Dutch Grand Prix
The Dutch Grand Prix (Dutch: Grote Prijs van Nederland) is a Formula One automobile race held at Circuit Zandvoort, North Holland, Netherlands, from 1948 to 1985 and scheduled to be held from 2021 onwards. It was a part of the World Championship from 1952, and designated the European Grand Prix twice, 1962 and 1976, when this title was an honorary designation given each year to one Grand Prix race in Europe.
| Circuit Zandvoort | |
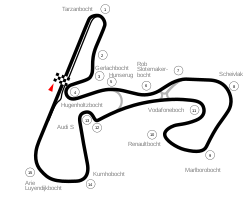 | |
| Race information | |
|---|---|
| Number of times held | 34 |
| First held | 1948 |
| Last held | 1985 |
| Most wins (drivers) | |
| Most wins (constructors) | |
| Circuit length | 4.259 km (2.646 mi) |
| Race length | 306.648 km (190.542 mi) |
| Laps | 72 |
| Last race (1985) | |
| Pole position | |
| |
| Podium | |
| Fastest lap | |
| |
History
Original circuit
The town of Zandvoort is situated in the dunes of the North Holland's North Sea coastline half an hour west from the Dutch capital of Amsterdam, and the circuit itself is located right next to the beach. There were minor races on a street circuit in the town in the 1930s but it was the German invasion of the Netherlands which proved to be a stroke of luck for the locals. In an effort to stop his townsfolk being sent to Germany to work, legend has it that the Mayor of Zandvoort convinced the Germans to allow them to construct a straight road through the dunes down which the Germans could hold impressive parades once victory had been achieved. This was later linked to other roads which were used to access coastal defence positions.
After the war some of these roads were widened and linked together and a racing circuit was designed, not as legend has it by John Hugenholtz, but rather by a group of officials from the Royal Dutch Motorcycle Association, with advice from Bentley Boy Sammy Davis, who had won the Le Mans 24 Hours in 1927. The first race took place in 1948, under the title of the Zandvoort Grand Prix. It was won by Thailand's Prince Bira in an old Maserati.[1] The race was then won by Louis Rosier in 1950 and 1951. 1952 was the year the Dutch Grand Prix was part of the third Formula One World Championship; this and the next year's races were won by Italian Alberto Ascari. The race was not held in 1954 due to a lack of money to hold the race,[2] and 1955 saw yet another demonstration of Mercedes-Benz's dominance, with Argentine Juan Manuel Fangio and Briton Stirling Moss dominating the proceedings; Moss followed Fangio closely all the way. The 1956 and 1957 races were cancelled because of apparent lack of money, which was indirectly caused by the 1956–1957 Suez Crisis. The 1958 Dutch Grand Prix was won by Moss in a Vanwall. 1959 saw Swede Jo Bonnier win his only Formula One championship event and 1960 saw Dan Gurney have an accident and a spectator was killed; the race was won by Jack Brabham in a Cooper.
From 1963 to 1965 saw Briton Jim Clark win all three events, and 1967 saw the introduction of the Lotus 49 with its brand new Ford-Cosworth DFV engine. The DFV won on its debut with Clark driving; this engine became the most successful and widely used engine among private teams until 1985. The 1970 Championship, however, saw the 49's successor, the 72 (which was just as advanced a design as the 49 had been 3 years earlier) win comprehensively with Jochen Rindt behind the wheel.
Tragedy struck, when Briton Piers Courage, driving a Frank Williams, crashed heavily near the notoriously fast Tunnel Oost corner after a wheel came off and hit him on the head, which killed him. The car, with Courage still in it, then caught fire and burned to the ground. The 1971 Championship saw Jacky Ickx win in a Ferrari after a spirited battle with Mexican Pedro Rodriguez in a BRM in rain-soaked conditions. There was no 1972 race. It was originally on that year's calendar, but the drivers refused to race at Zandvoort, because the facilities and conditions of the circuit were out-of-date with Grand Prix racing at that time.
Redeveloped circuit
Zandvoort had been extensively modified during its absence from the Grand Prix calendar. It had been lined with Armco and the cars were protected from the sand dunes and track-side obstacles. New pits were built, and the circuit also saw a chicane placed before Bosuit, the very high-speed corner that went into the pit-straight. For the 1973 race, in an indirect celebration of the efforts put forth, there was a special atmosphere at that weekend and everyone was happy, especially the organizers. But in a cruel twist of fate, that race was to be yet another black mark on Zandvoort's history and reputation. In a race that was thought to be one of the most well organized Grands Prix yet seen, it was actually disorganization and a total lack of clear communication that would be ultimately responsible for what was to happen. On the eighth lap of the race, Briton Roger Williamson (in only his second ever Formula One race) crashed heavily near Tunnel Oost and his car caught fire while scraping along the tarmac. Williamson was uninjured during the crash; but time was running out; he could not free himself from the car. Williamson's countryman David Purley stopped alongside, crossed the track and ran over to the burning March. Purley tried in vain to turn the car upright. There appeared to have been ample time to right the car and pull Williamson out, but as desperately as he tried, Purley was unable to do it by himself, and the marshals, who were not wearing flame retardant overalls, were unable and unwilling to help due to the intense heat. Race control assumed that it was Purley's car that had crashed and that the driver had escaped unharmed. Many drivers who saw Purley waving them down to stop assumed that he was trying to put a fire out from his own car, having safely exited it, and thus did not know that a second driver had been involved. As a result, the race continued at full pace while Purley desperately tried to save the life of Williamson. Due to a group of race officials standing around Williamson's burning car doing absolutely nothing to help and even hindering the situation (by throwing away the fire extinguisher Purley was using over the Armco and down a slope), this did not work, and Williamson died not of skin burns but of asphyxiation. Purley was later awarded the George Medal for his actions. The race was won by Tyrrell driver Jackie Stewart (who broke Jim Clark's record for the most career Grand Prix victories that weekend) and his teammate François Cevert finished 2nd; but no one felt like celebrating; it was one of the darkest moments in the history of the sport.
1974 saw the re-emerging Ferrari team dominate with Austrian Niki Lauda winning; and 1975 saw Briton James Hunt win his first championship Formula One race in his Hesketh. 1976 saw Hunt win again while Lauda was recovering from his dreadful crash at the Nürburgring. 1977 was probably remembered for an incident between Hunt and American Mario Andretti. Andretti attempted ambitiously to pass Hunt at the 180-degree Tarzan corner; the two cars touched and both were out of the race. Andretti won the 1978 running; his last Formula One victory. 1979 saw a change to the circuit to slow cars coming into Tunnel Oost; there was a high-speed temporary chicane put there. Canadian Gilles Villeneuve had crashed there while battling ferociously with Australian Alan Jones and damaged his left-rear suspension. But he carried on; but on the start of the next lap he went off again at Tarzan. Refusing to give up, Villeneuve, to the shock of many, went into reverse gear and drove his Ferrari out of the muddy run-off area and back onto the circuit. About halfway distance, the car's left rear rim and wheel with the suspension totally shattered was being dragged by the car as it went along; which made the Ferrari nearly impossible to drive. Villeneuve, displaying his now legendary car control, made it back to the pits without crashing or going off and retired from the race; the Grand Prix was won by Jones. 1980 saw the chicane removed and was replaced by a slower chicane before Tunnel Oost. 1981 saw a big battle between Frenchman Alain Prost in a Renault and Jones in a Williams; Prost came out on top to win. The 1982 event was won by Frenchman Didier Pironi in a Ferrari; his countryman René Arnoux had a dreadful crash at the end of the pit straight going into Tarzan; his front suspension failed on his ground-effect Renault and he went head on into the barriers; fortunately he was uninjured. 1983 saw a battle between championship contenders Prost and Brazilian Nelson Piquet. Prost attempted to pass Piquet at Tarzan but the Frenchman punted Piquet off and Prost crashed soon afterwards. 1985 saw Lauda take his 25th and final Grand Prix victory while holding off his charging McLaren teammate Prost near the end of the race.
1985 was the race's final running, as the company that ran the circuit (CENAV) went out of business, marking the end of the old Zandvoort circuit. The track, owned by the municipality of Zandvoort, was not used for some time and part of the grounds and approximately half of the track was sold in 1987 to Vendorado, a bungalow park developer at that time.[3] The track was eventually redesigned and is still used for other disciplines of motorsport.
2021–
On 14 May 2019, the Dutch Grand Prix at the Zandvoort track was announced for the 2020 Formula One calendar.[4] In March 2020 the return of event was postponed in response to the COVID-19 pandemic; it was later cancelled altogether with the event's return now due in 2021.
Official names
- 1952–1953, 1955, 1958–1963, 1984–1985: Grote Prijs van Nederland (no official sponsor)[5]
- 1964–1965: Grote Prijs der K.N.A.C. (no official sponsor)[6]
- 1966–1967, 1969–1971, 1973–1975: Grand Prix Zandvoort (no official sponsor)[7]
- 1968: Grrrand Prix Zandvoorrrt (no official sponsor)[8]
- 1976: Grand Prix van Europa/Grand Prix van Nederland[9]
- 1977–1983: Grand Prix (no official sponsor)[10]
- 2021: Heineken Dutch Grand Prix[11]
Winners of the Dutch Grand Prix
Repeat winners (drivers)
A pink background indicates an event which was not part of the Formula One World Championship.
| Wins | Driver | Years won |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | 1963, 1964, 1965, 1967 | |
| 3 | 1968, 1969, 1973 | |
| 1974, 1977, 1985 | ||
| 2 | 1950, 1951 | |
| 1952, 1953 | ||
| 1960, 1966 | ||
| 1975, 1976 | ||
| 1981, 1984 |
Repeat winners (constructors)
A pink background indicates an event which was not part of the Formula One World Championship.
Teams in bold are competing in the Formula One championship in the current season.
| Wins | Constructor | Years won |
|---|---|---|
| 9 | 1949, 1952, 1953, 1961, 1971, 1974, 1977, 1982, 1983 | |
| 6 | 1963, 1964, 1965, 1967, 1970, 1978 | |
| 3 | 1976, 1984, 1985 | |
| 2 | 1950, 1951 | |
| 1959, 1962 | ||
| 1968, 1969 | ||
| 1966, 1980 |
Repeat winners (engine manufacturers)
A pink background indicates an event which was not part of the Formula One World Championship.
Manufacturers in bold are competing in the Formula One championship in the current season.
| Wins | Manufacturer | Years won |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 1967, 1968, 1969, 1970, 1973, 1975, 1976, 1978, 1979, 1980 | |
| 9 | 1949, 1952, 1953, 1961, 1971, 1974, 1977, 1982, 1983 | |
| 4 | 1960, 1963, 1964, 1965 | |
| 2 | 1984, 1985 | |
| 1950, 1951 | ||
| 1959, 1962 |
* Designed and built by ![]()
** Built by ![]()
By year
All Dutch Grands Prix were held at Zandvoort.
A pink background indicates an event which was not part of the Formula One World Championship.
References
- "Grand Prix Circuits: Dutch Motor Racing". www.grandprix.com. Archived from the original on 3 February 2002. Retrieved 23 January 2020.
- "Grands Prix which were cancelled - The Nostalgia Forum". The Autosport Forums. Retrieved 23 January 2020.
- "Track description on www.autoevolution.com". Archived from the original on 18 May 2009. Retrieved 7 August 2010.
- "Formula 1 Dutch Grand Prix to return at Zandvoort from 2020". www.formula1.com. Retrieved 14 May 2019.
- 1952-1953, 1955,1958-1963, 1984-1985 programs:
- "1952 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1953 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1955 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1958 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1959 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1960 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1961 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1962 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1963 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1984 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1985 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- 1964-1965 programs:
- 1966-1967, 1969-1971, 1973-1975 programs:
- "1966 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1967 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1969 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1970 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1971 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1973 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1974 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1975 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1968 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1976 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- 1977-1983 programs:
- "1977 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1978 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1979 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1980 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1981 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1982 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "1983 Formula 1 World Championship Programmes | The Motor Racing Programme Covers Project". www.progcovers.com.
- "Netherlands". Formula1.com. Formula One World Championship Limited. Retrieved 16 January 2020.