Vismodegib
Vismodegib (trade name Erivedge /ˈɛrɪvɛdʒ/ ERR-i-vej) is a drug for the treatment of basal-cell carcinoma (BCC). The approval of vismodegib on January 30, 2012, represents the first Hedgehog signaling pathway targeting agent to gain U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval.[2] The drug is also undergoing clinical trials for metastatic colorectal cancer, small-cell lung cancer, advanced stomach cancer, pancreatic cancer, medulloblastoma and chondrosarcoma as of June 2011.[3] The drug was developed by the biotechnology/pharmaceutical company Genentech.[2]
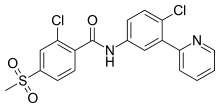 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˌvɪsmoʊˈdɛɡɪb/ VIS-moh-DEG-ib |
| Trade names | Erivedge |
| Other names | GDC-0449, RG-3616 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth (capsules) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 31.8% |
| Protein binding | >99% |
| Metabolism | <2% metabolised by CYP2C9, CYP3A4, CYP3A5 |
| Elimination half-life | 4 days (continuous use), 12 days (single dose) |
| Excretion | Fecal (82%), Urinary (4.4%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.234.019 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H14Cl2N2O3S |
| Molar mass | 421.29 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Indication
Vismodegib is indicated for patients with basal cell carcinoma (BCC) which has metastasized to other parts of the body, relapsed after surgery, or cannot be treated with surgery or radiation.[2][4]
Mechanism of action
The substance acts as a cyclopamine-competitive antagonist of the smoothened receptor (SMO) which is part of the hedgehog signaling pathway.[3] SMO inhibition causes the transcription factors GLI1 and GLI2 to remain inactive, which prevents the expression of tumor mediating genes within the hedgehog pathway.[5] This pathway is pathogenetically relevant in more than 90% of basal-cell carcinomas.[6]
Side effects
In clinical trials, common adverse effects included gastrointestinal disorders (nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, constipation), muscle spasms, fatigue, hair loss, and dysgeusia (distortion of the sense of taste). The effects were mostly mild to moderate.[1]
See also
- Cyclopamine, a naturally occurring SMO antagonist
References
- FDA Professional Drug Information
- "FDA approves Erivedge (vismodegib) capsule, the first medicine for adults with advanced basal cell carcinoma". Roche. 30 January 2012. Retrieved 9 August 2020.
- "Molecule of the Month". June 2011. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Lacroix, Marc (2014). Targeted Therapies in Cancer. Hauppauge, NY: Nova Sciences Publishers. ISBN 978-1-63321-687-7.
- "Vismodegib (GDC-0449) Smoothened Inhibitor - BioOncology".
- H. Spreitzer (4 July 2011). "Neue Wirkstoffe – Vismodegib". Österreichische Apothekerzeitung (in German) (14/2011): 10.
Further reading
External links
- "Vismodegib". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved vismodegib