Broch
A broch ( /ˈbrɒx/) is an Iron Age drystone hollow-walled structure found in Scotland. Brochs belong to the classification "complex Atlantic roundhouse" devised by Scottish archaeologists in the 1980s. Their origin is a matter of some controversy.

Origin and definition
The word broch is derived from Lowland Scots 'brough', meaning (among other things) fort. In the mid-19th century Scottish antiquaries called brochs 'burgs', after Old Norse borg, with the same meaning. Place names in Scandinavian Scotland such as Burgawater and Burgan show that Old Norse borg is the older word used for these structures in the north. Brochs are often referred to as duns in the west. Antiquarians began to use the spelling broch in the 1870s.
A precise definition for the word has proved elusive. Brochs are the most spectacular of a complex class of roundhouse buildings found throughout Atlantic Scotland. The Shetland Amenity Trust lists about 120 sites in Shetland as candidate brochs, while the Royal Commission on the Ancient and Historical Monuments of Scotland (RCAHMS) identifies a total of 571 candidate broch sites throughout the country. Researcher Euan MacKie has proposed a much smaller total for Scotland of 104.[1]
The origin of brochs is a subject of continuing research. Sixty years ago most archaeologists believed that brochs, usually regarded as the 'castles' of Iron Age chieftains, were built by immigrants who had been pushed northward after being displaced first by the intrusions of Belgic tribes into what is now southeast England at the end of the second century BC and later by the Roman invasion of southern Britain beginning in AD 43. Yet there is now little doubt that the hollow-walled broch tower was purely an invention in what is now Scotland; even the kinds of pottery found inside them that most resembled south British styles were local hybrid forms. The first of the modern review articles on the subject (MacKie 1965)[2] did not, as is commonly believed, propose that brochs were built by immigrants, but rather that a hybrid culture formed from the blending of a small number of immigrants with the native population of the Hebrides produced them in the first century BC, basing them on earlier, simpler, promontory forts. This view contrasted, for example, with that of Sir W. Lindsay Scott, who argued,[3] following V. Gordon Childe (1935),[4] for a wholesale migration into Atlantic Scotland of people from southwest England.
MacKie's theory has fallen from favour too, mainly because starting in the 1970s there was a general move in archaeology away from 'diffusionist' explanations towards those pointing to exclusively indigenous development. Meanwhile, the increasing number – albeit still pitifully few – of radiocarbon dates for the primary use of brochs (as opposed to their later, secondary use) still suggests that most of the towers were built in the 1st centuries BC and AD.[5] A few may be earlier, notably the one proposed for Old Scatness Broch in Shetland, where a sheep bone dating to 390–200 BC has been reported.[6]
The other broch claimed to be substantially older than the 1st century BC is Crosskirk in Caithness, but a recent review of the evidence suggests that it cannot plausibly be assigned a date earlier than the 1st centuries BC/AD.[7][8]
Distribution
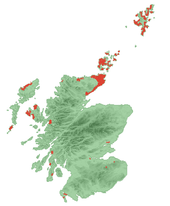
The distribution of brochs is centred on northern Scotland. Caithness, Sutherland and the Northern Isles have the densest concentrations, but there are a great many examples in the west of Scotland and the Hebrides. Although mainly concentrated in the northern Highlands and the Islands, a few examples occur in the Borders (for example Edin's Hall Broch and Bow Castle Broch), on the west coast of Dumfries and Galloway, and near Stirling. In a c.1560 sketch there appears to be a broch by the river next to Annan Castle in Dumfries and Galloway.[9] This small group of southern brochs has never been satisfactorily explained.
Purposes
The original interpretation of brochs, favoured by nineteenth century antiquarians, was that they were defensive structures, places of refuge for the community and their livestock. They were sometimes regarded as the work of Danes or Picts. From the 1930s to the 1960s, archaeologists such as V. Gordon Childe and later John Hamilton[10] regarded them as castles where local landowners held sway over a subject population.
The castle theory fell from favour among Scottish archaeologists in the 1980s, due to a lack of supporting archaeological evidence. These archaeologists suggested defensibility was never a major concern in the siting of a broch, and argued that they may have been the "stately homes" of their time, objects of prestige and very visible demonstrations of superiority for important families (Armit 2003). Once again, however, there is a lack of archaeological proof for this reconstruction, and the sheer number of brochs, sometimes in places with a lack of good land, makes it problematic.
Brochs' close groupings and profusion in many areas may indeed suggest that they had a primarily defensive or even offensive function. Some of them were sited beside precipitous cliffs and were protected by large ramparts, artificial or natural: a good example is at Burland near Gulberwick in Shetland, on a clifftop and cut off from the mainland by huge ditches. Often they are at key strategic points. In Shetland they sometimes cluster on each side of narrow stretches of water: the Broch of Mousa, for instance, is directly opposite another at Burraland in Sandwick. In Orkney there are more than a dozen on the facing shores of Eynhallow Sound, and many at the exits and entrances of the great harbour of Scapa Flow. In Sutherland quite a few are placed along the sides and at the mouths of deep valleys. Writing in 1956 John Stewart suggested that brochs were forts put up by a military society to scan and protect the countryside and seas.[11]
Finally, some archaeologists consider broch sites individually, doubting that there ever was a single common purpose for which every broch was constructed. There are differences in position, dimensions and likely status between the various areas in which brochs are found. For example, the broch "villages" which occur at a few places in Orkney have no parallel in the Western Isles.
Structures
Generally, brochs have a single entrance with bar-holes, door-checks and lintels. There are mural cells and there is a scarcement (ledge), perhaps for timber-framed lean-to dwellings lining the inner face of the wall. Also there is a spiral staircase winding upwards between the inner and outer wall and connecting the galleries.[12] Brochs vary from 5 to 15 metres (16–50 ft) in internal diameter, with 3 metre (10 ft) thick walls. On average, the walls only survive to a few metres in height. There are five extant examples of towers with significantly higher walls: Dun Carloway on Lewis, Dun Telve and Dun Troddan in Glenelg, Mousa in Shetland and Dun Dornaigil in Sutherland, all of whose walls exceed 6.5 m (21 ft) in height.[13]
Mousa's walls are the best preserved and are still 13 m tall; it is not clear how many brochs originally stood this high. A frequent characteristic is that the walls are galleried: with an open space between, the outer and inner wall skins are separate but tied together with linking stone slabs; these linking slabs may in some cases have served as steps to higher floors. It is normal for there to be a cell breaking off from the passage beside the door; this is known as the guard cell. It has been found in some Shetland brochs that guard cells in entrance passageways are close to large door-check stones. Although there was much argument in the past, it is now generally accepted among archaeologists that brochs were roofed, perhaps with a conical timber framed roof covered with a locally sourced thatch. The evidence for this assertion is still fairly scanty, although excavations at Dun Bharabhat, Lewis, may support it. The main difficulty with this interpretation continues to be identifying potential sources of structural timber, though bog and driftwood may have been plentiful sources.
Very few of the brochs on the islands of Orkney and Shetland have cells on the ground floor. Most brochs have scarcements (ledges) which may have allowed the construction of a very sturdy wooden first floor (first spotted by the antiquary George Low in Shetland in 1774), and excavations at Loch na Berie on the Isle of Lewis show signs of a further, second floor (e.g. stairs on the first floor, which head upwards). Some brochs such as Dun Dornaigil and Culswick in Shetland have unusual triangular lintels above the entrance door.[14][15]

As in the case of Old Scatness in Shetland (near Jarlshof and Burroughston on Shapinsay), brochs were sometimes located close to arable land and a source of water (some have wells or natural springs rising within their central space).[16] Sometimes, on the other hand, they were sited in wilderness areas (e.g. Levenwick and Culswick in Shetland, Castle Cole in Sutherland). Brochs are often built beside the sea (Carn Liath, Sutherland); sometimes they are on islands in lochs (e.g. Clickimin in Shetland).[17]
About 20 Orcadian broch sites include small settlements of stone buildings surrounding the main tower. Examples include Howe, near Stromness, Gurness Broch in the north west of Mainland, Orkney, Midhowe on Rousay and Lingro near Kirkwall (destroyed in the 1980s). There are "broch village" sites in Caithness, but elsewhere they are unknown.[18]
Most brochs are unexcavated.[19] The end of the broch building period seems to have come around AD 100–200.[20][21] Those that have been properly examined show that they continued to be in use for many centuries, with the interiors often modified and changed, and that they underwent many phases of habitation and abandonment.
Heritage status
The Crucible of Iron Age Shetland's Mousa, Old Scatness and Jarlshof sites are on the United Kingdom "Tentative List" of possible nominations for the UNESCO World Heritage Programme list of sites of outstanding cultural or natural importance to the common heritage of humankind. This list, published in July 2010, includes sites that may be nominated for inscription over the next 5–10 years.[22]
See also
- Oldest buildings in Scotland
- Irish round tower
- Fortified tower
- Nuraghe
References and footnotes
- General references
- Armit, I. (1991) The Atlantic Scottish Iron Age: five levels of chronology, Proc. Soc. Antiq. Scot. v. 121, pp. 181–214; ISSN 0081-1564
- Armit, I. (1996) The Archaeology of Skye and the Western Isles, Edinburgh University Press; ISBN 0-7486-0640-8
- Armit, I. (2003) Towers in the North: The Brochs of Scotland, Stroud : Tempus; ISBN 0-7524-1932-3
- Ballin Smith, B. and Banks, I. (eds) (2002) In the Shadow of the Brochs, the Iron Age in Scotland, Stroud: Tempus; ISBN 0-7524-2517-X
- Fojut, N. (1982) Towards a Geography of Shetland Brochs, Glasgow Archaeological Journal, v. 9, pp. 38–59; ISSN 0305-8980
- Harding, D.W. (2000) The Hebridean Iron Age: Twenty Years’ Research, University of Edinburgh Department of Archaeology, Occasional Paper No. 20; ISSN 0144-3313
- Harding, D.W. (2004) The Iron Age in Northern Britain, London : Routledge; ISBN 0-415-30150-5
- Specific references and notes
- Armit (2003) p. 16.
- MacKie, E. W. (1965) 'The origin and development of the broch and wheelhouse building cultures of the Scottish Iron Age'. Proceedings of the Prehistoric Society 31, pp. 93–146.
- Scott, Sir Lindsay (1947), 'The problem of the brochs', Proceedings of the Prehistoric Society 13, pages 1–36.
- Childe, V. G. (1935) The Prehistory of Scotland. London.
- Parker Pearson, M. & Sharples, N. et al. (1999) Between land and sea: excavations at Dun Vulan, South Uist. Sheffield.
- Dockrill, S. J., Outram, Z. and Batt, C. M. (2006) Time and place: a new chronology for the origin of the broch based on the scientific dating programme at the Old Scatness Broch, Shetland, PSAS, v. 136, pp. 89-110; ISSN 0081-1564
- MacKie, E. W. (2007) The Roundhouses, Brochs and Wheelhouses of Atlantic Scotland c. 700 BC – AD 500: architecture and material culture. Part 2 The Mainland and the Western Islands. British Archaeological Reports British Series. Oxford.
- For the C14 dates for the Shetland sites see Shetland Amenity Trust Archived 4 May 2009 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved 14 August 2007.
- Scotland. Royal Commission on the Ancient and Historical Monuments and Constructions; Maxwell, Herbert (14 May 2018). "Seventh report with inventory of monuments and constructions in the county of Dumfries". Edinburgh : H.M. Stationery Off. Archived from the original on 31 August 2016 – via Internet Archive.
- Hamilton, J.R.C. (1968) Excavations at Clickhimin, Shetland. Edinburgh.
- Stewart, J. (1956) An Outline of Shetland Archaeology, Lerwick: Shetland Times Ltd.
- Prehistoric Scotland (R.W. Feachem, 1992)
- Armit (2003) p. 55.
- "Dun Dornaigil" Archived 10 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine The Megalithic Portal. Retrieved 11 May 2008.
- "Culswick" Archived 13 May 2008 at the Wayback Machine RockStanza; retrieved 11 May 2008.
- Hogan, C. Michael (7 October 2007) Burroughston Broch Archived 10 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine The Megalithic Portal; retrieved 11 May 2008.
- "Welcome to Canmore | Canmore". canmore.org.uk. Retrieved 29 May 2020.
- Armit (2003) pp. 95-106.
- Armit (2003) p. 51 notes that of 140 Atlantic roundhouses in the Outer Hebrides only 14 have been "at least partially excavated".
- The Macmillan Encyclopedia (2nd ed.). Market House Books, Ltd. 2003 – via Credo Reference.
- Mackie, Euan W. (2010). "THE BROCH CULTURES OF ATLANTIC SCOTLAND. PART 2.THE MIDDLE IRON AGE: HIGH NOON AND DECLINE c. 200BC–AD 550". Academia.edu. Retrieved 15 May 2019.
- From Chatham to Chester and Lincoln to the Lake District – 38 UK places put themselves forward for World Heritage status, United Kingdom Department for Culture, Media and Sport, 7 July 2010, archived from the original on 13 July 2010, retrieved 7 July 2010
Further reading
- Armit, Ian (2002), Towers in the North: The Brochs of Scotland. The History Press. ISBN 0752419323
- MacKie, E W 1992 The Iron Age semibrochs of Atlantic Scotland: a case study in the problems of deductive reasoning. Archaeol Journ 149 (1991), 149–81.
- MacKie, E W 1995a Gurness and Midhowe brochs in Orkney: some problems of misinterpretation. Archaeol Journ 151 (1994), 98–157.
- MacKie, E W 1995b The early Celts in Scotland. Miranda Green (ed) The Celtic World. Routledge, London: 654–70.
- MacKie, E W 1997 Dun Mor Vaul re-visited, J.N.G. Ritchie (ed) The Archaeology of Argyll. Edinburgh: 141–80.
- MacKie, E W 1998 Continuity over three thousand years of northern prehistory: the ‘tel’ at Howe, Orkney. Antiq Journ 78, 1–42.
- MacKie, E W 2000 The Scottish Atlantic Iron Age: indigenous and isolated or part of a wider European world? 99–116 in Jon C Henderson (ed) The Prehistory and Early History of Atlantic Europe. BAR International Series 861: Oxford.
- MacKie, E W 2002a Excavations at Dun Ardtreck, Skye, in 1964 and 1965. Proc Soc Antiq Scot 131 (2000), 301–411.
- MacKie, E W 2002b The Roundhouses, Brochs and Wheelhouses of Atlantic Scotland c. 700 BC – AD 500: architecture and material culture. Part 1 The Orkney and Shetland Isles. British Archaeological Reports British Series 342. Oxford.
- MacKie, E. W. 2005 119. Scottish brochs at the start of the new millennium, 11–31 in Turner, Val E, Nicholson, Rebecca A, Dockrill, S J & Bond, Julie M (eds.) Tall stories? Two millennia of brochs. Lerwick.
- Ritchie, J N G (1998), Brochs of Scotland. Shire Publications. ISBN 0747803897
- Hunter, Mollie, The Stronghold, an historical novel about the building of the first broch.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Brochs. |
| Look up broch in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
