Regions of Burkina Faso
As per Law No.40/98/AN in 1998, Burkina Faso adhered to decentralization to provide administrative and financial autonomy to local communities. Most of these, according to their individual articles, were implemented on 2 July 2001.
 |
|---|
| This article is part of a series on the politics and government of Burkina Faso |
|
Parliament
|
|
Administrative divisions |
|
|
|
Burkina Faso is divided into 13 administrative regions. Each region is administered by a governor.
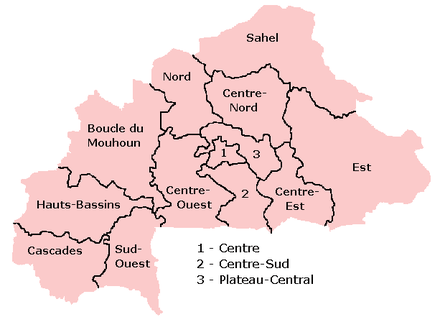  |
| Region | Area (km2) [1] | Population (2011) | Administrative capital |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boucle du Mouhoun | 34,333 | 1,631,321 | Dédougou |
| Cascades | 18,424 | 637,279 | Banfora |
| Centre | 2,869 | 2,136,581 | Ouagadougou |
| Centre-Est | 14,710 | 1,302,449 | Tenkodogo |
| Centre-Nord | 19,677 | 1,375,380 | Kaya |
| Centre-Ouest | 21,752 | 1,348,784 | Koudougou |
| Centre-Sud | 11,457 | 722,631 | Manga |
| Est | 46,694 | 1,416,229 | Fada N'gourma |
| Hauts-Bassins | 25,343 | 1,469,604 | Bobo Dioulasso |
| Nord | 16,414 | 1,185,604 | Ouahigouya |
| Plateau-Central | 8,545 | 696,372 | Ziniaré |
| Sahel | 35,360 | 968,442 | Dori |
| Sud-Ouest | 16,153 | 620,767 | Gaoua |
These regions are divided into 45 provinces and subdivided into 351 communes.
See also
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
