Battle of Hòa Mộc
The Battle of Hòa Mộc (2 March 1885) was the most fiercely fought action of the Sino-French War (August 1884 – April 1885). At heavy cost, Colonel Giovanninelli's 1st Brigade of the Tonkin Expeditionary Corps defeated forces of the Black Flag and Yunnan Armies blocking the way to the besieged French post of Tuyên Quang.[1]
Background
The French capture of Lạng Sơn in February 1885 in the Lạng Sơn Campaign allowed substantial French forces to be diverted further west to relieve the small and isolated French garrison in Tuyên Quang, which had been placed under siege in November 1884 by Liu Yongfu(劉永福)'s Black Flag Army and Tang Jingsong(唐景崧)'s Yunnan Army. The Siege of Tuyên Quang was the most evocative confrontation of the Sino-French War. The Chinese and Black Flags sapped methodically up to the French positions, and in January and February 1885 breached the outer defences with mines and delivered seven separate assaults on the breach. The Tuyên Quang garrison, 400 legionnaires and 200 Tonkinese auxiliaries under the command of chef de bataillon Marc-Edmond Dominé, beat off all attempts to storm their positions, but lost over a third of their strength (50 dead and 224 wounded) sustaining a heroic defence against overwhelming odds. By mid-February it was clear that Tuyên Quang would fall unless it was relieved immediately.[2]
Relief march of the 1st Brigade
The Battle of Hòa Mộc was fought to relieve the Siege of Tuyên Quang. Following his capture of Lạng Sơn on 13 February 1885, General Louis Brière de l'Isle personally led Colonel Giovanninelli's 1st Brigade to the relief of Tuyên Quang. The brigade left Lạng Sơn on 17 February, after replenishing its food and ammunition, and made a forced march back to Hanoi along the Mandarin Road, via Cut, Thanh Moy, Cau Son and Bắc Lệ. After briefly pausing at Bắc Lệ to pay homage to the French soldiers killed in June 1884 in the Bắc Lệ ambush, Giovanninelli's men pressed on to Hanoi via the French posts at Kép, Phu Lang Thuong and Dap Cau. The brigade reached Hanoi on the evening of 22 February. It had left Lạng Sơn 3,000 strong, but straggling had reduced its numbers by a sixth, and it set off to relieve Tuyên Quang with only a little over 2,400 men. Five gunboats of the Tonkin Flotilla (Éclair, Henri Rivière, Berthe de Villers, Moulun and Trombe) carried Giovanninelli's men from Hanoi up the Red and Clear Rivers and put the brigade ashore near the French post of Phu Doan on the Clear River, fifty kilometres southwest of Tuyên Quang.
The brigade was reinforced at Phu Doan on 24 February by two ad hoc infantry battalions (1,000 men) drawn from the garrisons of Sơn Tây and Hưng Hóa. This mixed force of Turcos, marine infantry and legionnaires, under the command of Lieutenant-Colonel de Maussion, had set out from Hưng Hóa on 21 February. The relief force now numbered 3,400 men.[Note 1]
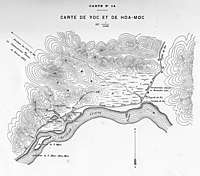
On 27 February Giovanninelli's men set out from Phu Doan towards the Yu Oc gorge, the most direct route to Tuyên Quang. The French knew that the Chinese and Black Flags had established a strong blocking position in the Yu Oc gorge, near the village of Hòa Mộc. In theory, the French column could have avoided this blocking position by advancing northwest along the Song Chay river and approaching Tuyên Quang from the west. Brière de l'Isle and Giovanninelli considered the possibility of making a flank march to bypass the Hòa Mộc position, but rejected it. If the column marched inland from the Clear River, it would lose the support of the gunboats. It would also be exposing its rear to a potentially devastating counterattack by the enemy troops at Hòa Mộc. It would be advancing through unknown country, along paths reported to be bad. Finally, whichever route the column took, it would not get to Tuyên Quang without a battle. Even if the flank march succeeded, the column would still have to fight its way through the Yunnan Army's siege lines around Ca Lanh or Phu An Binh, and these were reported to be as well-defended as the Hòa Mộc position.
Brière de l'Isle and Giovanninelli therefore decided to advance directly on Tuyên Quang through the Yu Oc gorge, forcing the defences of Hòa Mộc. This was the route taken by Colonel Jacques Duchesne's column in November 1884, before the Battle of Yu Oc, and the French at least knew the lie of the land. Giovanninelli told his men that he was leading them 'into known dangers, by a known way'.
On 28 February the brigade crossed the Song Chay river and camped five kilometres below the village of Hòa Mộc, at the entrance to the Yu Oc gorge. There, as they expected, they found the route to Tuyên Quang blocked by a strong Chinese defensive position.[3]
Forces engaged


Giovanninelli's reinforced 1st Brigade consisted of seven infantry battalions (Mahias and Lambinet's marine infantry battalions, de Mibielle and Comoy's Turco battalions, Tonnot's battalion of Tonkinese riflemen and de Maussion's two mixed battalions) and two marine artillery batteries (Captains Jourdy and Péricaud).[Note 2]
The French gunboat flotilla was unable to ascend the Clear River as far as Hòa Mộc, despite the utmost efforts of the gunboat crews, who hauled their vessels along the shallow river bed. Their absence was recognised by the French officers as a serious loss. Had they been present, they could have sailed up the Clear River beyond the Black Flag positions and enfiladed them from the rear, as they had done in September 1883 in the Battle of Palan.
The Chinese and Black Flag forces blocking the way to Tuyên Quang were under the personal command of Liu Yongfu (Luu Vĩnh Phúc, as he was known to the French from the Vietnamese pronunciation of his name), and seem to have numbered around 6,000 men. They held three lines of trenches, one behind the other, and their flanks rested on the Clear River to the east and on impassable mountain terrain to the west. The position was well chosen, and the French had no option except to attack it frontally. Their single advantage was their artillery, which was stationed by Giovanninelli on hilltop positions from which the guns could fire down into the enemy trenches.
The battle of Hòa Mộc

The French approached the Chinese and Black Flag positions late in the morning of 2 March 1885. The enemy flags were down, and the Chinese trenches appeared to be deserted. The French shelled the trenches but there was no sign of life, so Giovanninelli sent forward a platoon of Tonkinese riflemen to draw any enemy fire. The Tonkinese were met with a murderous volley at point-blank range that killed or wounded 20 out of 30 men.
Having established that the Hòa Mộc position was occupied, Giovanninelli attacked the left flank of the Chinese defensive line early in the afternoon. The first assault was made by chef de bataillon Comoy's Turco battalion. The Chinese exploded a mine in front of their trenches as the Algerians advanced, killing and wounding scores of the attackers, and the assault failed. One of the battalion's company commanders, Captain Rollandes, was mortally wounded in the attack.
A second French assault, in mid-afternoon, was made by chef de bataillon Mahias's marine infantry battalion. The attack was met by accurate close range rifle fire, and also failed with heavy casualties. Giovanninelli reinforced the attackers with Lambinet's marine infantry battalion, and a third and final assault was made. This time the French broke through, capturing a large section of the enemy's forward trenches. To distract their attention, Liu Yongfu launched a counterattack against the French left flank, but it was driven off with heavy losses by the French reserves.

Although the French had made some progress in the afternoon's fighting, their casualties had been disconcertingly high, and it was not clear whether the brigade was strong enough to break through on the following morning. According to Lieutenant Huguet of Lambinet's marine infantry battalion, both Brière de l'Isle and Giovanninelli had been shaken by the ferocity of the enemy's resistance and were contemplating the possibility of defeat:
The general-in-chief was sitting behind a bank, anxious, his head in his hands, surrounded by his staff, perhaps wondering whether he would have to retreat. Colonel Giovanninelli, who valued the life of the humblest soldier as dearly as his own, was pale and shaken as he watched the lines of bloodstained stretchers file past him, and kept exclaiming in a strangled voice, 'My children! My poor children!' The bullets whistled incessantly in the close air, and the groans of the wounded men lying in the rose bushes, inside the bamboo groves, and against the sides of the enemy works, rose ever more distinctly.[4]
During the night of 2 March the Chinese and Black Flags made a counterattack in an attempt to recover the trenches they had lost, but were met with the bayonet by Comoy's Turcos and driven off after vicious hand-to-hand fighting.
On the morning of 3 March Giovanninelli brought up his reserves and ordered the entire brigade to assault the stretch of trench line still in enemy hands. The French infantry moved forward at the trot, then accelerated into a charge, expecting to be met by a volley at point-blank range. Instead, they found the enemy trenches deserted. The Chinese and Black Flags had evacuated their positions before dawn, leaving the way to Tuyên Quang clear.
Casualties

French casualties at Hòa Mộc were 76 dead and 408 wounded. This was the highest casualty rate and the heaviest loss in a single day's fighting sustained by the French during the Sino-French War. The casualties included six officers killed or mortally wounded (Captains Rollandes and Tailland, Lieutenants Embarck, Moissenet and de l'Étoile, and 2nd Lieutenant Brun) and 21 officers wounded. Three of the 21 wounded officers (Captains Bourguignon and Chanu and 2nd Lieutenant Peyre) later died of their wounds. The heaviest losses fell on Mahias's marine infantry battalion. The battalion's strength on 26 December 1884 was 600 men and 19 officers. Its casualties in the Battle of Núi Bop (4 January 1885) and during the Lạng Sơn Campaign (February 1885) had been relatively light, but after Hòa Mộc it could only muster 307 men and 6 officers.[5]
The French wounded were evacuated back to Hanoi aboard the gunboats, but many of them later died of their wounds in the overcrowded military hospitals of Dap Cau and Thi Cau.
Significance
Costly though it had been, Giovanninelli's victory cleared the way to Tuyên Quang. The Yunnan Army and the Black Flags raised the siege and drew off to the west, and the relieving force entered the beleaguered post on 3 March. Brière de l'Isle praised the courage of the hard-pressed garrison in a widely quoted order of the day. 'Today, you enjoy the admiration of the men who have relieved you at such heavy cost. Tomorrow, all France will applaud you!'[6]
The French public did indeed applaud chef de bataillon Marc-Edmond Dominé's defence of Tuyên Quang, and it eventually became the defining image of the Sino-French War in France. The battle of Hòa Mộc, fought to relieve the besieged garrison, is far less well known, and some of its participants were aggrieved at how quickly their achievements faded from the public's memory. They took what comfort they could from the order of day issued by Brière de l'Isle to the 1st Brigade on 5 March 1885:
Vous venez d'ajouter une glorieuse page à l'histoire du corps expéditionnaire. Après vos victoires sur la route de Chu à Lang-Son, sans vous accorder un repos déjà bien mérité, j’ai dû vous demander de nouveaux efforts, vous conduire à de nouveaux dangers. L’entrain que vous avez montré dans vos belles marches de Lang-Son à Hanoï et sur les rives de la rivière Claire a prouvé que vous sentiez l'importance de vos nouvelles opérations. Le 2 mars, vous avez rencontré l'armée chinoise, descendue du Yun-Nan, retranchée dans une série d'ouvrages formidables, sur un terrain d'une difficulté inouïe. L’ennemi, renforcé de tous les bandits de Luu-Vinh-Phuoc, avait annoncé bien haut qu’il vous barrerait la route de Tuyen-Quan, assiégé avec rage par lui. Sans tenir compte du nombre de vos adversaires, vous avez enlevé de vive force les ouvrages de Hoa-Moc après une lutte de près de vingt-quatre heures. Le résultat a répondu à vos sacrifices, et, le 3 mars, vous serriez la main des braves de l'héroïque garnison que vous veniez d'égaler. Honneur à vous tous![7]
(You have just added a glorious page to the annals of the expeditionary corps. After your victories on the march from Chu to Lang Son I was obliged, without giving you the rest you so richly deserved, to require of you new efforts and to lead you into new dangers. The energy which you showed during your fine marches from Lang Son to Hanoi and up the banks of the Clear River demonstrated that you appreciated the importance of your new mission. On 2 March you met the Chinese army that had come down from Yunnan, entrenched within a complex of formidable defences, on ground of the most appalling difficulty.
The enemy, reinforced by all Luu Vinh Phuc's bandits, had boasted that he would block your way to Tuyen Quang, which he was furiously besieging.
Taking no heed of the number of your adversaries, you stormed and captured the positions of Hoa Moc after a struggle lasting nearly twenty-four hours. The outcome justified your sacrifices, and on 3 March you shook hands with the brave men of the heroic garrison whose courage you had just matched.
Honour to you all!)
Notes
- De Maussion's two mixed battalions were under the command of chefs de bataillon Beranger and Frauger. They included two companies of the 1st Battalion, 1st Foreign Legion Regiment (Captains Chmitelin and Broussier) and a marine infantry company (Captain Kuntz).
- Mahias's battalion consisted of the 25th, 29th, 34th and 36th Companies, 1st Marine Infantry Regiment (Captains Tailland, Salles, Hougnon and Bourguignon). Lambinet's battalion included the 25th A, 28th and 31st D Companies, 1st Marine Infantry Regiment (Captains Chanu, Herbin and de Damian) and a fourth, unidentified company (Lieutenant de l'Étoile). De Mibielle's Turco battalion was the 3rd Battalion, 3rd Algerian Rifle Regiment (Captains Camper, Chirouze, Polère and Valet). Comoy's Turco battalion was the 4th Battalion, 1st Algerian Rifle Regiment (Captains Gérôme, Boëlle, Bigot and Rollandes).
Footnotes
- Hubert, 109–16; Huguet, 89–93; Lecomte, Lang-Son, 324–9; Vie militaire, 215–31; Nicolas, 402–9; Thomazi, Conquête, 247–8; Histoire militaire, 107–8
- Thomazi, Conquête, 237–41 and 246–8; Histoire militaire, 102–3 and 107–8
- Huguet, 83–9; Lecomte, Lang-Son, 318–24; Vie militaire, 161–77, 195–206 and 207–13; Nicolas, 400–402
- Huguet, 92
- Nicolas, 409
- Thomazi, Conquête, 241
- Huguet, 96
References
- Hubert, C., Le colonel Dominé – Algérie, Armée de la Loire, Tonkin, Défense de Tuyen-Quan 1885 (Paris, 1938)
- Huguet, E, En colonne: souvenirs d'Extrême-Orient (Paris, 1888)
- Lecomte, J., La vie militaire au Tonkin (Paris, 1893)
- Lecomte, J., Lang-Son: combats, retraite et négociations (Paris, 1895)
- Lung Chang [龍章], Yueh-nan yu Chung-fa chan-cheng [越南與中法戰爭, Vietnam and the Sino-French War] (Taipei, 1993)
- Nicolas, V., Livre d'or de l'infanterie de la marine (Paris, 1891)
- Thomazi, A., Histoire militaire de l'Indochine français (Hanoi, 1931)
- Thomazi, A., La conquête de l'Indochine (Paris, 1934)