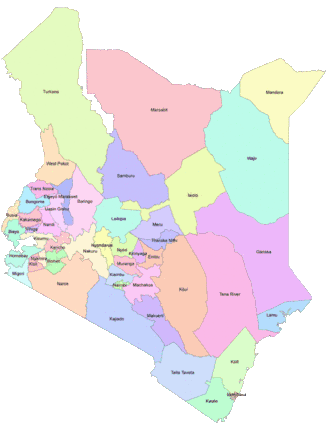
Counties of Kenya
The counties of Kenya (Swahili: Kaunti za Kenya) are geographical units envisioned by the 2010 Constitution of Kenya as the units of devolved government.[1] The powers are provided in Articles 191 and 192, and in the fourth schedule of the Constitution of Kenya and the County Governments Act of 2012. The counties are also single-member constituencies for the election of members of parliament to the Senate of Kenya[2] and special women members of parliament to the National Assembly of Kenya.[3] As of 2013 general elections, there are 47 counties whose size and boundaries are based on the 47 legally recognised Districts of Kenya. Following the re-organisation of Kenya's national administration, counties were integrated into a new national administration with the national government posting county commissioners to represent it at the counties.[4]
| Counties of Kenya Kaunti za Kenya (Swahili) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Category | Semi-Devolved State |
| Location | Republic of Kenya |
| Number | 47 Counties |
| Populations | 143,920 (Lamu) – 4,397,073 (Nairobi) |
| Areas | 294.7 km2 (113.8 sq mi) (Mombasa) – 71,597.8 km2 (27,644.1 sq mi) (Turkana) |
| Government | County Government, Government of Kenya |
| Subdivisions | Sub-Counties |
.svg.png) |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Kenya |
|
|
|
Administrative divisions |
|
|
|
Economic schemes |
|
|
Establishment
County governments were established in 47 counties (largely based on the 1992 Districts of Kenya),[5] after the scheduled general elections in March 2013. The counties' names are set out in the First Schedule of the Constitution of Kenya.
List of counties
Under the new constitution, Kenya is now divided into 47 counties for administrative purposes. They are grouped below according to the former province of which they were part, with their areas and populations as of the 2009 census:[6]
| Code | County | Former province | Area (km2) | Population census (2009) | Population census (2019) | Capital |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mombasa (County) | Coast | 212.5 | 939,370 | 1,208,333 | Mombasa (City) |
| 2 | Kwale | Coast | 8,270.3 | 649,931 | 866,820 | Kwale |
| 3 | Kilifi | Coast | 12,245.9 | 1,109,735 | 1,453,787 | Kilifi |
| 4 | Tana River | Coast | 35,375.8 | 240,075 | 315,943 | Hola |
| 5 | Lamu | Coast | 6,497.7 | 191,539 | 143,920 | Lamu |
| 6 | Taita–Taveta | Coast | 17,083.9 | 284,657 | 340,671 | Mwatate |
| 7 | Garissa | North Eastern | 45,720.2 | 623,060 | 841,353 | Garissa |
| 8 | Wajir | North Eastern | 55,840.6 | 661,941 | 781,263 | Wajir |
| 9 | Mandera | North Eastern | 25,797.7 | 1,025,756 | 867,457 | Mandera |
| 10 | Marsabit | Eastern | 66,923.1 | 291,166 | 459,785 | Marsabit |
| 11 | Isiolo | Eastern | 25,336.1 | 143,294 | 268,002 | Isiolo |
| 12 | Meru | Eastern | 7,003.1 | 1,356,301 | 1,545,714 | Meru |
| 13 | Tharaka-Nithi | Eastern | 2,609.5 | 365,330 | 393,177 | Kathwana |
| 14 | Embu | Eastern | 2,555.9 | 516,212 | 608,599 | Embu |
| 15 | Kitui | Eastern | 24,385.1 | 1,012,709 | 1,136,187 | Kitui |
| 16 | Machakos | Eastern | 5,952.9 | 1,098,584 | 1,421,932 | Machakos |
| 17 | Makueni | Eastern | 8,008.9 | 884,527 | 987,653 | Wote |
| 18 | Nyandarua | Central | 3,107.7 | 596,268 | 638,289 | Ol Kalou |
| 19 | Nyeri | Central | 2,361.0 | 693,558 | 759,164 | Nyeri |
| 20 | Kirinyaga | Central | 1,205.4 | 528,054 | 610,411 | Kerugoya / Kutus |
| 21 | Murang'a | Central | 2,325.8 | 942,581 | 1,056,640 | Murang'a |
| 22 | Kiambu | Central | 2,449.2 | 1,623,282 | 2,417,735 | Kiambu |
| 23 | Turkana | Rift Valley | 71,597.8 | 855,399 | 926,976 | Lodwar |
| 24 | West Pokot | Rift Valley | 8,418.2 | 512,690 | 621,241 | Kapenguria |
| 25 | Samburu | Rift Valley | 20,182.5 | 223,947 | 310,327 | Maralal |
| 26 | Trans-Nzoia | Rift Valley | 2,469.9 | 818,757 | 990,341 | Kitale |
| 27 | Uasin Gishu | Rift Valley | 2,955.3 | 894,179 | 1,163,186 | Eldoret |
| 28 | Elgeyo-Marakwet | Rift Valley | 3,049.7 | 369,998 | 454,480 | Iten |
| 29 | Nandi | Rift Valley | 2,884.5 | 752,965 | 885,711 | Kapsabet |
| 30 | Baringo | Rift Valley | 11,075.3 | 555,561 | 666,763 | Kabarnet |
| 31 | Laikipia | Rift Valley | 8,696.1 | 399,227 | 518,560 | Rumuruti |
| 32 | Nakuru | Rift Valley | 7,509.5 | 1,603,325 | 2,162,202 | Nakuru |
| 33 | Narok | Rift Valley | 17,921.2 | 850,920 | 1,157,873 | Narok |
| 34 | Kajiado | Rift Valley | 21,292.7 | 687,312 | 1,117,840 | Kajiado |
| 35 | Kericho | Rift Valley | 2,454.5 | 752,396 | 901,777 | Kericho |
| 36 | Bomet | Rift Valley | 1,997.9 | 730,129 | 875,689 | Bomet |
| 37 | Kakamega | Western | 3,033.8 | 1,660,651 | 1,867,579 | Kakamega |
| 38 | Vihiga | Western | 531.3 | 554,622 | 590,013 | Vihiga |
| 39 | Bungoma | Western | 2,206.9 | 1,375,063 | 1,670,570 | Bungoma |
| 40 | Busia | Western | 1,628.4 | 743,946 | 893,681 | Busia |
| 41 | Siaya | Nyanza | 2,496.1 | 842,304 | 993,183 | Siaya |
| 42 | Kisumu | Nyanza | 2,009.5 | 968,909 | 1,155,574 | Kisumu(City) |
| 43 | Homa Bay | Nyanza | 3,154.7 | 963,794 | 1,131,950 | Homa Bay |
| 44 | Migori | Nyanza | 2,586.4 | 917,170 | 1,116,436 | Migori |
| 45 | Kisii | Nyanza | 1,317.9 | 1,152,282 | 1,266,860 | Kisii |
| 46 | Nyamira | Nyanza | 912.5 | 598,252 | 605,576 | Nyamira |
| 47 | Nairobi (County) | Nairobi (Province) | 694.9 | 3,138,369 | 4,397,073 | Nairobi (City) |
| 581,309.0 | 38,610,997 | 47,564,296 | Nairobi |
County governments
County governments are responsible for county legislation (outlined in article 185 of the Constitution of Kenya), executive functions (outlined in article 183), functions outlined in the fourth schedule of the constitution of Kenya, functions transferred from the national government through article 187 of the constitution of Kenya, functions agreed upon with other counties under article 189(2) of the constitution of Kenya, and establishment and staffing of a public service (under article 235 of the Constitution of Kenya).[7] The functions of governments assigned to counties by the fourth schedule of the Constitution of Kenya are:[8]
Agriculture
- Crop and animal husbandry
- Livestock sale yards
- County abattoirs (slaughterhouses)
- Plant and animal disease control
- Fisheries
County health services
- County health facilities and pharmacies
- Ambulance services
- Promotion of primary health care
- Licensing and control of undertakings that sell food to the public
- Veterinary services (excluding regulation of the profession)
- Cemeteries, funeral parlors and crematoria
- Refuse removal, refuse dumps and solid waste disposal.
- Food distribution and Free services for pregnant mothers
Pollution, nuisances and advertising control
- Control of air pollution, noise pollution, other public nuisances and outdoor advertising
Cultural activities, public entertainment and public amenities
- Betting, casinos and other forms of gambling
- Racing
- Liquor licensing
- Cinemas
- Video shows and hiring
- Libraries
- Museums
- Sports and cultural activities and facilities
- County parks, beaches and recreation facilities
- Ice skating
- Sport fishing
- Golf
- Horse racing
- Rugby
County transport
- County roads
- Street lighting
- Traffic and parking
- Public road transport
- Ferries and harbours, excluding the regulation of international and national shipping and matters related thereto
- SGR- Madaraka Express (modern railway experience)
Trade development and regulation
- Markets
- Trade licences, excluding regulation of professions
- Fair trading practices
- Local tourism
- Cooperative societies
County planning and development
- Statistics
- Land surveying, planning and mapping of resources
- Boundaries and fencing
- Housing
- Electricity and gas reticulation and energy regulation
Education and childcare
- Pre-primary education, village polytechnics, homecraft centres and childcare facilities
- Adult education and national exam registration for the same.
Policy implementation
- Implementation of specific national government policies on natural resources and environmental conservation
- Soil and water conservation
- Forestry
County public works and services
- Storm water management systems in built-up areas
- Water and sanitation services
Fire fighting services and disaster management
Counties are mandated by the 2010 constitution of Kenya to enact legislation and laws that ensures management and controls of fire fighting.
Control of drugs and pornography
Coordination
- Ensuring and co-ordinating the participation of communities and locations in governance at the local level
- Assisting communities and locations to develop the administrative capacity for the effective exercise of the functions and powers and participation in governance at the local level
County executive committee
The county governor and the deputy county governor are the chief executive and deputy chief executive of the county, respectively.[9] The Independent Electoral and Boundaries Commission shall not conduct a separate election for the deputy governor but shall declare the running mate of the person who is elected county governor to have been elected as the deputy governor.[10] Each county will be run by an executive committee, consisting of:
- A governor, elected directly by the people
- A deputy, elected as running mate of the successful candidate for governorship
- A number of committee members not exceeding a third (or ten where a county assembly has more than 30 members) of the members of the respective county assembly
- A county secretary, nominated by the governor and approved by the county assembly, who will double up as head of the county public service, and secretary to the county executive committee[11]
As a speciality in the democratic system Kenyan law requires governors to have a recognised university degree (it is not necessary for the President of the United States, for example, to hold a degree).[12]
County assemblies
The counties will each have an assembly whose members are elected from single member constituencies known as wards. There may also be a number of nominated members as is necessary to ensure that neither male nor female members constitute more than two-thirds of the assembly.[13] There will also be six nominated members to represent marginalised groups (persons with disabilities, and the youth) and a speaker who will be an ex officio member of the assembly.[14][15]
County governors
Current list of governors
The governors listed below were elected on 8 August 2017.
| County No | Name | Governor | Deputy Governor | Party |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mombasa (County) | Ali Hassan Joho | Dr. William Kingi | ODM |
| 2 | Kwale | Salim Mvurya | Fatuma Mohamed Achani | JP[16] |
| 3 | Kilifi | Amason Kingi | Kenneth Mwakombo Kamto | ODM |
| 4 | Tana River | Dhadho Gadae Godhana | Jire Siyat Mohamed | ODM |
| 5 | Lamu | Fahim Yassin Twaha | Abdulhakim Aboud Bwana | JP |
| 6 | Taita-Taveta | Granton Graham Samboja | Majala Mlagui Delina | WDM-K |
| 7 | Garissa | Bunow Ali Korane | Dagame Abdi | JP |
| 8 | Wajir | Mohamed Abdi Mahamud | Ahmed Muktar Ali | JP |
| 9 | Mandera | Ali Ibrahim Roba | Mohamed Ahmed Arai | JP |
| 10 | Marsabit | Mohamud Mohamed Ali | Solomon Gubo Riwe | JP |
| 11 | Isiolo | Mohammed Abdi Kuti | Dr. Ibrahim Abdi Issa | IND |
| 12 | Meru | Kiraitu Murungi | Titus Ntuchiu | JP |
| 13 | Tharaka | Onesmus Muthomi Njuki | Francis Nyamu Kagwima | JP |
| 14 | Embu | Martin Wambora | Dorothy Nditi Muchungu[17] | JP[18] |
| 15 | Kitui | Charity Ngilu | Dr. Wathe Nzau | NARC |
| 16 | Machakos | Alfred Mutua | Eng. Francis Maliti | Maendeleo Chap Chap Party |
| 17 | Makueni | Kivutha Kibwana | Adelina Ndeto Mwau | WDM-K |
| 18 | Nyandarua | Francis Kimemia | Cecilia Wanjiru Mbuthia | JP |
| 19 | Nyeri | Mutahi Kahiga | Caroline Karugu | JP |
| 20 | Kirinyaga | Anne Waiguru | Peter Ndambiri | JP |
| 21 | Murang'a | Mwangi wa Iria | Augustine J Gakure Monyo | JP |
| 22 | Kiambu | Dr .James Nyoro | Joyce Ngugi | JP |
| 23 | Turkana | Josphat Nanok | Peter Lotethiro Emuria | ODM |
| 24 | West Pokot | John Krop Lonyangapuo[19] | Dr. Nicholas Atudonyang | KANU |
| 25 | Samburu | Moses Kasaine | Julius Leseeto | JP |
| 26 | Trans-Nzoia | Patrick Simonyu Khaemba | Stanley Kiptoo Kenei Tarus | FORD-KENYA |
| 27 | Uasin Gishu | Jackson Kiplagat Mandago | Daniel Kiplagat Kiprotich | JP |
| 28 | Elgeyo-Marakwet | Alex Tolgos | Gabriel Lagat Kosgey | JP |
| 29 | Nandi | Stephen Kipyego Sang | Dr Yulita Jebotip Cheruiyot Mitei | JP |
| 30 | Baringo | Stanley Kiptis | Jacob Kurui Chepkwony | JP |
| 31 | Laikipia | Ndiritu Muriithi | John Mwaniki | IND |
| 32 | Nakuru | Lee Kinyanjui | Erick Korir | JP |
| 33 | Narok | Samuel ole Tunai | Aruasa Evalyn Chepkirui | JP |
| 34 | Kajiado | Joseph Ole Lenku | Martin Moshisho | JP |
| 35 | Kericho | Paul Kiprono Chepkwony | Susan Chepkoech Kikwai | JP |
| 36 | Bomet | Dr. Hillary Barchok | JP | |
| 37 | Kakamega | Wycliffe Oparanya | Philip Museve Kutima | ODM |
| 38 | Vihiga | Wilber Otichilo | Dr. Patrick Lumumba Saisi | ODM |
| 39 | Bungoma | Wycliffe Wafula Wangamati | Prof. Charles Ngome Kibanani | FORD-KENYA |
| 40 | Busia | Sospeter Ojaamong | Solomon Abwaku Akadake | ODM |
| 41 | Siaya | Cornel Rasanga | Wilson Ouma Onyango | ODM |
| 42 | Kisumu | Peter Anyang' Nyong'o | Mathews Owili | ODM |
| 43 | Homa Bay | Cyprian Awiti | Hamiliton Onyango Orata | ODM |
| 44 | Migori | Zacharia Obado | Nelson Mahanga Mwita | ODM |
| 45 | Kisii | James Ongwae | Arthur Maangi Gongera | ODM |
| 46 | Nyamira | John Obiero | Amos Kimwomi Nyaribo | ODM |
| 47 | Nairobi (County) | Mbuvi Gideon Kioko "Mike Sonko" | JP |
See also
- List of counties of Kenya by GDP
- Provinces of Kenya
- Kenyan general election, 2013
- ISO 3166-2:KE
References
- Article 6, Devolution and access to Services, The 2010 Constitution of Kenya
- Article 98, (1) (a), Membership of the Senate, the 2010 Constitution of Kenya
- Article 97, (1) (b) Membership of the National Assembly, The 2010 Constitution of Kenya
- Kenyan County Commissioners Re-Organised Under New Structure, http://allafrica.com/stories/201307230067.html
- "List and Format Used to Number Kenya's 47 Counties". Soko Directory. 11 July 2019. Retrieved 24 May 2020.
- Kenya National Bureau of Statistics; and the final report of the IEBC as ratified in the National Assembly Constituencies and County Assembly Wards Order, 2012.
- County Governments Act, 2012
- "2. County Governments". Kenya Law Reform Commission. 29 August 2012.
- "179. County executive committees". Kenya Law Reform Commission. 29 August 2012.
- "180. Election of county governor and deputy county governor". Kenya Law Reform Commission. 29 August 2012.
- Appointment of county secretary, Section 44, County Government Act 2012
- "SHITANDA, WANJIRU OUT OVER DEGREES". The Standard. 18 January 2013. Archived from the original on 22 January 2013. Retrieved 20 January 2013.
- Article 177, (1) Membership of a County Assembly, The 2010 Constitution of Kenya.
- Article 177 (c), The 2010 Constitution of Kenya
- "Home". Jubilee Pamoja. Retrieved 14 August 2017.
- "Embu new governor assures she is equal to the task". Retrieved 15 February 2014.
- "Public RTS". public.rts.iebc.or.ke. Archived from the original on 8 August 2017. Retrieved 14 August 2017.
- "John Krop Lonyangapuo". Mzalendo. Retrieved 14 August 2017.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Counties of Kenya. |