Bagnères-de-Luchon
Bagnères-de-Luchon (French: [baɲɛʁ də lyʃɔ̃]; Occitan: Banhèras de Luishon), also referred to as just Luchon, is a French commune and spa town in the Haute-Garonne department in the Occitanie region of south-western France.
Bagnères-de-Luchon | |
|---|---|
 The Luchon Valley from the Cable Car | |
.svg.png) Coat of arms | |
Location of Bagnères-de-Luchon 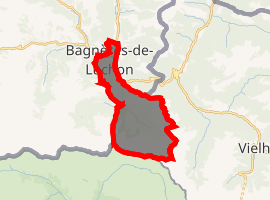
| |
 Bagnères-de-Luchon  Bagnères-de-Luchon | |
| Coordinates: 42°47′30″N 0°35′41″E | |
| Country | France |
| Region | Occitanie |
| Department | Haute-Garonne |
| Arrondissement | Saint-Gaudens |
| Canton | Bagnères-de-Luchon |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2008–2020) | Louis Ferré |
| Area 1 | 52.80 km2 (20.39 sq mi) |
| Population (2017-01-01)[1] | 2,312 |
| • Density | 44/km2 (110/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| INSEE/Postal code | 31042 /31110 |
| Elevation | 611–2,737 m (2,005–8,980 ft) (avg. 630 m or 2,070 ft) |
| 1 French Land Register data, which excludes lakes, ponds, glaciers > 1 km2 (0.386 sq mi or 247 acres) and river estuaries. | |
The inhabitants of the commune are known as Luchonnais or Luchonnaises.[2]
The commune has been awarded three flowers by the National Council of Towns and Villages in Bloom in the Competition of cities and villages in Bloom.[3]
Geography
Bagnères-de-Luchon is located on the Spanish border some 50 km south-west of Saint-Gaudens and 40 km south of Montréjeau at the end of a branch line of the Southern railway at the foot of the central Pyrenees. To the south the Luchonnais Mountains form a natural barrier and there is no crossing point into Spain. Access to the commune is by the D125 road from Salles-et-Pratviel in the north which passes through the town and continues south through the commune to its termination in the mountains. The D618A branches off the D125 south of the town and goes east to Saint-Mamet continuing through the Val d'Aran and the Col du Portillon to the Spanish border. The D618 goes west from the town to Saint-Aventin. The D46 goes north-east to Sode. The D125C goes north by north-west to Moustajon.[4]
The town is located in a valley at the confluence of the L'One river from the west and the Pique river from the south. Numerous streams flow into these rivers including the Ruisseau de Sahage into L'One, the Ruisseau de Bagnartigue, the Ruisseau de Jean, the Lys, the Ruisseau des Barguieres, the Ruisseau de Laus d'Esbas, the Ruisseau de Garante, the Ruisseau de Sajust, the Ruisseau de Layrous, the Ruisseau de Roumingau, and the Ruisseau du Port de Venasque all flowing into the Pique. The Ruisseau de Bouneu forms much of the western border of the commune as it flows north to join the Lys. There are several high mountain lakes in the south of the commune which feed the Pique including the Boums de Port and the Etang de la Freche.[4]
Transport
The Gare de Luchon railway station is the SNCF terminal station for the Montréjeau to Gourdan-Polignan and Luchon line that also connects to Toulouse via Montréjeau. On weekends (daily in summer), a night train connects Bagneres-de-Luchon directly to Paris. The Montréjeau to Bagnères-de-Luchon train line was suspended in 2014. The connection is now made by bus.
A Gondola lift since 1993 has connected Bagneres-de-Luchon to Superbagnères. It replaced the Chemin de fer de Luchon à Superbagnères (Luchon to Superbagnères railway) rack railway (Strub system) which operated from 1912 to 1966.
There is also a small public aerodrome in the commune just east of the town where the Aeroclub de Luchon is based.
Climate
The commune is located on a slope that ensures a dry climate. Winter temperatures range from −10 to 10 degrees Celsius and summer temperatures range from 10 to 35 degrees Celsius. The northerly wind brings more anticyclonic conditions and south-west or north-west winds are very often a harbinger of a disturbance (rain or snow). Sometimes the north and south winds are reversed causing storms on the valley which are sometimes strong with hail due to the moist air in the south and dry air in the north.
Toponymy
The name Bagnères-de-Luchon comes in part from its hydrotherapy (bagnères = baths) and the other part from a local god (Lixon or Illixon).
After some confusion the Académie Julien Sacaze confirmed that Lixon is the correct Roman name for Luchon and not Ilixon.
History
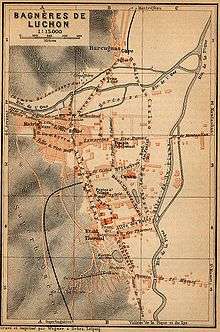
.jpg)

The town has existed for more than 2,000 years. The presence of a population has been attested since Neolithic times at least in the Saint-Mamet Cave. The presence of Stone circles also attests to an ancient occupation.[6]
In 76 BC Pompey, returning from a policing expedition in Spain (where he founded the city of Pamplona named after him), stopped in the area and founded the new city of Lugdunum Convenarum where he brought together the scattered Convènes tribe: this was the future Saint-Bertrand-de-Comminges.
One of his soldiers who suffered from a skin disease immersed himself in the thermal waters of Luchon and its "Onésiens" baths where he discovered their thermal properties. After 21 days (the traditional and still current duration of a cure) he came out completely healed.
In 25 BC Tiberius Claude dug three pools and developed thermal baths. The baths had a modest motto: "Balneum Lixonense post Neapolitense primum" (the Luchon baths are the best after those of Naples) which is still today the motto of the town. Julius Caesar spoke of the region his "Commentaries".
The invasions of the Goths and Visigoths passed through the region as well as the incursions of the Moors. People took refuge in the high valleys of Larboust or Oueil. Traces of these invasions remain in some local myths and legends.
Charlemagne and Gaston Phoebus gave the area a special status of a border March with a certain amount of autonomy between France and Spain.
The area was relatively untouched by the Hundred Years' War, as well as by the suppression of Catharism and the Protestant Reformation. People remained loyal to a 'modified' Catholicism, which it took the bishops of Saint-Béat centuries to rein in; priests lived in communities, sometimes armed and married, and were poorly educated and poorly trained. They extorted payment for funeral Masses in the form of well-watered meals, and they were loyal to the interests of their house of origin, rather than to Rome.
In 987 the village of "Banières" and its thermal baths around its church was described as quite successful. At Toussaint there was a major fair which did not have, however, the fame of that of Saint-Béat, which benefited more from trade with Spain.
Around 1200 the hospitallers of St. John of Jerusalem installed a commandery at Frontés, between Montauban and Juzet-de-Luchon. The goal was to control the passage to the mountain, which was a secondary road on the Camino de Santiago, and to organize hospices for pilgrims and merchants who risked their lives in winter. The building of the Hospice de France dates from this period and is the only trace remaining of the Knights Hospitaller. The opening of the Port de Venasque Pass followed later.
Then commenced a continuous struggle for centuries between the Knights hospitaller and the people who were guided by their priests. The objective quickly became more economic than religious and it was not a question of sharing taxes. Finally the order abandoned the region.
There have always been very few nobles in the region where the peasantry has always fought for their survival. The old treaties of Lies et passeries[7] gave the people of both sides of the mountain free movement and free trade even if the kingdoms were at war. Any boycott would have little support as it would easily decimate the population. These treaties were systematically renewed and imposed on kings and bishops. A popular form of elected representation existed: the consuls. It was thus possible to speak of Pyrenean republics.
The kings of France sought to put an end to this situation which seemed to them abnormal.
In 1759 Baron Antoine Mégret d'Etigny, intendant of Gascony, was sent to Luchon. He began by creating a passable road using collective labour and expropriations. He was forced to appeal to a company of dragoons to hold the population in check as they were unaccustomed to such authoritarian treatment. In 1761 he reorganized the baths and gave them a foundation for their future development. In 1763 Marshal Duke of Richelieu came to take the waters and he returned in 1769 with much of the Court. The spa was launched. The Baron also developed forestry to provide timber for the navy and charcoal for forges. He died in 1767 at the age of 47, ruined and disgraced.
His successor gave his name to the Alleys of Étigny, the main artery of the town, and in 1889 a statue in his likeness was still displayed in front of the baths.
The French Revolution and the French empires had little impact in Luchon.
Many famous visitors came to Luchon, attracted by the popularity of the thermal waters which was launched by the Empress Eugenie or by the beginnings of "Pyreneism" by Count Russell-Killough. Lamartine, José-Maria de Heredia (who also lived in Marignac, a village near Luchon where he was inspired by the Pic du Gar for his collection of poems Les Trophées), Prince Napoleon III, the Prince Imperial, Edmond Rostand, Gustave Flaubert, Guy de Maupassant, Octave Mirbeau, and Stephen Liégeard. Moulay Mohammed (the future Mohammed V of Morocco), Alfonso XIII of Spain, Sacha Guitry, Francis Carco, and François Mauriac were some of the more illustrious guests.
The arrival of the railway in 1873 and the construction of the casino in 1880 further developed the popularity of the town where upscale and cosmopolitan tourists came until the Roaring Twenties. Social benefits such as paid leave and social security then democratized the tourist population.
A hydroelectric power plant was in place as early as 1890 by the La Luchonnaise company.
The Tour de France made the town one of its obligatory stages since its inception.
The opening of the mountain hotel of Superbagnères (finished work in 1922), then connected by a rack railway and today by gondola, completed the spa town with a winter sports resort. In the 1968 Winter Olympics, Ingrid Lafforgue was successful. Her twin sister Britt Lafforgue was successful at the FIS Alpine World Ski Championships.
The commune was mentioned with the nickname "Queen of the Pyrenees" by Vincent de Chausenque in 1834 in his book Les Pyrénées ou voyages pédestres (The Pyrenees or Hiking journeys).
Luchon mineral water has been marketed throughout France.
Excavations have uncovered traces of three large pools lined with marble with circulating hot air and steam.
Cyclone Xynthia at the end of February 2010 caused the death of 50 people in France and hit Luchon and its region. The winds blew at 200 km/h on the peaks which caused substantial damage.
Heraldry
.svg.png) Arms of Bagnères-de-Luchon |
Blazon: Or, a mountain Sable mouvant from dexter where a jet of water spurts into a bath Azure the whole on a terrace in base Sable; in chief parti per pale, 1 of Gules charged with 4 otelles Argent, 2 of Azure with a votive altar the same with the inscription ILIXIONI DEO V.S.L.M. in roman capital letters of Sable. |
Administration
| From | To | Name |
|---|---|---|
| 1790 | Bernard Cazat | |
| 1791 | 1793 | Julien Rey |
| 1793 | 1793 | Etienne Sourd-Sacarrere |
| 1793 | 1795 | Henri Colomic |
| 1795 | 1799 | Bernard Cazat |
| 1799 | 1800 | Paul Boileau |
| 1800 | 1800 | Pierre Jean Soulerat |
| 1800 | 1805 | Bernard Cazat |
| 1805 | 1807 | Gabriel Nadau |
| 1807 | 1808 | Pierre Gascon |
| 1808 | 1814 | Etienne Sengez |
| 1814 | 1815 | Henry Colomic |
| 1815 | 1816 | Gabriel Soutiran |
| 1816 | 1830 | Paul Boileau |
| 1830 | 1830 | Bertrand Saint Martin |
| 1830 | 1830 | Arnaud Soulerat |
| 1830 | 1841 | Pierre Azemar |
| 1841 | 1848 | Mathieu Soulerat |
| 1848 | 1870 | Charles Tron |
| 1870 | 1871 | Bertrand Baque |
| 1871 | 1871 | Edouard Azemar |
| 1871 | 1872 | Charles Tron |
| 1872 | 1874 | Edouard Azemar |
| 1874 | 1875 | Bernard Larrieu |
| 1875 | 1878 | Charles Tron |
| 1878 | 1884 | Edouard Azemar |
| 1884 | 1886 | Lucien Colomic |
| 1886 | 1892 | Aimé Trescazes |
| 1892 | 1894 | Edouard Azemar |
| 1894 | 1912 | Paul Bonnemaison |
| 1912 | 1914 | Gabriel Estradere |
| 1914 | 1919 | Jean Bigourdan |
- Mayors from 1919
| From | To | Name | Party | Position |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1919 | 1944 | Guillaume Germes | ||
| 1944 | 1944 | Rémy Comet | ||
| 1946 | 1947 | Alain Bochet | ||
| 1947 | 1971 | Alfred Coste Fleuret | ||
| 1971 | 1974 | Albert Castaigne | ||
| 1974 | 1995 | Jean Peyrafitte | ||
| 1995 | 2008 | René Rettig | ||
| 2008 | 2020 | Louis Ferré |
(Not all data is known)
Demography
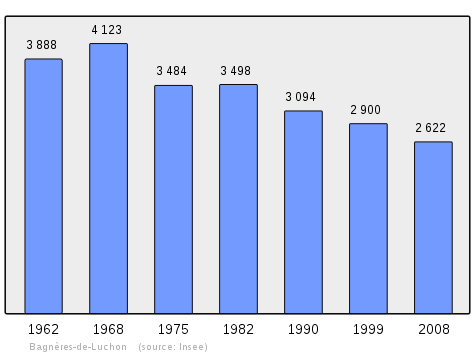
In 2010 the commune had 2,593 inhabitants. The evolution of the number of inhabitants is known from the population censuses conducted in the commune since 1793. From the 21st century, a census of communes with fewer than 10,000 inhabitants is held every five years, unlike larger communes that have a sample survey every year.[Note 1]
| 1793 | 1800 | 1806 | 1821 | 1831 | 1836 | 1841 | 1846 | 1851 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1,164 | 1,080 | 1,396 | 1,683 | 2,077 | 2,385 | 2,629 | 2,770 | 2,770 |
| 1856 | 1861 | 1866 | 1872 | 1876 | 1881 | 1886 | 1891 | 1896 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3,016 | 3,294 | 3,921 | 3,829 | 4,012 | 4,256 | 3,729 | 3,528 | 3,720 |
| 1901 | 1906 | 1911 | 1921 | 1926 | 1931 | 1936 | 1946 | 1954 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3,260 | 3,465 | 3,415 | 3,635 | 3,820 | 3,884 | 3,591 | 4,105 | 3,666 |
| 1962 | 1968 | 1975 | 1982 | 1990 | 1999 | 2006 | 2010 | - |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3,888 | 4,123 | 3,484 | 3,498 | 3,094 | 2,900 | 2,619 | 2,593 | - |
Economy
- Hydrotherapy (Thermes de Luchon)
- Winter sports (Superbagneres)
- Mineral water
- Tourism
Culture and heritage
Civil heritage
The commune has a number of buildings and sites that are registered as historical monuments:
- The Villa Pyrène at 13 Allée des Bains (19th century)

- The Villa Luisa at Boulevard Charles-Tron (1884)

- The Villa Edouard at 2 Boulevard Edmond-Rostand (1864)

- The Château Lafont at Allées d'Etigny (18th century)

- The Chalets Spont at 56 Allées d'Etigny (19th century)

- The Charles Tron Residence at 1 Avenue Galliéni (1854)

- The Villa Santa Maria at 14 Boulevard Henri-de-Gorsse (1840)

- The Chambert Thermal Baths at Cours de Quinconces (1854).

- A Sarcophagus (Gallo-Roman)
- An Altar and Sarcophagus (Gallo-Roman)

- A Sarcophagus (Gallo-Roman)
- The Casino (1878)

- A Stone circle (Neolithic)

- A Stone row (Neolithic)

- Other sites of interest
- The Arboretum de Jouéou
- The Léon-Elissalde Aeronautical Museum at the Aerodrome
- Civil heritage Photo Gallery
- The Villa Pyrène
- The Villa Edouard
.jpg) The Villa Luisa
The Villa Luisa- The Charles Tron Residence
- Plaque on the Chateau Lafont
- The Chalet Spont
- The Casino
- The mountains from the Casino
- The Lake in Quinconces Park
- The covered market
_-_Fonds_Ancely_-_B315556101_A_MALBOS_1_011.jpg) Sawmill in Luchon near 1840 by Eugène de Malbos
Sawmill in Luchon near 1840 by Eugène de Malbos
Religious heritage
The commune has several religious buildings and structures that are registered as historical monuments:
- The Chapel of Saint Etienne Portal at Quartier de Barcugnas (12th century).


- The Church of Our Lady of the Assumption (1847)

- Religious heritage picture gallery
- The Chapel of Saint Etienne
- The Church of Our Lady of the Assumption
- The Portal of the Church
 The Church Organ
The Church Organ The Pulpit
The Pulpit.jpg) The Chapel of the Sacred Heart in the Church
The Chapel of the Sacred Heart in the Church- Stained glass in the Church
- The Church nave
Thermal springs
Bagnères-de-Luchon is celebrated for its thermal springs. There are 48 springs which vary in composition but are chiefly impregnated with sodium sulphate, and range in temperature from 17 °C to 65 °C. The discovery of numerous Roman remains attests to the antiquity of the baths which are identified with the Onesiorum Thermae of Strabo. Their revival in modern times dates from the latter half of the 18th century, and was due to Antoine Mégret d'Étigny, intendant of Auch.[28]
There is a more modern entrance to the baths next to the older buildings. The bathing experience consists of repeated spells within a hot sulphurous atmosphere in caves that run approximately 100 metres inside the Superbagnères mountain in a cool swimming pool within the entrance building. It was these sulphur springs that led to a twinning of the settlement with Harrogate in 1952.
Bagnères-de-Luchon is celebrated as a fashionable resort. Of the promenades, the finest and most frequented are the Allées d'Étigny, an avenue planted with lime-trees, at the southern extremity of which is the Thermes, or hot baths. The road is lined with bars and restaurants.
- Thermal Baths Picture Gallery
%2C_Luchon%2C_septembre_1899_(2654646757).jpg) The Baths in 1899
The Baths in 1899- The Thermal Baths
- Stained glass in the baths
- Stained glass in the baths
Cultural events and festivities

- Film festivals: the Luchon Television Film Festival
- The Festival of Flowers.
The Rencontres lyriques de Luchon (Music Festival of Luchon)
In literature
Bagnères-de-Luchon is mentioned briefly in the short ghost Story, "Cannon Alberic's Scrap-Book" by M.R. James published in Ghost Stories of an Antiquary in 1904
It is also the setting for an early scene in François Mauriac's novel Le Noeud de Vipères, published in 1932.
Sports
Superbagnères is a ski resort located on the territory of Saint-Aventin commune to the south-west of the town only accessible from Bagnères-de-Luchon. Historically it was connected to the town by a railway being the second resort in France to install a rack railway but today it is connected with a gondola lift. Each cabin holds up to four people and takes about ten minutes to reach the summit, running in summer as well as winter. It is not possible to ski back down to Luchon, except in times of exceptional snow for talented locals who know the woods.
 Ski slopes in the summer
Ski slopes in the summer Superbagneres Chapel
Superbagneres Chapel
Cycling is a popular sport in the region in the summer. The climbs of Superbagnères, Col de Peyresourde, Port de Balès, Col de Menté, Col du Portillon and the Col de Portet d'Aspet are all nearby.
Bagnères-de-Luchon has been a permanent stage on the Tour de France since its inception in 1910.

In addition to the Tour de France the pro series race Route du Sud also passes through Luchon with a stage finishing in Superbagnères in 2008 and Luchon in 2009.
Luchon is also a mountain biking destination. Its position at the confluence of two valleys gives a wide variety of routes up into the mountains – although most of them start with a large climb (the gondola can carry mountain bikes). There is one mountain biking guide organisation based in Luchon itself and another further down the valley. (See external links).
Luchon also offers a golf course, tandem paragliding (from Superbagnères), tennis courts, and an aerodrome with gliding.
Luchon has a nine-hole golf course close to the town centre. It dates to the early 1900s, making it one of the oldest golf courses in the department. In 2008 the "Club de Golf Luchon" celebrated its 100-year anniversary.
Notable people linked to the commune
- Antoine Mégret d'Étigny (1719–1767), intendant of the generality of Gascony, Béarn, and Navarre. The commune named the Allées d'Étigny, the main street in the town, after him and a statue stands in front of the thermal baths.
- Nérée Boubée (1806–1862), naturalist, entomologist, geologist, and teacher at the University of Paris, died at Luchon.
- Théodore Gobley (1811–1876), pharmacist and chemist, member of the Académie Nationale de Médecine, established the chemical structure of phospholipids, died in Bagnères-de-Luchon on 1 September 1876 at the Hôtel des Bains, cour d'Etigny, where he was staying with his family.
- Stéphen Liégeard (1830–1925), French writer and poet, author of Twenty days as a tourist in Luchon country (1874)
- Auguste Scheurer-Kestner (1833–1899), chemist and Senator, died in Bagnères-de-Luchon.
- Jean-Marie Mengue (1855–1939), sculptor, born in Bagnères-de-Luchon.
- Henri Gadeau de Kerville (1858–1940), zoologist, botanist, and archaeologist, died in Bagnères-de-Luchon.
- Henry de Gorsse or Henri de Gorsse (1868–1936), man of letters, playwright, screenwriter, and songwriter, born at Luchon.
- Edmond Rostand (1868–1918), playwright who spent 22 summers in Luchon in his youth where he composed Les Musardises. In Cyrano de Bergerac, Act IV, Scene VI, the author was inspired by the place names in the Luchon Valley, among others, to name his Gascon cadets: there is one called a "Knight of Antignac-Juzet".
- Jules Brévié (1880–1964), colonial administrator, Governor-General of French West Africa (AOF), and of French Indochina, Minister, born in Bagnères-de-Luchon.
- Georges Lucien Guyot (1885–1973), wildlife artist, his work "Bear of the Pyrénées" is in the Thermal Baths grounds.
- Jean Arlaud (1896–1938), doctor and mountaineer.
- Lys Gauty (1908–1994), singer, took over management of the Luchon Casinor in 1950 and created the Festival of the Voice.
- Michel Warlop (1911–1947), jazz violinist, died in Bagnères-de-Luchon.
- Guy Lapébie (1916–2010), racing cyclist, died in Bagnères-de-Luchon.
- Alexis Kanner (1942–2003), Anglo-Canadian actor, born in Bagnères-de-Luchon.
- Britt Lafforgue and Ingrid Lafforgue, ski champions, born in 1948 in Bagnères-de-Luchon.
Literature
Bagnères-de-Luchon is a location mentioned in the M.R. James ghost story Canon Alberic's Scrap-Book published in Ghost Stories of an Antiquary in 1904.
Bibliography
- Nérée Boubée, Promenade de Bagnères au lac d'Oô. Reprinted 2009, Éditions Aux pages d'antan, 88 p. (in French)
- Anne Dupic, Économie et démographie dans la commune de Bagnères-de-Luchon, 1815–1870, mém. de maitrise, Université Toulouse II, 1976 (in particular noted the difficulty of measuring the true impact of tourism development for the local population). (in French)
- Philippe Francastel, Luchon et ses vallées, Éditions Privat, 1999 ISBN 2-7089-9123-X (in French)
- Philippe Francastel, Le Pays de Luchon – poésie et lumière, Atlantica, 2004 ISBN 2-84394-711-1 (in French)
- Jean-Bernard Frappé, Autrefois Bagnères de Luchon, 2 tomes, Atlantica, 2001 ISBN 2-84394-432-5 (in French)
- Henri Gadeau de Kerville, Autour du canton de Bagnères-de-Luchon (France et Espagne), Toulouse, Privat, 1928 (in French)
- Henri Gadeau de Kerville, Bagnères-de-Luchon et son canton (Haute-Garonne), Toulouse, Édouard Privat, 1925 ; Lorisse, 2003 ISBN 9782843733543 (in French)
- Alban et André Leymarie, Le Chemin de fer à crémaillère de Luchon à Superbagnères, 1912–1966, Éditions Lacour-Olle, 2006 ISBN 2-7504-0702-8 (in French)
- Henri Pac, Luchon et son passé, Éditions Privat, 1984 ISBN 2-7089-2385-4 (in French)
- Anne Samson, Thermes tragiques, ISBN 2-9501-3090-9 (a detective novel set in Luchon) (in French)
- Patrick Turlan, Bagnères-de-Luchon à la Belle époque. Pau, imprimerie Ipadour, 1999, 63 pp., [Many reproductions of old postcards of Luchon.], Preface by Henri Dénard (General Councilor for the Canton of Luchon). (in French)
- Patrick Turlan, La fête des fleurs de Bagnères-de-Luchon à la Belle époque. Pau, imprimerie Ipadour, 1999, 32 pp., [Many reproductions of old postcards of Luchon. History of Guides...], Preface by Jean Peyrafitte (former senator-mayor of Luchon). (in French)
- Ernest Philippe Lambron, Les Pyrénées et les eaux thermales sulfurées de Bagnères-de-Luchon, N. Chaix, Paris, 1863–1864, 1152 pages, consulted on 6 June 2014 (in French)
Notes
- At the beginning of the 21st century, the methods of identification have been modified by Law No. 2002-276 of 27 February 2002 Archived 6 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine, the so-called "law of local democracy" and in particular Title V "census operations" allows, after a transitional period running from 2004 to 2008, the annual publication of the legal population of the different French administrative districts. For communes with a population greater than 10,000 inhabitants, a sample survey is conducted annually, the entire territory of these communes is taken into account at the end of the period of five years. The first "legal population" after 1999 under this new law came into force on 1 January 2009 and was based on the census of 2006.
References
- "Populations légales 2017". INSEE. Retrieved 6 January 2020.
- Inhabitants of Haute-Garonne (in French)
- Bagnères-de-Luchon in the Competition for Towns and Villages in Bloom Archived 10 December 2014 at the Wayback Machine (in French)
- "Bagnères-de-Luchon". Bagnères-de-Luchon.
- Géoportail, IGN (in French)
- Bagnères-de-Luchon official website (in French)
- Agreements between rural communities in the Spanish and French valleys in the Pyrenees
- List of mayors of France (in French)
- National Commission for Decentralised cooperation (in French)
- Ministry of Culture, Mérimée PA31000061 Villa Pyrène at 13 Allée des Bains (in French)
- Ministry of Culture, Mérimée PA31000091 Villa Luisa at Boulevard Charles-Tron (in French)
- Ministry of Culture, Mérimée PA31000060 Villa Edouard at 2 Boulevard Edmond-Rostand (in French)
- Ministry of Culture, Mérimée PA00094277 Château Lafont at Allées d'Etigny (in French)
- Ministry of Culture, Mérimée PA00125564 Chalets Spont at 56 Allées d'Etigny (in French)
- Ministry of Culture, Mérimée PA00094280 Charles Tron Residence at 1 Avenue Galliéni (in French)
- Ministry of Culture, Mérimée PA31000077 Villa Santa Maria at 14 Boulevard Henri-de-Gorsse (in French)
- Ministry of Culture, Mérimée PA00094281 Chambert Thermal Baths at Cours de Quinconces (in French)

- Ministry of Culture, Palissy PM31001124 Sarcophagus (in French)
- Ministry of Culture, Palissy PM31000334 Altar and Sarcophagus (in French)
- Ministry of Culture, Mérimée PA31000035 Casino (in French)
- Ministry of Culture, Mérimée PA00094278 Stone circle (in French)
- Ministry of Culture, Mérimée PA00094275 Stone row (in French)
- Ministry of Culture, Mérimée PA00094276 Chapel of Saint Etienne Portal at Quartier de Barcugnas (in French)
- Ministry of Culture, Palissy PM31000333 Statuette: Virgin and child (in French)
- Ministry of Culture, Mérimée PA00094279 Church of Our Lady of the Assumption (in French)
- Ministry of Culture, Palissy PM31000332 Chalice (in French)
- Ministry of Culture, Palissy PM31000032 Abraham Bronze Bell (in French)
-

External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Bagnères-de-Luchon. |
- Tourism office website
- Bagnères-de-Luchon official website (in French)
- Aeroclub de Luchon website (in French)
- Bagnères-de-Luchon on Lion1906
- Bagnères-de-Luchon on Géoportail, National Geographic Institute (IGN) website (in French)
- Bagnères-de-Luchon on the 1750 Cassini Map