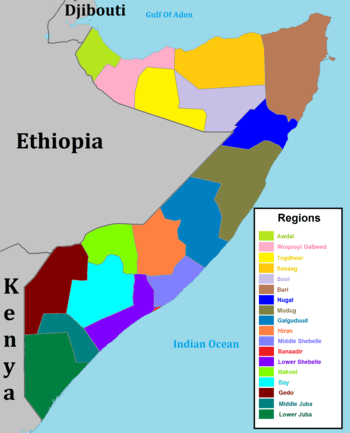
Administrative divisions of Somalia
Somalia is officially divided into eighteen (18) administrative regions (gobollo, singular gobol),[1] which in turn are subdivided into ninety (90) districts (plural degmooyin; singular degmo).
| Regions of Somalia Gobolada Soomaaliya (Somali) مناطق الصومال (Arabic) | |
|---|---|
| Also known as: Suddivisioni della Somalia (Italian) | |
 | |
| Category | Federal states |
| Location | Federal Republic of Somalia |
| Number | 18 Regions |
| Populations | Unknown |
| Areas | Unknown |
| Government | Region government |
| Subdivisions | District |
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Somalia |
|
Constitution |
|
|
Judiciary |
|
|
|
|
|
On a de facto basis, northern Somalia is now divided up among the autonomous regions of Puntland (which considers itself an autonomous state) and Somaliland (a self-declared but unrecognized sovereign state). In between Puntland and Somaliland, there also exists the state of Khatumo, which claims to be an autonomous state of Somalia but is unrecognized by the federal government, Puntland, and Somaliland. In central Somalia, Galmudug is another regional entity that emerged south of Puntland.[1] For these civil war divisions, see States and regions of Somalia.
Regions and districts
Historical divisions
Pre-independence
In 1931, Italian Somaliland consisted of seven commissariats.[3]
- Alto Giuba
- Alto Uebi-Scebeli
- Basso Giuba
- Basso Uebi-Scebeli
- Migiurtinia
- Mogadiscio
- Mudugh
Following the 1935–36 Second Italo-Abyssinian War, Italian Somaliland became part of Italian East Africa with Abyssinia (Ethiopia) and Eritrea. Italian Somaliland was one of six governorates of the new colony, the Somalia Governorate, and incorporated Somali-inhabited parts of the former Abyssinia. The governorate was subdivided into 10 commissariats, which were themselves divided into residencies.
- Alto Giuba (English: Upper Juba) (capital: Baidoa)
- Alto Scebeli (Upper Shabele) (Bulo Burti)
- Basso Scebeli (Lower Shabele) (Merca)
- Migiurtinia (Migiurtinia) (Dante)
- Mogadiscio (Mogadishu) (Mogadiscio)
- Mudugh (Mudug) (Rocca Littorio)
- Ogaden (Ogaden) (Uarder)
- Uebi Gestro (Gestro River) (Callafo)
- Basso Giuba (Lower Juba) (Chisimaio)
- Nogal (Nugaal) (Eil)
Following World War II, the Italian-administered Trust Territory of Somalia consisted of six Regions.[3]
- Alto Giuba
- Basso Giuba
- Benadir
- Hiran
- Migiurtinia
- Mudugh
The British Somaliland protectorate also consisted of two Regions.[3]
- Burao
- Hargeisa
Somalia
Upon independence in 1960, the Somali Republic maintained the 12 districts of the former Italian Somaliland and British Somaliland that merged to form the new country.[3] In 1964, a new Northeastern (Burao) Province was established by merging Burao, Erigavo, and Las Anod and a Northwestern (Hargeisa) Province was formed from Berbera, Borama, and Hargeisa districts.[3] In 1968, the capital of Basso Giuba was moved from Kismayo to Jamame. The 8 provinces at this time were:[3]
| Province | Area(km²) | Capital |
|---|---|---|
| Benadir | 45,004 | Mogadishu |
| Burao | 128,000 | Burao |
| Hargeisa | 48,000 | Hargeisa |
| Hiran | 25,647 | Beled Weyne |
| Lower Juba | 49,917 | Jamame |
| Bosaso | 90,744 | Bosaso (Bender Cassim) |
| Mudug | 118,737 | Galkayo |
| Upper Juba | 131,492 | Baidoa |
In 1982, Somalia reorganized from eight provinces into 16 regions.[3] In June 1984, Awdal was split from Woqooyi Galbeed and Sool was split from Nugaal to form the current 18 regions.[3]
See also
References
- "Somalia". World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. 2009-05-14. Archived from the original on 10 June 2009. Retrieved 2009-05-31.
- UNFPA Population Estimation Survey 2014
- "Regions of Somalia". Statoids. Retrieved 20 February 2011.