale are actually ten times larger than those of the blue whale[14] – with each weighing up to 525 kilograms (1,160 lb), they are by far the largest of any animal on Earth.[15] Gestation tends to last a year, and calves are born at 1 short ton (0.91 t; 0.89 long tons) in weight and 4–6 m (13–20 ft) in length. Weaning occurs after eight months.
Right whales were a preferred target for whalers because of their docile nature, their slow surface-skimming feeding behaviors, their tendency to stay close to the coast, and their high blubber content (which makes them float when they are killed, and which produced high yields of whale oil). Today, the North Atlantic and North Pacific right whales are among the most endangered whales in the world,[16] and both species are protected in the United States by the Endangered Species Act. The North Atlantic right whale has a single surviving breeding population in the western North Atlantic, and is classed as critically endangered, with a total population best estimate of 411 individuals remaining alive as of 2017.[17][18] The North Pacific right whale population is classed overall as endangered and has two surviving populations, eastern and western, with the western Pacific population much larger at an estimated 1147 individuals in 2016.[18] The eastern North Pacific population has fewer than 50 individuals remaining, and this population is considered critically endangered.[19]
Although the whales no longer face pressure from commercial whaling, mankind remains by far the greatest threat to these species: the two leading causes of death are being struck by ships and entanglement in fishing gear. Ingestion of plastic marine debris also presents a growing threat. For the North Atlantic right whale, for example, whose population was estimated at 411 in 2017 which was down from 451 in 2016 and 458 in 2015, these two anthropogenic factors alone account for 48% of all known right whale deaths since 1970.[20][21] Entanglement is now the greatest source of mortality in the North Atlantic right whale, with 85% of recent mortalities (2010-2015) caused by entanglement in fishing lines.[18] More than 85% of North Atlantic right whales have been entangled at least once.[22]
In 2017, at least 118 right whales were in the Gulf of St Lawrence, or roughly a quarter of the local population, which previously fed in summer and fall months in the Bay of Fundy and Roadway basin. The habitat shift moved this population away from existing conservation efforts and into the path of busy shipping lanes and also snow crab fisheries where Fisheries and Oceans Canada doubled the quotas in 2017.[22]
Naming
A common explanation for the name right whales is that they were regarded as the right ones to hunt,[23] as they float when killed and often swim within sight of shore. They are quite docile and do not tend to shy away from approaching boats. As such, they were hunted nearly to extinction during the active years of the whaling industry. However, this origin is questionable: in his history of American whaling, Eric Jay Dolin writes:
Despite this highly plausible rationale, nobody actually knows how the right whale got its name. The earliest references to the right whale offer no indication why it was called that, and some who have studied the issue point out that the word "right" in this context might just as likely be intended "to connote 'true' or 'proper,' meaning typical of the group."
— E.J. Dolin, Leviathan: The History of Whaling in America, quoting a 1766 Connecticut Courant newspaper article.[24]
Taxonomy

The right whales were first classified in the genus Balaena in 1758 by Carl Linnaeus, who at the time considered all of the right whales (including the bowhead) as a single species. Through the 1800s and 1900s, in fact, the family Balaenidae has been the subject of great taxonometric debate. Authorities have repeatedly recategorized the three populations of right whale plus the bowhead whale, as one, two, three or four species, either in a single genus or in two separate genera. In the early whaling days, they were all thought to be a single species, Balaena mysticetus. Eventually, it was recognized that bowheads and right whales were in fact different, and John Edward Gray proposed the genus Eubalaena for the right whale in 1864. Later, morphological factors such as differences in the skull shape of northern and southern right whales indicated at least two species of right whale—one in the Northern Hemisphere, the other in the Southern Ocean.[25] As recently as 1998, Rice, in his comprehensive and otherwise authoritative classification, Marine mammals of the world: systematics and distribution, listed just two species: Balaena glacialis (the right whales) and Balaena mysticetus (the bowheads).[26]

In 2000, two studies of DNA samples from each of the whale populations concluded the northern and southern populations of right whale should be considered separate species. What some scientists found more surprising was the discovery that the North Pacific and North Atlantic populations are also distinct, and that the North Pacific species is more closely related to the southern right whale than to the North Atlantic right whale.[27][28] The authors of one of these studies concluded that these species have not interbred for between 3 million and 12 million years.[28]
In 2001, Brownell et al. reevaluated the conservation status of the North Pacific right whale as a distinct species,[29] and in 2002, the Scientific Committee of the International Whaling Commission (IWC) accepted Rosenbaum's findings, and recommended that the Eubalaena nomenclature be retained for this genus.[30] A 2007 study by Churchill provided further evidence to conclude that the three different living right whale species constitute a distinct phylogenetic lineage from the bowhead, and properly belong to a separate genus.[31]
The cladogram is a tool for visualizing and comparing the evolutionary relationships between taxa; the point where each node branches is analogous to an evolutionary branching – the diagram can be read left-to-right, much like a timeline. The following cladogram of the family Balaenidae serves to illustrate the current scientific consensus as to the relationships between the three right whales and the bowhead whale.
| Family Balaenidae | |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| The right whales, genus Eubalaena, in the family Balaenidae[27] |

Whale lice, parasitic cyamid crustaceans that live off skin debris, offer further information through their own genetics. Because these lice reproduce much more quickly than whales, their genetic diversity is greater. Marine biologists at the University of Utah examined these louse genes and determined their hosts split into three species 5–6 million years ago, and these species were all equally abundant before whaling began in the 11th century.[32] The communities first split because of the joining of North and South America. The rising temperatures of the equator then created a second split, into northern and southern groups, preventing them from interbreeding.[33] "This puts an end to the long debate about whether there are three Eubalaena species of right whale. They really are separate beyond a doubt", Jon Seger, the project's leader, told BBC News.[34]
Others
The pygmy right whale (Caperea marginata), a much smaller whale of the Southern Hemisphere, was until recently considered a member of the Family Balaenidae. However, they are not right whales at all, and their taxonomy is presently in doubt. Most recent authors place this species into the monotypic Family Neobalaenidae,[35] but a 2012 study suggests that it is instead the last living member of the Family Cetotheriidae, a family previously considered extinct.[36]
Yet another species of right whale was proposed by Emanuel Swedenborg in the 18th century - the so-called Swedenborg whale. The description of this species was based on a collection of fossil bones unearthed at Norra Vånga, Sweden, in 1705 and believed to be those of giants. The bones were examined by Swedenborg, who realized they belong to a species of whale. The existence of this species has been debated, and further evidence for this species was discovered during the construction of a motorway in Strömstad, Sweden in 2009.[37] To date, however, scientific consensus still considers Hunterius swedenborgii to be a North Atlantic right whale.[38] According to a DNA analysis conducted by scientists, it was later confirmed that the fossil bones are actually from a bowhead whale.[39]
Synonyms and common names

Due to their familiarity to whalers over a number of centuries, the right whales have had many names. These names were used throughout the world, reflecting the fact that only one species was recognized at the time. In his novel Moby-Dick, Herman Melville writes:
"Among the fishermen, the whale regularly hunted for oil is indiscriminately designated by all the following titles: The Whale; the Greenland whale; the black whale; the great whale; the true whale; the right whale. There is a deal of obscurity concerning the identity of the species thus multitudinously baptised. ... Some pretend to see a difference between the Greenland whale of the English and the Right whale of the Americans."
— Melville, Moby Dick: or, The White Whale, Ch. XXXII Cetology[40]
In fact, there was indeed a difference between the two – Melville's "Greenland whale", or "Greenland right whale", was in fact the modern-day bowhead whale, Balaena mysticetus.
The following are junior synonyms for the genus Eubalaena:[8]
- Baloena Robineau, 1989
- Halibalaena Gray, 1873
- Hunterius Gray, 1866
- Hunterus Gray, 1864
- Macleayanus Marschall, 1873
- Macleayius Gray, 1865
Although the right whale is now officially in the genus Eubalaena, the type species for a genus remains as it was first described – in the case of Eubalaena the type species is Balaena australis Desmoulins, 1822.[1]
Some of the species-level synonyms are:[1]
- For E. australis:[41]
- B. antarctica Lesson, 1828
- B. mysticetus antarctica Schlegel, 1841
- B. antipodarum Gray, 1843
- B. glacialis Mueller, 1776
- B. glacialis australis Scheffer & Rice, 1963
- E. capensis Gray, 1866
- E. glacialis australis Tomilin, 1962
- Halibalaena britannica Gray, 1873
- Hunterus temminckii Gray, 1864
- Macleayius australiensis Gray, 1865
- For E. glacialis:[42]
- For E. japonica:[43]
- B. japonica Lacépède, 1804 (basionym)
- B. sieboldii Gray, 1864
- Balaenoptera antarctica Temminck, 1841 (lapsus for Balaena)
- E. glacialis japonica Imaizumi, 1958
- E. sieboldii Gray, 1868
Description


Unlike other whales, a right whale has distinctive callosities (roughened patches of skin) on its head, along with a broad back without a dorsal fin, occasionally with white belly patches, and a long, arching rostrum, or upper jaw, that begins above the eye. The callosities appear white due to large colonies of cyamids (whale lice).[25][44] Each individual has a unique callosities pattern. In 2016, a competitive effort resulted in the use of facial recognition software to derive a process to uniquely identify right whales with about 87% accuracy based on their callosities.[45] The primary role of callosities has been considered to be protection against predators. Right whale declines might have also reduced barnacles.[46] Right whales are very large, robust whales that can grow up to and over 18 m (59 ft) long and weigh up to 100 short tons (91 t; 89 long tons), almost as big as bowhead whales and much larger than other species with high dependencies on shallow waters. An unusually large 40% of their body weight is blubber, which is of relatively low density. Consequently, unlike many other species of whale, dead right whales tend to float.[47][48] Right whales swim slowly, reaching only 5 kn (9.3 km/h) at top speed. However, they are highly acrobatic and frequently breach (jump clear of the sea surface), tail-slap and lobtail.[49]
Anatomy
Adults may be between 11–18 m (36–59 ft) in length and typically weigh 60–80 short tons (54–73 t; 54–71 long tons). The most typical lengths are 13–16 m (43–52 ft). The body is extremely thick with girth as much as 60% of total body length in some cases. The tail fluke is broad (up to 40% of body length).[49] The North Pacific species is on average the largest of the three species. The largest specimens may weigh 100 short tons (91 t; 89 long tons).[31] Right whales have a distinctive wide V-shaped blow, caused by the widely spaced blowholes on the top of the head. The blow rises 5 m (16 ft) above the surface.[14] Right whales have between 200 and 300 baleen plates on each side of their mouths. These are narrow and approximately 2 m (6.6 ft) long, and are covered in very thin hairs. The plates enable the whale to filter feed.

The penis on a right whale can be up to 2.7 m (8.9 ft) – the testes, at up to 2 m (6.6 ft) in length, 78 cm (2.56 ft) in diameter, and weighing up to 525 kg (1157 lbs), are also by far the largest of any animal on Earth.[15] The blue whale may be the largest animal on the planet, yet the testicles of the right whale are ten times the size of those of the blue whale. They also exceed predictions in terms of relative size, as well – they are six times larger than would be expected on the basis of body mass. Together, the testicles make up nearly 1% of the right whale's total body weight. This strongly suggests sperm competition is important in mating, which correlates to the fact that right whales are highly promiscuous.[14][50]
Many of southern right whales are seen with rolls of fats behind blowholes that northern species often lack, and these are regarded as a sign of better health condition due to sufficient nutrition supply, and could have contributed in vast differences in recovery status between right whales in the southern and northern hemisphere, other than direct impacts by mankind.[51]
Life history and ecology
Courtship and reproduction

During the mating season, which can occur at any time in the North Atlantic, right whales gather into "surface-active groups" made up of as many as 20 males consorting a single female. The female has her belly to the surface while the males stroke her with their flippers or keep her underwater. The males do not compete as aggressively against each other as male humpbacks. The female may not become pregnant but she is still able to assess the condition of potential mates.[31] The mean age of first parturition in North Atlantic right whales is estimated at between 7.5[52] and 9[53] years. Females breed every 3–5 years;[52][54] the most commonly seen calving intervals are 3 years and may vary from 2 up to 21 years due to multiple factors.[55][56]
Both reproduction and calving take place during the winter months.[57] Calves are approximately 1 short ton (0.91 t; 0.89 long tons) in weight and 4–6 m (13–20 ft) in length at birth following a gestation period of 1 year. The right whale grows rapidly in its first year, typically doubling in length. Weaning occurs after eight months to one year and the growth rate in later years is not well understood—it may be highly dependent on whether a calf stays with its mother for a second year.[31]
Respective congregation areas in the same region may function as for different objectives for whales.[58]
Lifespan
Very little is known about the life span of right whales. One of the few well-documented cases is of a female North Atlantic right whale that was photographed with a baby in 1935, then photographed again in 1959, 1980, 1985, and 1992. Consistent callosity patterns ensured it was the same animal. She was last photographed in 1995 with a seemingly fatal head wound, presumably from a ship strike. By conservative estimates (e.g. she was a new mother who had just reached sexual maturity in 1935), she was nearly 70 years to more than 100 years of age, if not older.[59] Research on the closely related bowhead whale exceeding 210 years or more suggests this lifespan is not uncommon and may even be exceeded.[31][60]
Diet and predation
The right whales' diets consist primarily of zooplankton, primarily the tiny crustaceans called copepods, as well as krill, and pteropods, although they are occasionally opportunistic feeders. As with other baleens, they feed by filtering prey from the water. They swim with an open mouth, filling it with water and prey. The whale then expels the water, using its baleen plates to retain the prey. Prey must occur in sufficient numbers to trigger the whale's interest, be large enough that the baleen plates can filter it, and be slow enough that it cannot escape. The "skimming" may take place on the surface, underwater, or even at the ocean's bottom, indicated by mud occasionally observed on right whales' bodies.[31]
The right whales' two known predators are humans and orcas. When danger lurks, a group of right whales may cluster into a circle, and thrash their outwards-pointing tails. They may also head for shallow water, which sometimes proves to be an ineffective defense. Aside from the strongly-build tails and massive heads equipped with callosities,[46] the sheer size of this animal is its best defense, making young calves are the most vulnerable to orca and shark attacks.[14]
Range and habitat
The three Eubalaena species inhabit three distinct areas of the globe: the North Atlantic in the western Atlantic Ocean, the North Pacific in a band from Japan to Alaska and all areas of the Southern Ocean. The whales can only cope with the moderate temperatures found between 20 and 60 degrees in latitude. The warm equatorial waters form a barrier that prevents mixing between the northern and southern groups with minor exclusions.[13] Although the southern species in particular must travel across open ocean to reach its feeding grounds, the species is not considered to be pelagic. In general, they prefer to stay close to peninsulas and bays and on continental shelves, as these areas offer greater shelter and an abundance of their preferred foods.[33]
Because the oceans are so large, it is very difficult to accurately gauge whale population sizes. Approximate figures:[31]
- 400 North Atlantic right whales (Eubalaena glacialis) live in the North Atlantic;
- 23 North Pacific right whales have been identified in the eastern North Pacific (Eubalaena japonica) and
- 15,000 southern right whales (Eubalaena australis) are spread throughout the southern part of the Southern Hemisphere.
North Atlantic right whale
Almost all of the 400 North Atlantic right whales live in the western North Atlantic Ocean. In northern spring, summer and autumn, they feed in areas off the Canadian and northeast U.S. coasts in a range stretching from New York to Newfoundland. Particularly popular feeding areas are the Bay of Fundy and Cape Cod Bay. In winter, they head south towards Georgia and Florida to give birth.[61] There have been a smattering of sightings further east over the past few decades; several sightings were made close to Iceland in 2003. These are possibly the remains of a virtually extinct eastern Atlantic stock, but examination of old whalers' records suggests they are more likely to be strays.[31] However, a few sightings are regular between Norway, Ireland, Spain, Portugal, the Canary Islands and even Italy[62] and Sicily;[63] at least the Norway individuals come from the Western stock.[64]
North Pacific right whale
The North Pacific right whale appears to occur in two populations. The population in the eastern North Pacific/Bering Sea is extremely low, numbering about 30 individuals.[65] A larger western population of 100–200 appears to be surviving in the Sea of Okhotsk, but very little is known about this population. Thus, the two northern right whale species are the most endangered of all large whales and two of the most endangered animal species in the world. Based on current population density trends, both species are predicted to become extinct within 200 years.[66] The Pacific species was historically found in summer from the Sea of Okhotsk in the west to the Gulf of Alaska in the east, generally north of 50°N. Today, sightings are very rare and generally occur in the mouth of the Sea of Okhotsk and in the eastern Bering Sea. Although this species is very likely to be migratory like the other two species, its movement patterns are not known.[67]
Southern right whale
The last major population review of southern right whales by the International Whaling Commission was in 1998. Researchers used data about adult female populations from three surveys (one in each of Argentina, South Africa and Australia) and extrapolated to include unsurveyed areas and estimated counts of males and calves (using available male:female and adult:calf ratios), giving an estimated 1997 population of 7,500 animals. More recent data from 2007 indicate those survey areas have shown evidence of strong recovery, with a population approaching twice that of a decade earlier. However, other breeding populations are still very small, and data are insufficient to determine whether they, too, are recovering.[3]
The southern right whale spends the summer months in the far Southern Ocean feeding, probably close to Antarctica. It migrates north in winter for breeding, and can be seen around the coasts of Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Chile, Mozambique, New Zealand, South Africa and Uruguay.[68] Since hunting of the southern right whale ceased, stocks are estimated to have grown by 7% a year. The South American, South African and Australasian groups apparently intermix very little, if at all, because of the strong fidelity of mothers to their feeding and calving grounds. The mother passes these instincts to her calves.[31]
Vocalization and hearing
Vocalizations made by right whales are not elaborate compared to those made by other whale species. The whales make groans, pops and belches typically at frequencies around 500 Hz. The purpose of the sounds is not known but may be a form of communication between whales within the same group. Northern right whales responded to sounds similar to police sirens—sounds of much higher frequency than their own. On hearing the sounds, they moved rapidly to the surface. The research was of particular interest because northern rights ignore most sounds, including those of approaching boats. Researchers speculate this information may be useful in attempts to reduce the number of ship-whale collisions or to encourage the whales to surface for ease of harvesting.[66][69]
Relationship to humans
Whaling
In the early centuries of shore-based whaling before 1712, right whales were virtually the only catchable large whales, for three reasons:
- They often swam close to shore where they could be spotted by beach lookouts, and hunted from beach-based whaleboats.
- They are relatively slow swimmers, allowing whalers to catch up to them in their whaleboats.
- Once killed by harpoons, they were more likely to float, and thus could be retrieved. However, some did sink when killed (10–30% in the North Pacific) and were lost unless they later stranded or surfaced.[70]
Basque people were the first to hunt right whales commercially, beginning as early as the 11th century in the Bay of Biscay. They initially sought oil, but as meat preservation technology improved, the animal was also used for food. Basque whalers reached eastern Canada by 1530[31] and the shores of Todos os Santos Bay (in Bahia, Brazil) by 1602. The last Basque voyages were made before the Seven Years' War (1756–1763). All attempts to revive the trade after the war failed. Basque shore whaling continued sporadically into the 19th century.
"Yankee whalers" from the new American colonies replaced the Basques. Setting out from Nantucket, Massachusetts, and Long Island, New York, they took up to a hundred animals in good years. By 1750, the commercial hunt of the North Atlantic right whale was essentially over. The Yankee whalers moved into the South Atlantic before the end of the 18th century. The southernmost Brazilian whaling station was established in 1796, in Imbituba. Over the next hundred years, Yankee whaling spread into the Southern and Pacific Oceans, where the Americans were joined by fleets from several European nations. The beginning of the 20th century saw much greater industrialization of whaling, and the harvest grew rapidly. According to whalers' records, by 1937 there had been 38,000 takes in the South Atlantic, 39,000 in the South Pacific, 1,300 in the Indian Ocean, and 15,000 in the North Pacific. The incompleteness of these records means the actual take was somewhat higher.[71]
As it became clear the stocks were nearly depleted, the world banned right whaling in 1937. The ban was largely successful, although violations continued for several decades. Madeira took its last two right whales in 1968. Japan took twenty-three Pacific right whales in the 1940s and more under scientific permit in the 1960s. Illegal whaling continued off the coast of Brazil for many years, and the Imbituba land station processed right whales until 1973. The Soviet Union illegally took at least 3,212 southern right whales during the 1950s and '60s, although it reported taking only four.[72]

Whale watching
The southern right whale has made Hermanus, South Africa one of the world centers for whale watching. During the winter months (July–October), southern right whales come so close to the shoreline, visitors can watch whales from strategically placed hotels.[73] The town employs a "whale crier" (cf. town crier) to walk through the town announcing where whales have been seen.[74] Southern right whales can also be watched at other winter breeding grounds.
In Brazil, Imbituba in Santa Catarina has been recognized as the National Right Whale Capital and holds annual Right Whale Week celebrations in September[75] when mothers and calves are more often seen. The old whaling station there has been converted to a museum dedicated to the whales.[76] In winter in Argentina, Península Valdés in Patagonia hosts the largest breeding population of the species, with more than 2,000 animals catalogued by the Whale Conservation Institute and Ocean Alliance.[77]
Conservation
Both the North Atlantic and North Pacific species are listed as a "species threatened with extinction which [is] or may be affected by trade" (Appendix I) by CITES, and as "endangered" by the IUCN Red List. In the United States, the National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS), a subagency of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) has classified all three species as "endangered" under the Endangered Species Act. Under the Marine Mammal Protection Act, they are listed as "depleted".[78][79][80]
The southern right whale is listed as "endangered" under the Australian Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act, as "nationally endangered" under the New Zealand Threat Classification System, as a "natural monument" by the Argentine National Congress, and as a "State Natural Monument" under the Brazilian National Endangered Species List.[80]
The US and Brazil added new protections for right whales in the 2000s to address the two primary hazards. While environmental campaigners were, as reported in 2001, pleased about the plan's positive effects, they attempted to force the US government to do more.[81] In particular, they advocated 12 knots (22 km/h) speed limits for ships within 40 km (25 mi) of US ports in times of high right whale presence. Citing concerns about excessive trade disruption, it did not institute greater protections. The Defenders of Wildlife, the Humane Society of the United States and the Ocean Conservancy sued the NMFS in September 2005 for "failing to protect the critically endangered North Atlantic Right Whale, which the agency acknowledges is 'the rarest of all large whale species' and which federal agencies are required to protect by both the Marine Mammal Protection Act and the Endangered Species Act", demanding emergency protection measures.[82] According to NOAA researchers, about 83% of right whale sightings in the mid-Atlantic region occur within 20 nautical miles (37 km) of shore.
The southern right whale, listed as "endangered" by CITES and "lower risk - conservation dependent" by the IUCN, is protected in the jurisdictional waters of all countries with known breeding populations (Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Chile, New Zealand, South Africa and Uruguay). In Brazil, a federal Environmental Protection Area encompassing some 1,560 km2 (600 sq mi) and 130 km (81 mi) of coastline in Santa Catarina State was established in 2000 to protect the species' main breeding grounds in Brazil and promote whale watching.[83]
On February 6, 2006, NOAA proposed its Strategy to Reduce Ship Strikes to North Atlantic Right Whales.[84] The proposal, opposed by some shipping interests, limited ship speeds during calving season. The proposal was made official when on December 8, 2008, NOAA issued a press release that included the following:[85]
- Effective January 2009, ships 65 feet (20 m) or longer are limited to 10 knots (19 km/h) in waters off New England when whales begin gathering in this area as part of their annual migration. The restriction extends to 20 nautical miles (37 km) around major mid-Atlantic ports.
- The speed restriction applies in waters off New England and the southeastern US, where whales gather seasonally:
- Southeastern US from St. Augustine, Florida to Brunswick, Georgia from Nov 15 to April 15
- Mid-Atlantic U.S. areas from Rhode Island to Georgia from Nov 1 to April 30.
- Cape Cod Bay from Jan 1 to May 15
- Off Race Point at the northern end of Cape Cod from March 1 to April 30
- Great South Channel of New England from April 1 to July 31
- Temporary voluntary speed limits in other areas or times when a group of three or more right whales is confirmed
- Scientists will assess the rule's effectiveness before the rule expires in 2013.
The Stellwagen Bank area has implemented an autobuoy program to acoustically detect right whales in the Boston Approaches and notify sailors via the Right Whale Listening Network website.
Threats

The leading cause of death among the North Atlantic right whale, which migrates through some of the world's busiest shipping lanes while journeying off the east coast of the United States and Canada, is being struck by ships.[note 1][86] At least sixteen ship-strike deaths were reported between 1970 and 1999, and probably more remain unreported.[31] According to NOAA, twenty-five of the seventy-one right whale deaths reported since 1970 resulted from ship strikes.[85]
A second major cause of morbidity and mortality in the North Atlantic right whale is entanglement in plastic fishing gear. Right whales ingest plankton with wide-open mouths, risking entanglement in any rope or net fixed in the water column. Rope wraps around their upper jaws, flippers and tails. Some are able to escape, but others remain tangled.[87] Whales can be successfully disentangled, if observed and aided. In July 1997, the U.S. NOAA introduced the Atlantic Large Whale Take Reduction Plan, which seeks to minimize whale entanglement in fishing gear and record large whale sightings in an attempt to estimate numbers and distribution.[88]
In 2012, the U.S. Navy proposed to create a new undersea naval training range immediately adjacent to northern right whale calving grounds in shallow waters off the Florida/Georgia border. Legal challenges by leading environmental groups including the Natural Resources Defense Council were denied in federal court, allowing the Navy to proceed.[89][90] These rulings were made despite the extremely low numbers (as low as 313 by some estimates) of right whales in existence at this time, and a very poor calving season.[91]
Notes
- The Lloyd's mirror effect results in low frequency propeller sounds not being discernible near the surface, where most accidents occur. Combined with spreading and acoustic shadowing effects, the result is that the animal is unable to hear an approaching vessel before it has been run over or entrapped by the hydrodynamic forces of the vessel's passage.
References
- Mead, J.G.; Brownell, R. L. Jr. (2005). "Order Cetacea". In Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 723–743. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- "Fossilworks".
- Reilly, S.B.; Bannister, J.L.; Best, P.B.; Brown, M.; Brownell Jr., R.L.; Butterworth, D.S.; Clapham, P.J.; Cooke, J.; Donovan, G.P.; Urbán, J.; et al. (2008). "Eubalaena australis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2008. Retrieved September 30, 2012.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Bisconti M, Lambert O, Bosselaers M. (2017) Revision of “Balaena” belgica reveals a new right whale species, the possible ancestry of the northern right whale, Eubalaena glacialis, and the ages of divergence for the living right whale species. PeerJ 5:e3464 https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.3464
- Reilly, S.B.; Bannister, J.L.; Best, P.B.; Brown, M.; Brownell Jr., R.L.; Butterworth, D.S.; Clapham, P.J.; Cooke, J.; Donovan, G.P.; Urbán, J.; et al. (2008). "Eubalaena glacialis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2008. Retrieved September 30, 2012.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Reilly, S.B.; Bannister, J.L.; Best, P.B.; Brown, M.; Brownell Jr., R.L.; Butterworth, D.S.; Clapham, P.J.; Cooke, J.; Donovan, G.P.; Urbán, J.; et al. (2008). "Eubalaena japonica". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2008. Retrieved September 30, 2012.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Kimura, T.; Narita, K. (2007). "A new species of Eubalaena (Cetacea: Mysticeti: Balaenidae) from the Gonda Formation (latest Miocene-early Pliocene) of Japan". Bulletin of the Gunma Museum of Natural History. 11: 15–27.
- Perrin, W.F. (2012). "Eubalaena Gray, 1864". World Cetacea Database. Retrieved September 29, 2012.
- Ivashchenko YV, Clapham PJ (2011). "Pushed to the Edge: Soviet Catches of Right Whales in the Eastern North Pacific". Alaska Fisheries Science Center Quarterly Research Reports (Apr–May–June 2011).
- Omura, H., S. Ohsumi, K. N. Nemoto, K. Nasu, and T. Kasuya. 1969. Black right whales in the North Pacific. Scientific Reports of the Whales Research Institute, Tokyo. 21:1-78.
- Scarff JE (1986a). "Historic and present distribution of the right whale (Eubalaena glacialis) in the eastern North Pacific south of 50°N and east of 180°W" (PDF). Rep. Int. Whal. Comm. (Special Issue 10): 43–63.
- "Right Whales, Right Whale Pictures, Right Whale Facts - National Geographic". National Geographic. Retrieved December 8, 2015.
- Waerebeek, V. K.; Santillán, L.; Suazo, E.; The Peruvian Centre for Cetacean Research (2009). "ON THE NATIVE STATUS OF THE SOUTHERN RIGHT WHALE EUBALAENA AUSTRALIS IN PERU" (PDF). Boletín del Museo Nacional de Historia Natural, Chile. 58: 75–82. Retrieved August 3, 2016.
- Crane, J.; Scott, R. (2002). "Eubalaena glacialis: North Atlantic right whale: Information". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan Museum of Zoology. Retrieved April 30, 2006.
- Feldhamer, George A.; Thompson, Bruce C.; Chapman, Joseph A. (2003). Wild mammals of North America : biology, management, and conservation (2nd ed.). Baltimore, Md.: Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 432. ISBN 9780801874161.
- "North Atlantic right whale (Eubalaena glacialis) 5-year review: Summary and Evaluation" (PDF). Gloucester, MA: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Fisheries Service. August 2012. Retrieved December 9, 2012.
The western North Atlantic population numbered at least 361 individuals in 2005 and at least 396 in 2010 (Waring et al. 2012).
- Pettis, H. M.; Pace, R. M. III; Hamilton, P. K. (2018). "North Atlantic Right Whale Consortium 2018 Annual Report Card" (PDF). Report to the North Atlantic Right Whale Consortium: 2–4. Retrieved September 13, 2019.
- Harcourt, R.; van der Hoop, J.; Kraus, S.; Carroll, E.L. (2019). "Future directions in Eubalaena spp.: comparative research to inform conservation". Front. Mar. Sci. 5. doi:10.3389/fmars.2018.00530.
- Reilly, S.B.; Bannister, J.L.; Best, P.B.; Brown, M.; Brownell Jr., R.L.; Butterworth, D.S.; Clapham, P.J.; Cooke, J.; Donovan, G.P.; Urbán, J.; et al. (2008). "Eubalaena japonica (Northeast Pacific subpopulation)". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2008. Retrieved September 30, 2012.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Fisheries and Oceans Canada (2007). "Recovery potential assessment for right whale (Western North Atlantic population)" (PDF). Canadian Science Advisory Secretariat Science Advisory Report 2007/027. Retrieved June 17, 2011.
- "Fisheries and Oceans Canada". www.dfo-mpo.gc.ca. Retrieved November 26, 2018.
- Lindsay Jones (October 23, 2017). "Scientists predict dire future for North Atlantic right whale population". Globe and Mail. p. A7.
- "North Atlantic right whale | Basic Facts About Right Whales | Defenders of Wildlife". Defenders.org. Retrieved May 10, 2012.
- Dolin, Eric Jay (2007). Leviathan: The History of Whaling in America. W.W. Norton & Co. p. 22. ISBN 978-0-393-06057-7. Retrieved September 30, 2012.; (quoting "Boston, August 21". Connecticut Courant. September 1, 1766.); (also quoting Spears, John Randolph (1908). The story of the New England whalers. The Macmillan Company. pp. 80–81.)
- Müller, J. (1954). "Observations of the orbital region of the skull of the Mystacoceti" (PDF). Zoologische Mededelingen. 32: 239–90.
- Rice, Dale W. (1998). Marine mammals of the world: systematics and distribution. Special Publication No. 4. Society of Marine Mammalogy. ISBN 1891276034.
- Rosenbaum, H. C.; R. L. Brownell Jr.; M. W. Brown; C. Schaeff; V. Portway; B. N. White; S. Malik; L. A. Pastene; N. J. Patenaude; C. S. Baker; M. Goto; P. Best; P. J. Clapham; P. Hamilton; M. Moore; R. Payne; V. Rowntree; C. T. Tynan; J. L. Bannister & R. Desalle (2000). "World-wide genetic differentiation of Eubalaena: Questioning the number of right whale species". Molecular Ecology. 9 (11): 1793–802. doi:10.1046/j.1365-294x.2000.01066.x. PMID 11091315.
- Malik, S.; M. W. Brown; S.D. Kraus & B.N. White (2000). "Analysis of mitochondrial DNA diversity within and between North and South Atlantic right whales". Marine Mammal Science. 16 (3): 545–558. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.2000.tb00950.x.
- Brownell, R. L. Jr.; P.J. Clapham; T. Miyashita & T. Kasuya (2001). "Conservation status of North Pacific right whales". Journal of Cetacean Research and Management. 2: 269–286.
- "List of Marine Mammal Species and Subspecies". Committee on Taxonomy. Society for Marine Mammalogy. April 3, 2012. Retrieved September 29, 2012.
- Kenney, Robert D. (February 26, 2009). "North Atlantic, North Pacific and Southern Right Whales". In Perrin, William F.; Wursig, Bernd; Thewissen, J.G.M. 'Hans' (eds.). Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals. Academic Press. pp. 806–813. ISBN 978-0-08-091993-5.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Kaliszewska, Z. A.; J. Seger; S. G. Barco; R. Benegas; P. B. Best; M. W. Brown; R. L. Brownell Jr.; A. Carribero; R. Harcourt; A. R. Knowlton; K. Marshalltilas; N. J. Patenaude; M. Rivarola; C. M. Schaeff; M. Sironi; W. A. Smith & T. K. Yamada (2005). "Population histories of right whales (Cetacea: Eubalaena) inferred from mitochondrial sequence diversities and divergences of their whale lice (Amphipoda: Cyamus)". Molecular Ecology. 14 (11): 3439–3456. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2005.02664.x. PMID 16156814.
- Palaeobiology and Biodiversity Research Group Archived July 12, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, University of Bristol
- Ross, Alison (September 20, 2005). "Whale riders' reveal evolution". BBC News.
- Jackson, Stephen; Groves, Colin (2015). Taxonomy of Australian Mammals. Csiro Publishing. p. 315. ISBN 9781486300136. Retrieved February 22, 2016.
The placement of Caperea within the monotypic Family Neobalaenidae is done with the qualification that future work may corroborate the referral of Caperea to the † Family Cetotheriidae.
- Fordyce, R. Ewan; Marx, Felix G. (2013). "The pygmy right whale Caperea marginata: the last of the cetotheres". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 280 (1753): 20122645. doi:10.1098/rspb.2012.2645. PMC 3574355. PMID 23256199.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- "Prehistoric Whale Discovered On The West Coast Of Sweden". Sciencedaily.com. June 5, 2009. Retrieved May 10, 2012.
- Perrin, W.F. (2012). "Hunterius swedenborgii Lilljeborg, 1867". World Cetacea Database. Retrieved September 29, 2012.
- "Whale bones found in highway were not from mystery whale". ScienceNordic.com. February 7, 2013. Retrieved March 26, 2013.
- Melville, Herman (1892). "XXXII Cetology". Moby Dick: or, the White Whale. Boston: L.C. Page & Company. p. 131.
- Perrin, W.F. (2012). "Eubalaena australis Desmoulins, 1822". World Cetacea Database. Retrieved September 29, 2012.
- Perrin, W.F. (2012). "Eubalaena glacialis Müller, 1776". World Cetacea Database. Retrieved September 29, 2012.
- Perrin, W.F. (2012). "Eubalaena japonica Lacépède, 1818". World Cetacea Database. Retrieved September 29, 2012.
- Carwardine, Mark; Camm, Martin (July 1, 2010). Whales, Dolphins, and Porpoises. Dorling Kindersley. ISBN 978-1-4053-5794-4.
- Brueck, Hilary (January 19, 2016). "A Surprising Tool for Saving the Whales: Facial Recognition Software". Fortune. Retrieved January 22, 2016.
- "Fig. S3. Stranded Pacific right whale Eubalaena japonica at Izu..."
- Woodward, Becky L.; Winn, Jeremy P.; Fish, Frank E. (2006). "Morphological Specializations of Baleen Whales Associated With Hydrodynamic Performance and Ecological Niche" (PDF). Journal of Morphology. 267 (11): 1284–1294. doi:10.1002/jmor.10474. PMID 17051544. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 5, 2016.
The true buoyancy of a particular whale is dependent upon its body composition, particularly the relative quantities of muscle and blubber tissues. Balaenopterid whales have a higher proportion of muscle tissue and tend to be negatively buoyant while the opposite is true for right whales (Lockyer, 1976).
- Lockyer, C. (1976). "Body weights of some species of large whales". Journal du Conseil International pour l'Exploration de la Mer. 36 (3): 259–273. doi:10.1093/icesjms/36.3.259.
- Kenney, Robert D. (2008). "Right Whales (Eubalaena glacialis, E. japonica, and E. australis)". In Perrin, W. F.; Wursig, B.; Thewissen, J. G. M. (eds.). Encyclopedia of Marine Mammals. Academic Press. pp. 962–69. ISBN 978-0-12-373553-9. Retrieved May 20, 2012.
- Brownell Jr., Robert L.; Ralls, K. (1986). "Potential for sperm competition in baleen whales". Report of the International Whaling Commission. 8 (8): 97–112.
- Oceanus Magazine. Images: Doing the Right Thing for the Right Whale. Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution. Retrieved on November 5. 2014
- A.R. Knowlton; S.D. Kraus & R.D. Kenney (1994). "Reproduction in North Atlantic right whales (Eubalaena glacialis)". Canadian Journal of Zoology. 72 (7): 1297–1305. doi:10.1139/z94-173.
- P.K. Hamilton; A.R. Knowlton; M.K. Marx & S.D. Kraus (1998). "Age structure and longevity in North Atlantic right whales (Eubalaena glacialis) and their relation to reproduction". Marine Ecology Progress Series. 171: 285–292. Bibcode:1998MEPS..171..285H. doi:10.3354/meps171285.
- R. Payne; V. Rowntree; J.S. Perkins; J.G. Cooke & K. Lankester (1990). "Population size, trends and reproductive parameters of right whales (Eubalaena australis) off Peninsula Valdez, Argentina". Report of the International Whaling Commission. Special Issue 12: 271–278.
- Leaper R.; Cooke J.; Trathan P.; Reid K.; Rowntree V.; Payne R. (2005). "Global climate drives southern right whale (Eubalaena australis) population dynamics" (PDF). Biology Letters. 2 (2): 289–292. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2005.0431. PMC 1618902. PMID 17148385. Retrieved August 16, 2016.
- Boesak T. (2015). "Southern right whales distribution and reproduction". The Ocean Blue. Retrieved August 16, 2016.
- P.B. Best (1994). "Seasonality of reproduction and the length of gestation in southern right whales Eubalaena australis". Journal of Zoology (London). 32 (2): 175–189. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.1994.tb01567.x.
- Payne R. (1986). "Long term behavioral studies of the southern right whale (Eubalaena australis)" (PDF). Scientific Reports at International Whaling Commission 10: 161–167. Retrieved August 16, 2016.
- "Southern Right Whales". New Zealand Whale and Dolphin Trust. Retrieved August 16, 2016.
- Katona, S. K.; Kraus, S. D. (1999). "Efforts to conserve the North Atlantic right whale". In Twiss, John R.; Reeves, Randall R.; Montgomery, Suzanne (eds.). Conservation and Management of Marine Mammals. Smithsonian Press. pp. 311–331. ISBN 978-1-56098-778-9.
- Moore, M. (November 3, 2004). "Whither the North Atlantic Right Whale?: Scientists explore many facets of whales' lives to help species on the edge of extinction". Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution. Retrieved August 10, 2012.
- Notarbartolo di Sciara, G.; E. Politi; A. Bayed; P.-C. Beaubrun & A. Knowlton (1998). "A winter cetacean survey off Southern Morocco, with a special emphasis on suitable habitats for wintering right whales". Reports of the International Whaling Commission. 48: 547–550.
- Martin AR, Walker FJ (May 16, 1996). "Sighting of a right whale (Eubalaena glacialis) with calf off S. W. Portugal". Marine Mammal Science. 13 (1): 139–140. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.1997.tb00617.x. Archived from the original on August 13, 2011. Retrieved October 26, 2006.
- Jacobsen, K.O.; Marx, M.; Øien, N. (May 21, 2003). "Two-Way Trans-Atlantic Migration of a North Atlantic Right Whale (Eubalaena Glacialis)". Marine Mammal Science. 20 (1): 161–166. doi:10.1111/j.1748-7692.2004.tb01147.x. Archived from the original on August 13, 2011. Retrieved October 26, 2006.
- Viegas, Jennifer (June 30, 2010). "Smallest whale population identified". Discovery News. Retrieved May 19, 2012.
- Rincon, Paul (December 3, 2003). "Northern Right Whales respond to emergency sirens". BBC News. Retrieved May 10, 2012.
- "North Pacific Right Whale". Alaska Sea Grant Marine Education. Retrieved August 9, 2012.
- "Southern right whales of Patagonia" (PDF). Whale and Dolphin Conservation Society. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 6, 2010. Retrieved August 7, 2012.
- Gaines CA, Hare MP, Beck SE, Rosenbaum HC (March 7, 2005). "Nuclear markers confirm taxonomic status and relationships among highly endangered and closely related right whale species". Proceedings of the Royal Society B. 272 (1562): 533–542. doi:10.1098/rspb.2004.2895. PMC 1578701. PMID 15846869.
- Scarff, JE (2001). "Preliminary estimates of whaling-induced mortality in the 19th century Pacific northern right whale (Eubalaena glacialis) fishery, adjusting for struck-but-lost whales and non-American whaling". J. Cetacean Res. Manag. (Special Issue 2): 261–268.
- Tønnessen, Johan Nicolay; Johnsen, Arne Odd (1982). The History of Modern Whaling. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-03973-5.
- National Audubon Society (2002). Guide to Marine Mammals of the World. A. A. Knopf. ISBN 978-0-375-41141-0.
- "Whale Watching in Hermanus at the Windsor Hotel". Windsor Hotel website. Retrieved August 10, 2012.
- "Hermanus Whale Crier". SA Venues.com. Retrieved August 7, 2012.
- "News From Brazil". Cetacean Society International. Archived from the original on April 14, 2013. Retrieved August 10, 2012.
- Ribeiro, P. "Whale Watching in Santa Catarina, Brazil: Fascinating Encounters With Southern Right Whales". About.com Brazil Travel. Retrieved August 10, 2012.
- "Ocean Alliance website". Oceanalliance.org. Archived from the original on March 4, 2015. Retrieved May 10, 2012.
- "North Atlantic Right Whales (Eubalaena glacialis)". NOAA Fisheries Office of Protected Resources. National Marine Fisheries Service. Retrieved September 4, 2012.
- "North Pacific Right Whales (Eubalaena japonica)". NOAA Fisheries Office of Protected Resources. National Marine Fisheries Service. Retrieved September 4, 2012.
- "Southern Right Whales (Eubalaena australis)". NOAA Fisheries Office of Protected Resources. National Marine Fisheries Service. Retrieved September 4, 2012.
- "Right whales need extra protection". BBC News. BBC News. November 28, 2001. Retrieved May 2, 2006.
- The Southeast United States Right Whale Recovery Plan Implementation Team and the Northeast Implementation Team (November 2005). "NMFS and Coast Guard Inactions Bring Litigation" (PDF). Right Whale News. 12 (4). Retrieved May 2, 2006.
- "Área de Proteção Ambiental" (in Portuguese). Projeto Baleia Franca. Archived from the original on July 28, 2012. Retrieved September 4, 2012.
- NOAA. Proposed Strategy to Reduce Ship Strikes to North Atlantic Right Whales.
- NOAA (December 8, 2008). "Press Release on Effective Date of Speed Regulations" (PDF). Retrieved December 21, 2008.
- Vanderlaan & Taggart (2007). "Vessel collisions with whales: the probability of lethal injury based on vessel speed" (PDF). Mar. Mam. Sci. Retrieved May 10, 2008.
- "Whales Entangled In Fishing Lines: What Can Be Done?". Science Daily. Retrieved August 7, 2012.
- "Atlantic Large Whale Take Reduction Plan". National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. 1997. Archived from the original on September 24, 2008. Retrieved May 2, 2006.
- Strachan, Deshayla (September 12, 2012). "Whale Defenders Lose Navy Training Challenge". Courthouse News Service. Archived from the original on September 23, 2015. Retrieved September 20, 2012.
- Heimer, Taryn Kiekow (September 10, 2012). "Right Whales Wronged: Judge allows Navy to expand sonar use in Florida calving area". Natural Resources Defense Council. Retrieved October 9, 2012.
- "Poor calving season for right whales". savannahnow.com. Archived from the original on January 7, 2015.
Further reading
- Kraus, Scott D.; Rolland, Rosalind, eds. (2010). The Urban Whale: North Atlantic Right Whales at the Crossroads. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-03475-4.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Eubalaena. |
| Wikispecies has information related to Eubalaena |

