Crimean Goths
Crimean Goths were Greuthungi-Gothic tribes who remained in the lands around the Black Sea, especially in Crimea. They were the least-impactful on the fate of Europe and the longest-lasting of the Gothic communities. Their existence is well attested through the ages though the exact period when they ceased to exist as a distinct culture is unknown; as with the Goths in general, they may have been diffused with the surrounding peoples. In the Fourth Turkish letter by Ogier Ghiselin de Busbecq, they are described as "a warlike people, who to this day inhabit many villages" though in the 5th century, Theodoric the Great failed to rouse Crimean Goths to support his war in Italy.[3] At the time, it was customary to refer to a wide range of Germanic tribes as "Goths", so the exact ethnic origin of the Germanic peoples in Crimea is a subject of debate.
Aside from textual reports of the existence of the Goths in Crimea, both first and second hand, from as early as 850,[4] numerous archaeological examples also exist, including the ruins of the former capital city of the Crimean Goths: Doros, or Mangup as it is now known. On top of this, there are numerous articles of jewelry, weaponry, shields, buttons, pins, and small personal artifacts on display in museums in Crimea and in the British Museum which have led to a better understanding of the Gothic Kingdom.
Definition
In the report made by Ogier Ghiselin de Busbecq in 1595 of the Crimean Goths, he claims to not be able to determine whether the Germanic peoples of Crimea were Goths or Saxons, certainly the language cannot be directly linked to the well-attested Gothic language. Though most scholars agree the peoples must have been of Gothic origin,[5][6] some others have maintained that the so-called "Crimean Goths" were in fact West or even North Germanic tribes who settled in Crimea, culturally and linguistically influenced by the Ostrogoths.[7]
History
Early history
According to Herwig Wolfram, following Jordanes, the Ostrogoths had a huge kingdom north of the Black Sea in the 4th century,[8] which the Huns overwhelmed in the time of the Gothic king Ermanaric (or Hermanric; i.e. "king of noblemen"[note 1]) when the Huns migrated to the Ukrainian steppe.

The Ostrogoths became vassals of the Huns until the death of Attila, when they revolted and regained independence. Like the Huns, the Goths in Crimea never regained their lost glory.
According to Peter Heather and Michael Kulikowski, the Ostrogoths did not even exist until the 5th century, when they emerged from other Gothic and non-Gothic groups.[9][10] Other Gothic groups may have settled in Crimea.[11] It has also been speculated that the Crimean Goths were in fact Saxons escaping Christian persecution from the west, or North Germanic tribes who migrated southwards. Either way, the existence of Goths in Crimea is first testified from around the 3rd century, and after that they were well reported.
During the late 5th and early 6th century, the Crimean Goths had to fight off hordes of Huns who were migrating back eastward after losing control of their European empire.[12] In the 5th century, Theodoric the Great tried to recruit Crimean Goths for his campaigns in Italy, but few showed interest in joining him.[3]
Byzantium
_02.jpg)
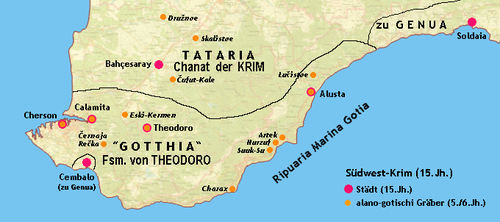
The Principality of Gothia or Theodoro formed after the Fourth Crusade out of parts of the Byzantine thema of Klimata which were not occupied by the Genoese. Its population was a mixture of Greeks, Crimean Goths, Alans, Bulgars, Kipchaks and other nations, which confessed Orthodox Christianity. The principality's official language was Greek. The territory was initially under the control of Trebizond, and possibly part of its Crimean possessions, the Perateia.
Many Crimean Goths were Greek speakers and many non-Gothic Byzantine citizens were settled in the region called "Gothia" by the government in Constantinople. A Gothic principality around the stronghold of Doros (modern Mangup), the Principality of Theodoro, continued to exist through various periods of vassalage to the Byzantines, Khazars, Kipchaks, Mongols, Genoese and other empires until 1475, when it was finally incorporated in the Khanate of Crimea and the Ottoman Empire. This is generally considered to be the fall of the Crimean Goths.[13]
There is a theory that some Anglo-Saxons who left England after the Battle of Hastings in 1066 arrived in Constantinople in time to help the Byzantines repel an invasion.[14] As a reward, the Byzantine emperor granted them lands near the Sea of Azov in what may have been the Crimean Peninsula.
16th century
By the 16th century, the existence of Goths in Crimea had become well known to European scholars. Many travelers visited Crimea and wrote about the Goths. One romantic report appears in Joachimus Cureus' Gentis Silesiae Annales in which he claims that during a voyage in the Black Sea, his ship was forced ashore by storms. There, to his surprise, he found a man singing a song in which he used "German words". When he asked him where he was from, he answered "that his home was nearby and that his people were Goths".[15]
Several inscriptions from the early 9th century found in the area use the word "Goth" only as a personal name, not ethnonym. Meanwhile, some legends about a Gothic state in Crimea existed in Europe throughout the Middle Ages. In the 16th century, an Imperial envoy in Suleiman's court Ogier Ghiselin de Busbecq reported having had a conversation with two Goths in Constantinople. He also left the Gothic-Latin dictionary with about a hundred Germanic words that share some traits in common with the ancient Gothic language.
Following the report by Busbecq, numerous European travelers went to visit Crimea, Torquatus visited Crimea in the mid- to late 16th century in which he reported the existence of Goths who spoke their own language, but used Greek, Tatar and Hungarian in dealing with outsiders.[15]
In 1690, Kampfer states:
The language spoke in the Peninsula Crimea, or Taurica Chersonesus, in Asia, still retains many German words, brought thither, as is suppos'd by a colony of Goths, who went to settle there about 850 years after the Deluge. The late Mr. Busbeq, who had been Imperial Ambassador at the Ottoman Port, collected and publish'd a great number of these words in his fourth letter; and in my own travels through that Country I took notice of many more.[16]
Religion
The first report of the Crimean Goths appears in the Vita of Saint Cyril, Apostle to the Slavs (Constantine the Philosopher) who went to Crimea to preach the gospel to the Khazars (c. 850). He lists "Goths" as people who read and praised the Christian God "in their own language".[17] In 1606 Joseph Justus Scaliger claimed that the Goths of Crimea read both the Old and New Testaments "in the letters of Wulfila's alphabet".[18] These are the only two reports which refer to the existence of a written form of Crimean Gothic, but also confirm their Christian faith.
While initially Arian Christians like other Gothic peoples, the Crimean Goths had converted to Chalcedonian Christianity by the 6th century. Following the split of Chalcedonian Christianity in the 11th century between the Roman and Orthodox branches, these peoples remained loyal to Constantinople as part of the Eastern Orthodox Church. In the 8th century John of Gothia, an Orthodox bishop, led an unsuccessful revolt against Khazar overlordship.
Language
The language of the Crimean Goths is poorly attested with only 101 certain independent forms surviving, few of which are phrases, and a three line song, which has never been conclusively translated. Possible loan words are still used in Crimean Tatar though this too remains highly speculative.
| English | Crimean Gothic | Bible Gothic | German | Dutch | Icelandic | Swedish | Danish |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apple | Apel | (unattested) | Apfel | Appel | Epli | (vild-)apel, Äpple | Æble |
| Hand | Handa | Handus (f.) | Hand | Hand | Hönd | Hand | Hånd |
| Sister | Schuuester | Swistar (f.) | Schwester | Zus (ter) | Systir | Syster | Søster |
| House | Hus | -hūs (n.) | Haus | Huis | Hús | Hus | Hus |
| Rain | Reghen | Rign (n.) | Regen | Regen | Regn | Regn | Regn |
| Sing | Singhen | Siggwan (vb.) | Singen | Zingen | Syngja | Sjunga | Synge |
| Go | Geen | Gaggan (vb.) | Gehen | Gaan | Ganga | Gå | Gå |
| English | Crimean Gothic | Bible Gothic | German | Dutch | Icelandic | Swedish | Danish |
In 2015, five Gothic graffiti inscriptions were found by Andrey Vinogradov, a Russian historian, on stone plates excavated in Mangup in 1938, and deciphered by him and Maksim Korobov. The reading of these inscription was made difficult because they were later overwritten by some Greek graffiti.[19][20]
The graffiti were scratched on two re-used fragments of early Byzantine cornice from the Mangup Basilica. The stone fragments on which the inscriptions were originally made were also probably reused later as part of the pavement, so they were also somewhat worn out. In any case, the full history of the use of these stones up to today is not entirely clear. The basilica that the stones belonged to was rebuilt several times through the centuries.
These Gothic inscriptions were written in the second half of the 9th century or in the first half of the 10th century - based on the dating of the later Greek graffiti.
Disappearance
There are numerous other sources referring to the existence of Goths in Crimea following Busbecq's report, though none providing details of their language or customs. The last known record of the Goths in Crimea comes from the Archbishop of Mohilev, Stanisław Bohusz Siestrzeńcewicz c. 1780, who visited Crimea at the end of the 18th century, and noted the existence of people whose language and customs differed greatly from their neighbors and who he concluded must be "Goths".[21]
Despite no further records of the language's existence since the late 18th century, communities of Germanic peoples with distinctly separate customs and physical features have been recorded living in Crimea, leading some to believe that the Gothic language may have survived as a "haussprache" (home language) until as late as 1945.[22]
According to the Soviet Ethnologist V.E. Vozgrin, the Goths interbred with the Crimean Tatars and converted to Islam. In The Crimean Tatars: the diaspora experience and the forging of a nation by Brian Glyn Williams, he quotes Vozgrin as saying: "In all probability their descendents are the Tatars of a series of villages in Crimea, who are sharply delineated from the inhabitants of neighboring villages by their tall height and other features characteristic of Scandinavians."
It is likely that the Goths had begun to speak Crimean Tatar and Crimean Greek from long before the arrival of Busbecq,[23] thus they may well have integrated into the wider population, as later visitors to Mangup were unable to discover "any trace" of Gothic peoples.[24]
Legacy
Almost no signs of the Crimean Goths exist today. It was claimed by the Third Reich and by Adolf Hitler that the Crimean Goths had survived long enough to interbreed with later German settlers in Crimea, and that the German communities in Crimea constituted native peoples of that area. Hitler had intended to re-settle German people to Crimea, and rename numerous towns with their previous Crimean Gothic names. During the Nazi occupation of Crimea, Sevastopol was changed to Theoderichshafen.[25] Hitler's ultimate goal for his planned "Gau Gotenland" ("Goth land") was to replace the local population with "pure Germans" and turn the Crimea into what he described as "the German Gibraltar"—a national foothold not contiguous to the rest of Germany, similar to how Gibraltar was not contiguous to the rest of the United Kingdom—to be connected to Germany proper by an autobahn. The plan was postponed for the duration of the war, and never went into effect due to Nazi Germany's eventual defeat.[26]
See also
Notes
- Here/Hari (army/noble) + mann/man + ric/rike (ruler))
References
- Śrimati Akshaya Kumari Devi, A Biographical Dictionary of Puranic Personages
- R1 expansion (R1a and R1b), indoeuropeans
- Wolfram 1988, pp. 271–280
- Vasiliev 1936, p. 114
- Streitberg 1920, p. 17
- Siebs 1922:170-72.
- Schwarz 1951, p. 162
- Wolfram 1988, pp. 78–263 passim
- Heather 1998, pp. 52–55
- Kulikowski 2006, p. 111
- Heather & Matthews 1991, p. 92 n. 87
- Wolfram 1988, p. 261
- "Tractatus de duabus Sarmatiis Asiana et Europiana et de contentis in eis". doi:10.1163/2451-9537_cmrii_com_26278. Cite journal requires
|journal=(help) - Shepard 1973
- Stearns 1971:7.
- Kempfer, Kaempfer 1631:1716
- loewe 1896:114.
- Stearns 1971:16.
- Nemalevich, Sergey (25 December 2015). "Молитвы на камнях Историк Андрей Виноградов рассказывает о первых надписях на крымско-готском языке" (in Russian). Meduza. Retrieved 26 December 2015.
- А. Ю. Виноградов; М. И. Коробов (2016). "Готские граффити из мангупской базилики" (PDF) (in Russian). pp. 57–75. A slightly revised German translation was published as "Gotische Graffito-Inschriften aus der Bergkrim", Zeitschrift für deutsches Altertum und Literatur 145 (2016) 141-157. English abstract
- Loewe (1869:200).
- Schwarz (1953:163-4).
- Stearns(1979:39–40).
- pallas(1801:363–364).
- Wolfram 2001, p. 12
- Chris Bellamy, Absolute War: Soviet Russia in the Second World War, 2008, Knopf Doubleday Publishing Group
Sources
- Bellamy, Chris (2008). Absolute War: Soviet Russia in the Second World War. Knopf Doubleday Publishing Group.
- Heather, Peter (1998). The Goths. Blackwell.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Heather, Peter; Matthews, John (1991). Goths in the Fourth Century. Liverpool Univ. Press.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Kulikowski, Michael (2006). Rome's Gothic Wars: From the Third Century to Alaric. Cambridge Univ. Press.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Schwarz, Ernst (1951). Goten, Nordgermanen, Angelsachsen. Bern: A. Francke.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Shepard, Jonathan (1973). "The English and Byzantium: A Study of Their Role in the Byzantine Army in the Later Eleventh Century". Traditio: Studies in Ancient and Medieval History, Thought, and Religion. New York: Fordham University Press. 29: 53–92. JSTOR 27830955.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Streitberg, Wilhelm (1920). Gotisches Elementarbuch (5th and 6th ed.). Heidelberg: Carl Winter's Universitätsbuchhandlung.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Vasiliev, Aleksandr A. (1936). The Goths in the Crimea. Cambridge, MA: The Mediaeval Academy of America.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Wolfram, Herwig (1988) [Originally published in German, 1980]. History of the Goths. Translated by Dunlap, Thomas J. Univ. of California Press.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Wolfram, Herwig (2001). Die Goten und ihre Geschichte. C.H. Beck.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)